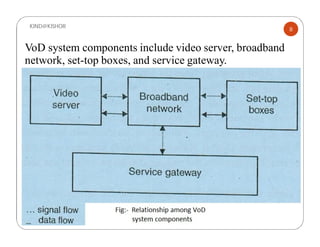
The document discusses the components and requirements of interactive television (ITV). ITV allows subscribers to access and interact with video programs on demand. Key components of an ITV system include set-top boxes at subscribers' homes, a broadband access network, video servers hosting content, and a service gateway. An effective ITV system demands high transmission speeds, quality of service guarantees, and point-to-point connections to enable on-demand video delivery and true video on demand services.