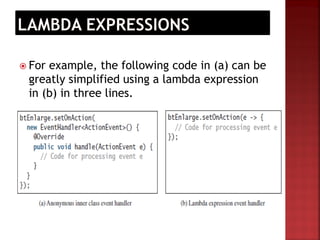
The document discusses lambda expressions in Java. It defines a lambda expression as a concise representation of an anonymous function that can be passed around. Lambda expressions allow for passing functions as arguments or returning them. They make code shorter and cleaner compared to anonymous classes. Functional interfaces are required for lambda expressions, where a functional interface defines a single abstract method that lambda expressions can implement.