- The DOM (Document Object Model) views an XML document as a tree structure where each node represents a component of the XML structure.
- The DOM parser constructs an internal representation of the XML data as a tree structure in memory, allowing traversal and manipulation of nodes.
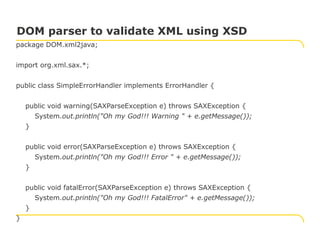
- To validate an XML document using a schema with DOM, the parser factory is configured to create a validating parser, the schema language and source are set, and errors are handled.




![SAX
•When a start tag or end tag is encountered, the name of the tag is passed
as a String to the startElement() or endElement() method, as appropriate.
When a start tag is encountered, any attributes it defines are also passed in
an Attributes list. Characters found within the element are passed as an
array of characters, along with the number of characters (length) and an
offset into the array that points to the first character.
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String
qName,Attributes attributes) throws SAXException
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String qName) throws
SAXException
public void characters(char buf[], int offset, int len) throws SAXException](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jaxp-161117112752/85/JAXP-5-320.jpg)
![SAX parser
package SAX.xml2java;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParser;
import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParserFactory;
import org.xml.sax.Attributes;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler;
/*
* This class parse the XML and print them.
*/
public class MySaxParser extends DefaultHandler{
StringBuffer textBuffer;
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultHandler handler = new MySaxParser();
try{
SAXParserFactory factory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
SAXParser parser = factory.newSAXParser();
parser.parse(new File("./Util/sax/employees.xml"), handler);
} catch(ParserConfigurationException pcEx){
pcEx.printStackTrace();
} catch(IOException ioEx){
ioEx.printStackTrace();
} catch(SAXException saxEx){
saxEx.printStackTrace();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jaxp-161117112752/85/JAXP-6-320.jpg)
![@Override
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String tagName, Attributes attrs) throws SAXException {
System.out.println("startElement "+tagName);
for(int i=0; i<attrs.getLength(); i++){
System.out.println("Attribute "+attrs.getQName(i)+"'s value
"+attrs.getValue(attrs.getQName(i)));
}
}
@Override
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String tagName) throws SAXException {
echoText(tagName);
System.out.println("endElement "+tagName);
}
@Override
public void characters(char buf[], int offset, int len) throws SAXException {
String s = new String(buf, offset, len);
if (textBuffer == null) {
textBuffer = new StringBuffer(s);
} else {
textBuffer.append(s);
}
}
private void echoText(String tagName) throws SAXException {
if (textBuffer == null || || textBuffer.toString().trim().length()<1) return;
String s = tagName+"'s text value :"+textBuffer.toString().trim();
System.out.println(s);
textBuffer = null;
}
}
SAX parser](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jaxp-161117112752/85/JAXP-7-320.jpg)





![SAX parser to validate XML using XSD
//The document must be associated with a schema.
/*If schema declaration is in XML doc, then no need to specify the schema here.
When the java pgm specifies the schema to use, it overrides any schema declaration in the XML doc.*/
//static final String schemaSource = "./Util/sax/employees.xsd";
//static final String JAXP_SCHEMA_SOURCE = "http://java.sun.com/xml/jaxp/properties/schemaSource";
public static void main(String[] args) {
DefaultHandler handler = new ParseXMLXSD();
SAXParserFactory factory = SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
factory.setValidating(true); // The parser factory must be configured to create a validating parser to
factory.setNamespaceAware(true); // notify the validation errors and namespace-aware parser.
try{
SAXParser parser = factory.newSAXParser();
// The appropriate properties must be set on the SAX parser.
parser.setProperty(JAXP_SCHEMA_LANGUAGE, W3C_XML_SCHEMA);
//The document must be associated with a schema.
parser.setProperty(JAXP_SCHEMA_SOURCE, new File(schemaSource));
parser.parse(new File("./Util/sax/employees1.xml"),handler);
} catch(ParserConfigurationException pcEx){
pcEx.printStackTrace();
} catch(SAXParseException saxPEx){ // The appropriate error handler must be set.
System.out.println("n** Parsing error"
+ ", line " + saxPEx.getLineNumber()
+ ", uri " + saxPEx.getSystemId());
System.out.println(" " + saxPEx.getMessage() );
saxPEx.printStackTrace();
} catch(SAXException saxEx){
saxEx.printStackTrace();
} catch(IOException ioEx){
ioEx.printStackTrace();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jaxp-161117112752/85/JAXP-13-320.jpg)
![SAX parser to validate XML using XSD
public void startElement(String namespaceURI, String sName, String qName, Attributes attrs)throws SAXException{
String eName = sName; // element name
if ("".equals(eName)) eName = qName; // not namespaceAware
System.out.print("<"+eName+">");
if (attrs != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < attrs.getLength(); i++) {
String aName = attrs.getLocalName(i); // Attr name
if ("".equals(aName)) aName = attrs.getQName(i);
System.out.print(aName+"=""+attrs.getValue(i)+""");
}
}
}
public void endElement(String namespaceURI, String sName, String qName) throws SAXException {
echoText();
String eName = sName; // element name
if ("".equals(eName)) eName = qName; // not namespaceAware
System.out.println("</"+eName+">");
}
public void characters(char buf[], int offset, int len) throws SAXException {
String s = new String(buf, offset, len);
if (textBuffer == null) {
textBuffer = new StringBuffer(s);
} else {
textBuffer.append(s);
}
}
private void echoText(String tagName) throws SAXException {
if (textBuffer == null || || textBuffer.toString().trim().length()<1) return;
String s = tagName+"'s text value :"+textBuffer.toString().trim();
System.out.print(s);
textBuffer = null;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jaxp-161117112752/85/JAXP-14-320.jpg)




![DOM parser
package DOM.xml2java;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.parsers.ParserConfigurationException;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import org.xml.sax.SAXParseException;
import DOM.java2xml.Employee;
/*
* This class parse the XML, store the element data into java object and print them.
*/
public class MyDomParser {
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = builder.parse(new File("./Util/dom/emps.xml")); // Parse the XML
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); // Get root Element of the XML
NodeList emps = root.getElementsByTagName("Employee"); //Get List of <Employee>
List<Employee> empList = new ArrayList<Employee>();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jaxp-161117112752/85/JAXP-19-320.jpg)






![/*If schema declaration in XML doc, then no need to specify the schema here.
When the java pgm specifies the schema to use, it overrides any schema declaration in the XML doc.*/
static final String schemaSource = "./Util/dom/employees.xsd";
static final String JAXP_SCHEMA_SOURCE = "http://java.sun.com/xml/jaxp/properties/schemaSource";
public static void main(String[] args){
try{
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
factory.setValidating(true);
factory.setNamespaceAware(true);
try{
factory.setAttribute(JAXP_SCHEMA_LANGUAGE, W3C_XML_SCHEMA);
factory.setAttribute(JAXP_SCHEMA_SOURCE, new File(schemaSource));
}catch(IllegalArgumentException iaEx){
iaEx.printStackTrace();
}
DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
builder.setErrorHandler(new SimpleErrorHandler());
Document doc = builder.parse(new File("./Util/dom/employees.xml"));
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement(); // Get root tag of the document
System.out.println("ROOT TAG : "+ root.getTagName());
NodeList nodes = root.getChildNodes(); // Get child nodes of the root tag
new ParseXMLXSD().printElements(nodes);
DOM parser to validate XML using XSD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jaxp-161117112752/85/JAXP-26-320.jpg)






![public class MyDomParser {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
List<Employee> empList = Employee.getEmployees(); //get employee list
DocumentBuilderFactory facory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder builder = facory.newDocumentBuilder();
Document document = builder.newDocument(); //create a new document
Element root = (Element)document.createElement("Employees"); //root element <Employees>
document.appendChild(root);
for(Employee e:empList){
Element emp = document.createElement("Employee"); //<Employee>
root.appendChild(emp);
Element name = document.createElement("Name"); //<Name> with attribute
name.setAttribute("employeeNo", Integer.toString(e.getId()));
Text nameVal = document.createTextNode(e.getName());
name.appendChild(nameVal);
emp.appendChild(name);
DOM parser to convert Java object to XML](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jaxp-161117112752/85/JAXP-34-320.jpg)


![/*
* This method reads employee details from a text file and generate
* list of employee objects
*/
public static List<Employee> getEmployees(){
List<Employee> empList = new ArrayList<Employee>();
try{
FileReader fr = new FileReader(new File("./Helpfiles/employees.txt"));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String line = null;
String[] tokens;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
tokens = line.split("-");
Employee e = new Employee(Integer.parseInt(tokens[0]),
tokens[1],Integer.parseInt(tokens[2]),tokens[3]);
empList.add(e);
}
return empList;
}catch(FileNotFoundException fnfEx){
fnfEx.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException ioEx){
ioEx.printStackTrace();
}
return empList;
}
}
Employee.java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jaxp-161117112752/85/JAXP-37-320.jpg)
