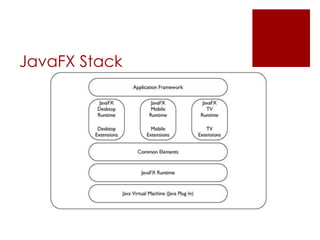
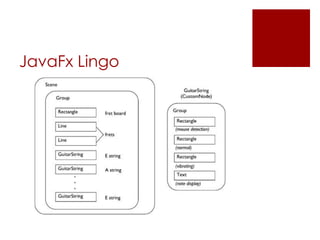
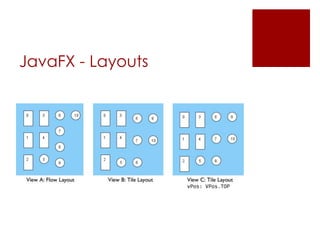
JavaFX is a software platform for building rich internet applications that can run across various platforms. It includes Java packages that allow developers to add graphical user interfaces to Java applications. JavaFX uses concepts like stages, scenes, and nodes to define application layout and user interface elements. Common JavaFX packages provide functionality for application lifecycles, stages, scenes, layouts, and controls.

![JavaFX
JavaFX is a software platform for creating Rich
Internet Applications that can run across variety
of platforms[1]
Collection of Java Packages with ability to add
fancy GUI’s to your Java application
Groovy and Scala can also be used to write
JavaFX. JVM Languages indeed!!!
JavaFX is official standard part of Java platform](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javafx-150314012015-conversion-gate01/85/Java-fx-2-320.jpg)
![JavaFX - History
Formerly called F3 (Form Follows Function) and
developed by Chris Oliver at Sun Microsystems
JavaFX was initially developed as a scripting
language however it was discontinued by Oracle
and declared dead in JavaOne (2010)[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javafx-150314012015-conversion-gate01/85/Java-fx-3-320.jpg)