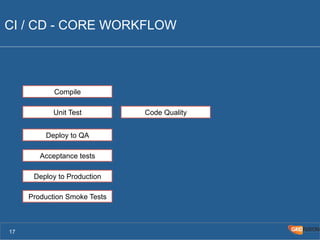
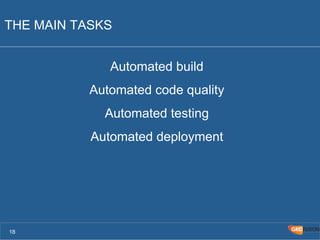
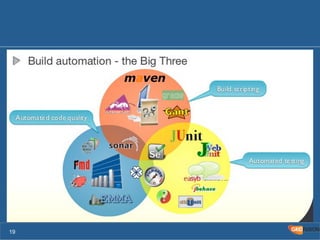
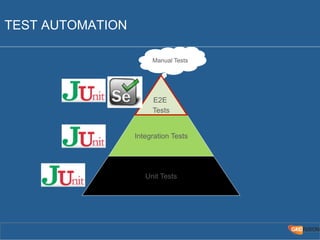
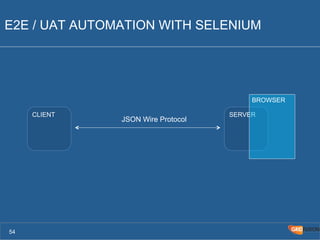
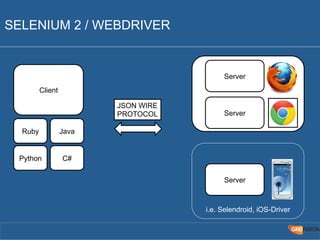
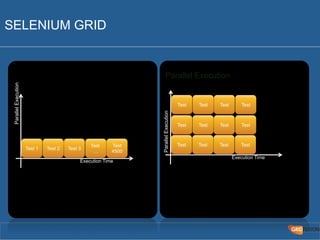
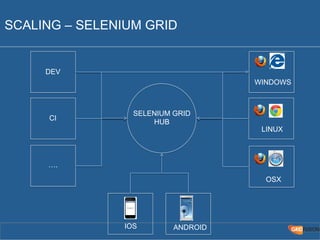
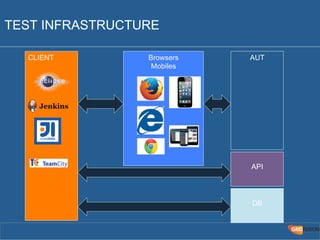
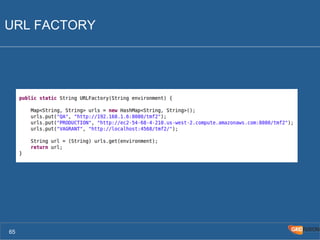
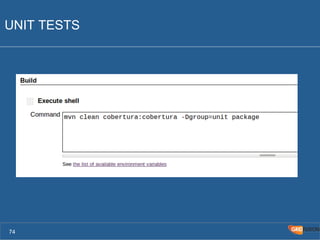
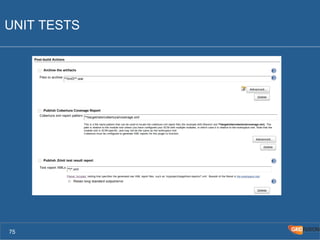
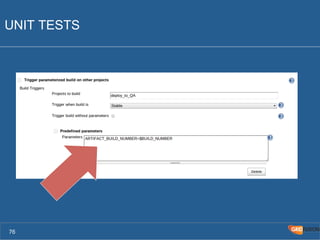
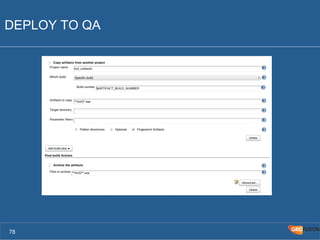
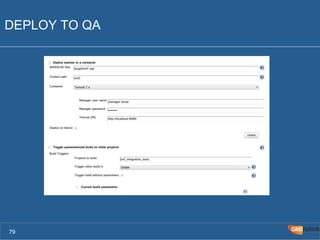
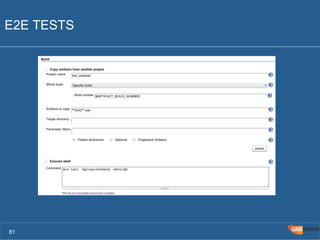
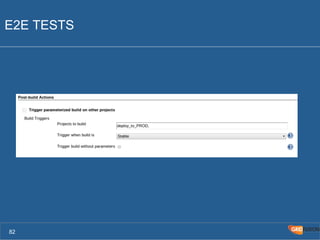
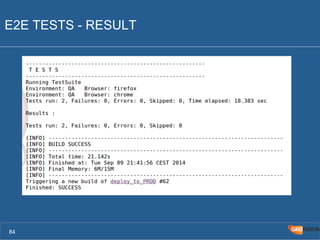
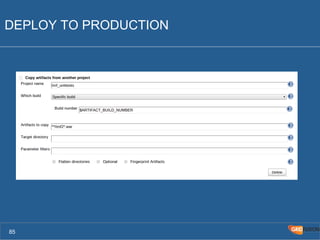
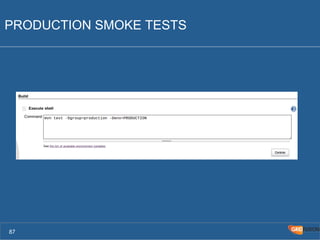
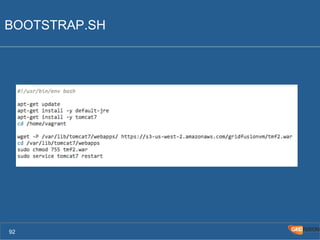
The document outlines the Agile Bodensee 2014 workshop focused on test automation and continuous integration, led by Michael Palotas from Gridfusion Software Solutions. It covers key concepts like Continuous Integration (CI), Continuous Delivery (CD), and the importance of automation in software development, along with tools such as Git, Maven, and Jenkins. The workshop also discusses the necessary organizational changes and best practices for implementing CI/CD effectively.