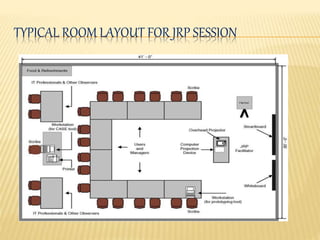
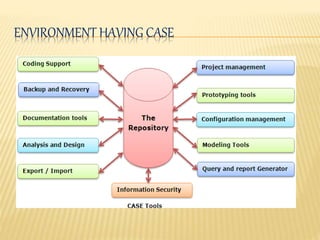
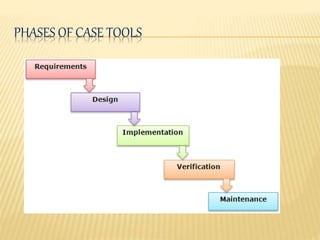
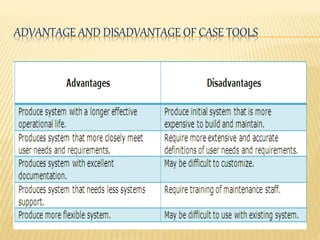
This document discusses Joint Application Development (JAD), Joint Requirement Planning (JRP), and Computer-Aided System Engineering (CASE) tools. It describes the typical participants in a JAD session and JRP meeting. It also outlines the advantages and disadvantages of using JRP to develop requirements for complex systems. Finally, it provides an overview of CASE tools, including examples of types of tools, how they support the development process, and their potential advantages and disadvantages.