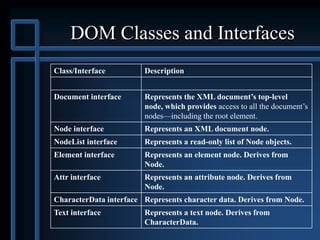
This document provides an overview of using the DOM (Document Object Model) API in Java to parse, traverse, modify, and generate XML documents. It describes the core DOM interfaces like Document and Node, how to parse an XML file into a DOM document tree using JAXP, and examples of traversing nodes, modifying content, and generating a new XML document from scratch using the DOM.



![Simple DOM program, I
import javax.xml.parsers.*;
import org.w3c.dom.*;
public class SecondDom {
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
...Main part of program goes here...
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dom2-130927130905-phpapp02/85/java-API-for-XML-DOM-6-320.jpg)





![intro.xml
<?xml version = "1.0"?>
<!-- Fig. 8.12 : intro.xml -->
<!-- Simple introduction to XML markup -->
<!DOCTYPE myMessage [
<!ELEMENT myMessage ( message )>
<!ELEMENT message ( #PCDATA )>
]>
<myMessage>
<message>Welcome to XML!</message>
</myMessage>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dom2-130927130905-phpapp02/85/java-API-for-XML-DOM-12-320.jpg)

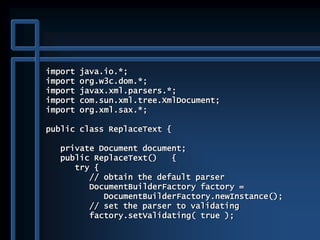
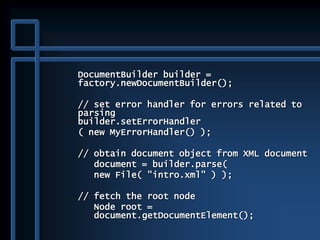
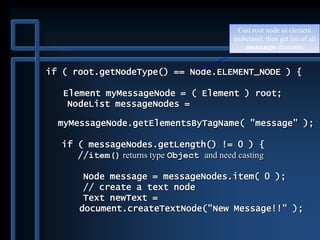
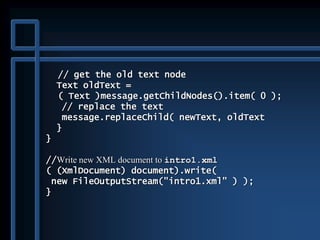
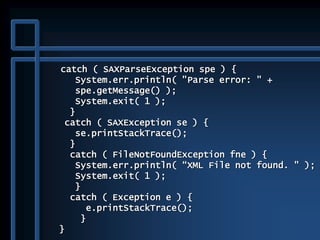
![public static void main( String args[] )
{
ReplaceText d = new ReplaceText();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dom2-130927130905-phpapp02/85/java-API-for-XML-DOM-19-320.jpg)

![ Desired Output
<root>
<!--This is a simple contact list-->
<contact gender="F">
<FirstName>Sue</FirstName>
<LastName>Green</LastName>
</contact>
<?myInstruction action silent?>
<![CDATA[I can add <, >, and ?]]>
</root>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dom2-130927130905-phpapp02/85/java-API-for-XML-DOM-21-320.jpg)
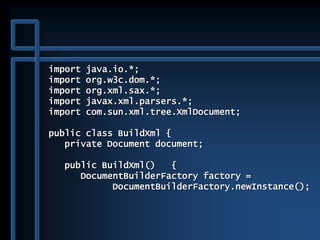
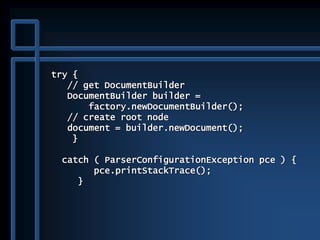
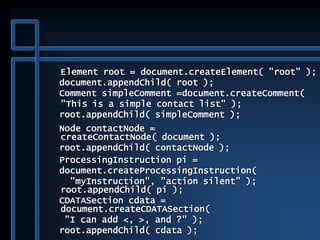
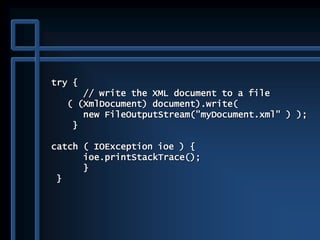
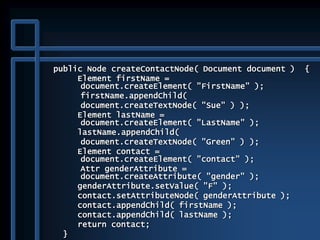
![public static void main( String args[] )
{
BuildXml buildXml = new BuildXml();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dom2-130927130905-phpapp02/85/java-API-for-XML-DOM-27-320.jpg)

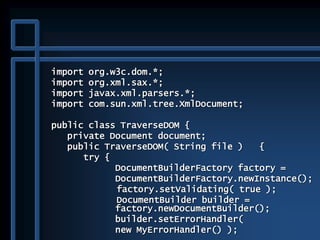
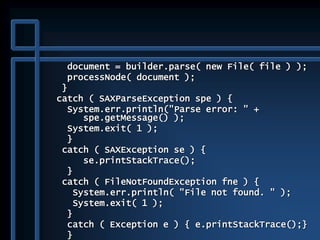
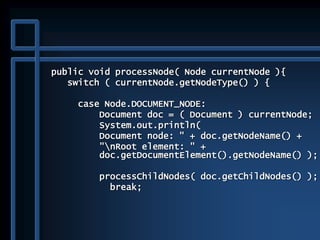
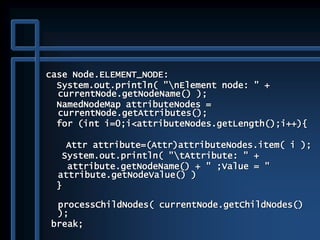
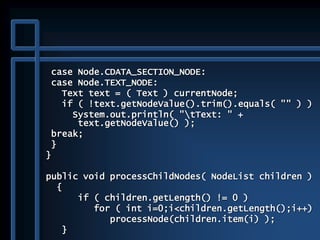
![public static void main( String args[] ) {
if ( args.length < 1 ) {
System.err.println("Usage: java
TraverseDOM <filename>" );
System.exit( 1 );
}
TraverseDOM traverseDOM = new
TraverseDOM( args[ 0 ] );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dom2-130927130905-phpapp02/85/java-API-for-XML-DOM-34-320.jpg)