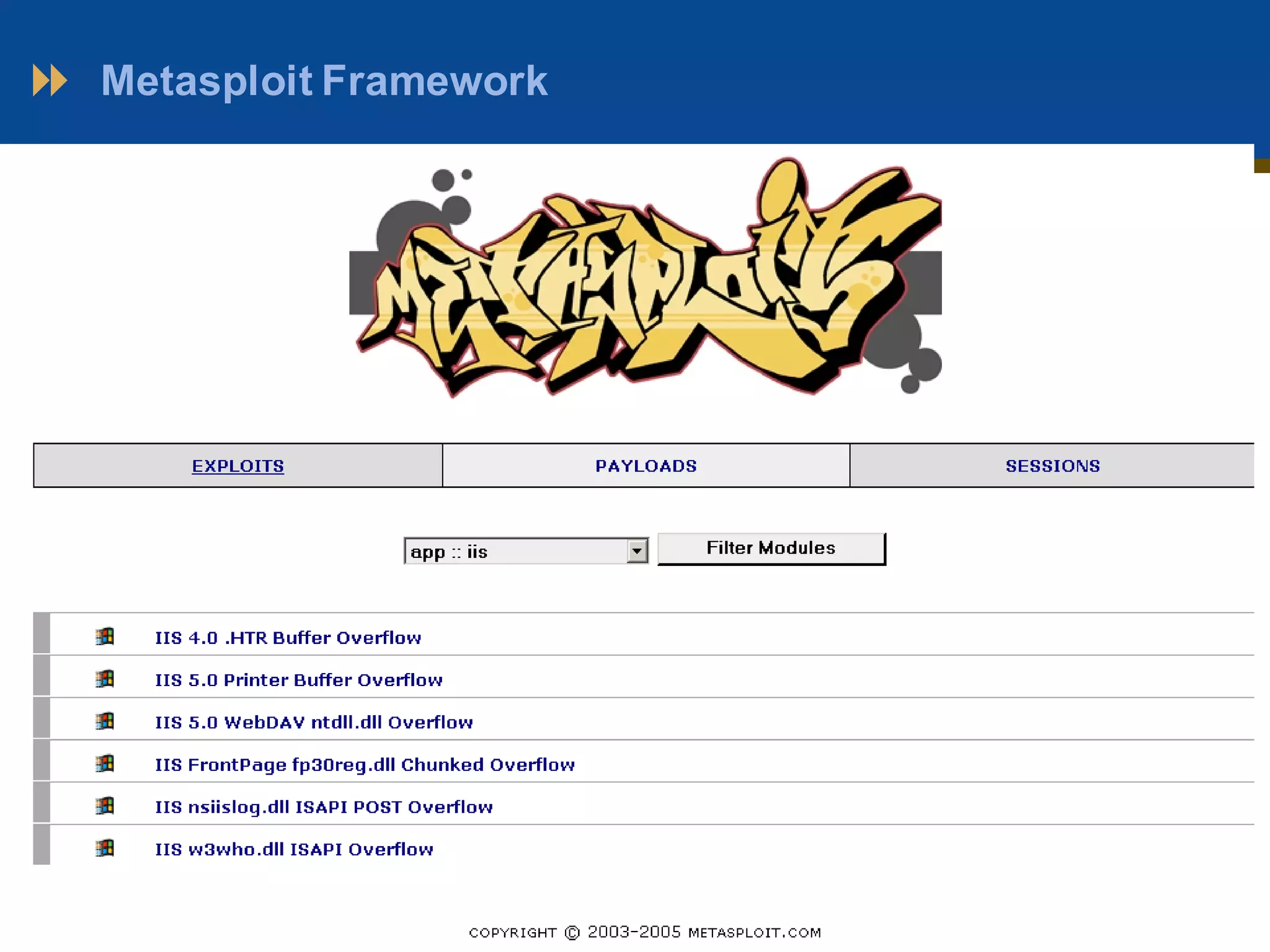
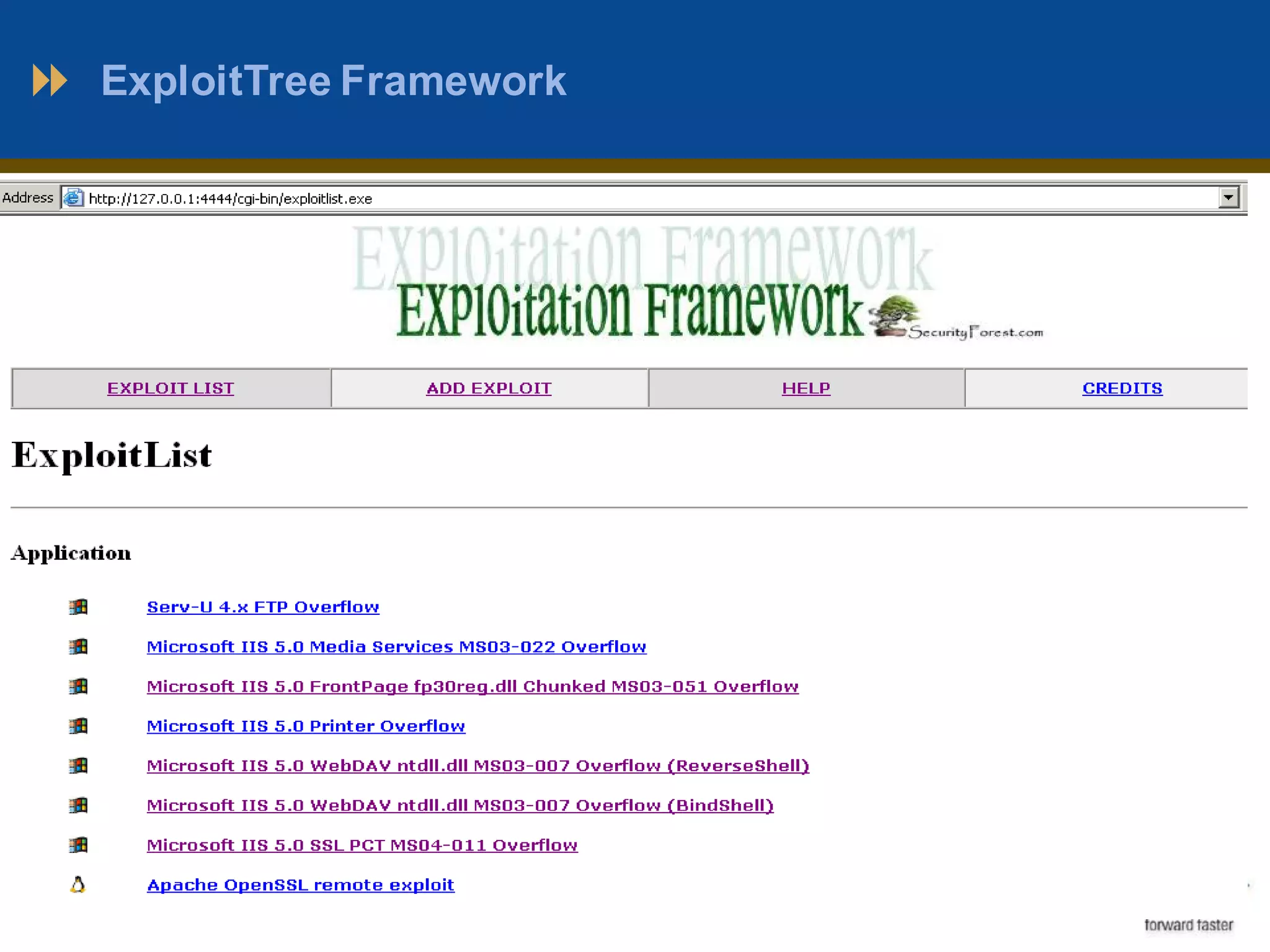
This document outlines a presentation on penetration testing. It discusses what penetration testing is, the need for it, and common methods and techniques used. The methodology typically involves 7 stages: scope definition, information gathering, vulnerability detection, analysis and planning, attack and privilege escalation, results analysis and reporting, and cleanup. Various tools used for penetration testing are also listed, including Nmap, Metasploit, ExploitTree, and Whopix. The document concludes with questions from the audience.