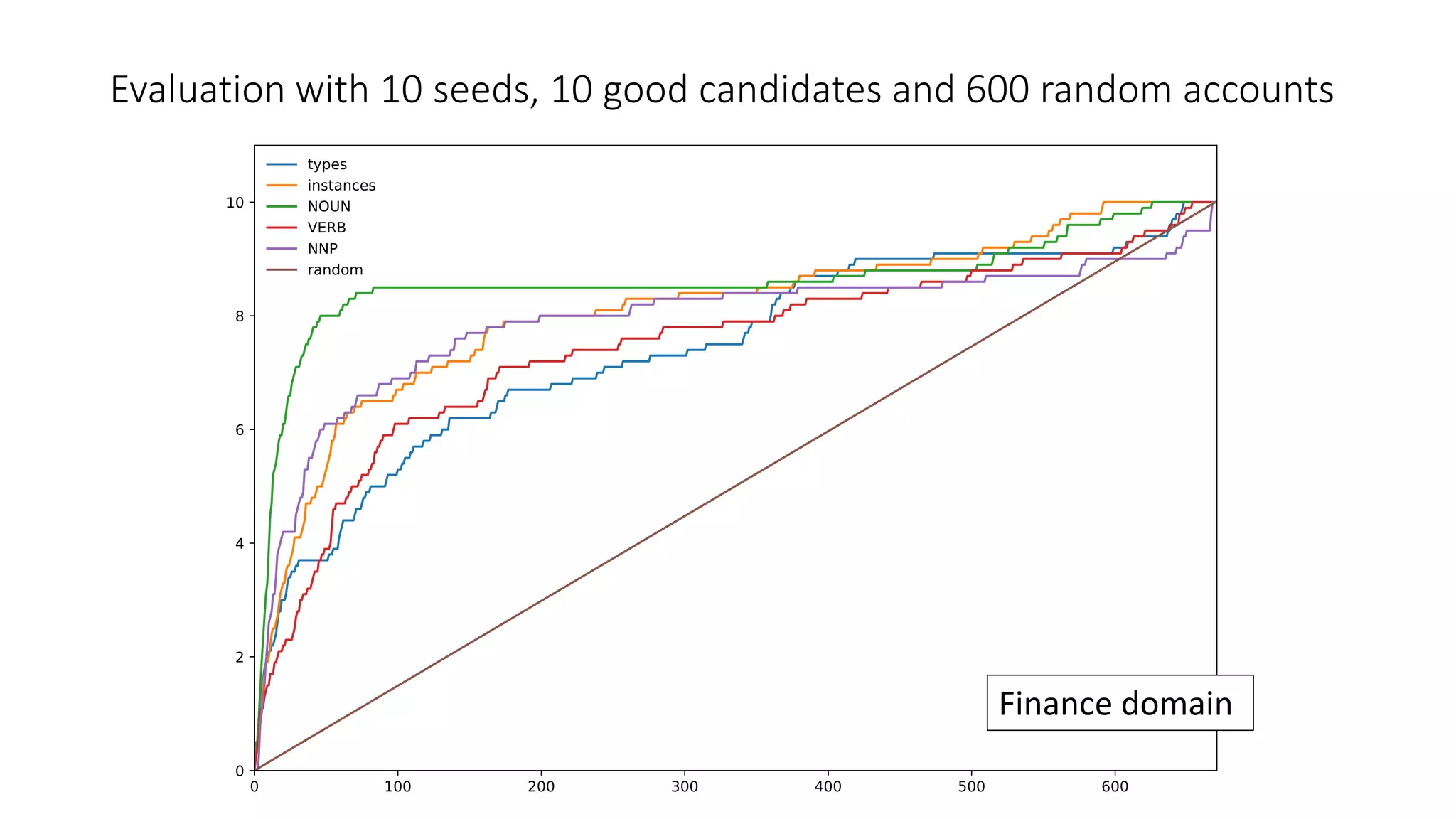
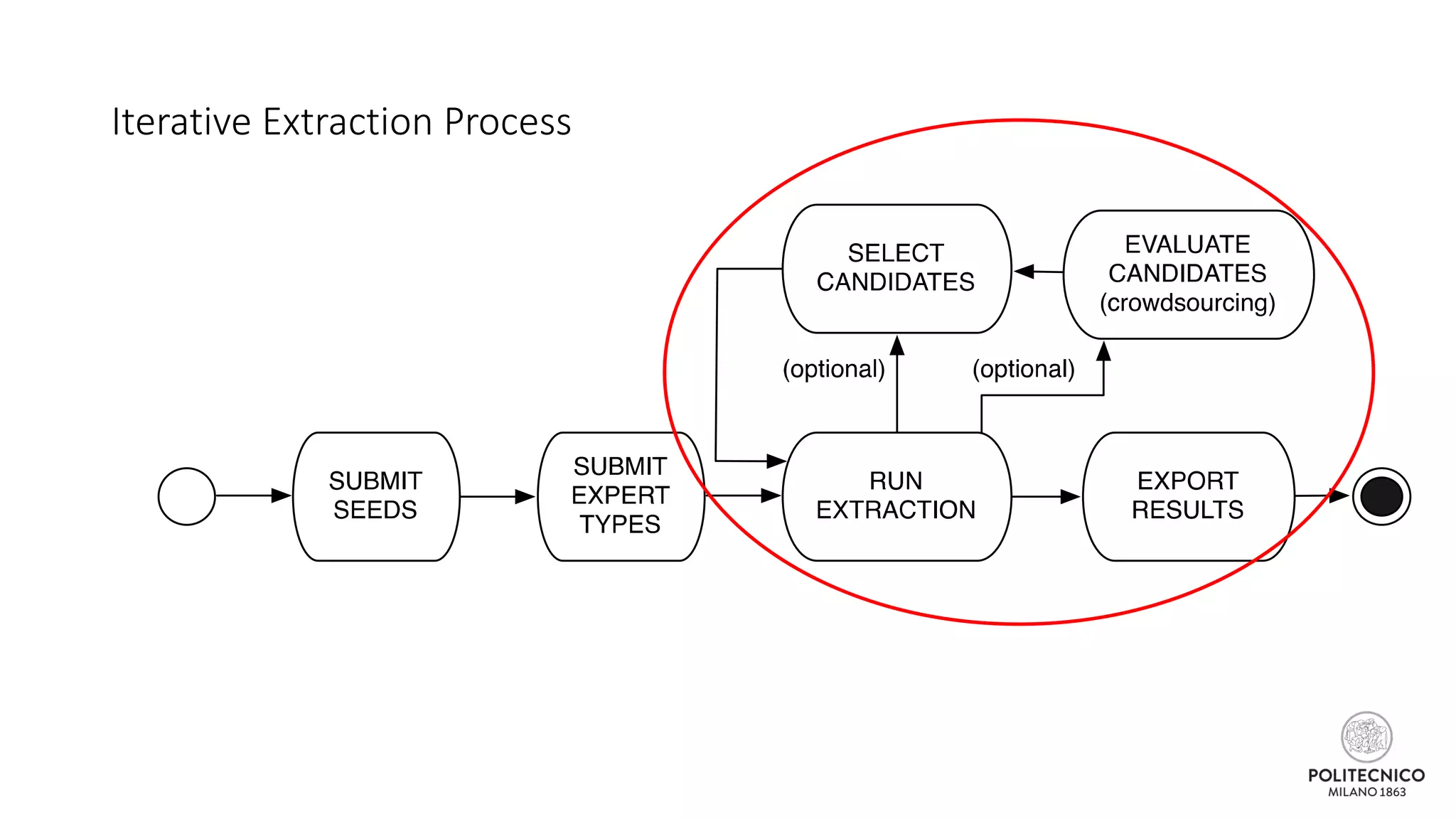
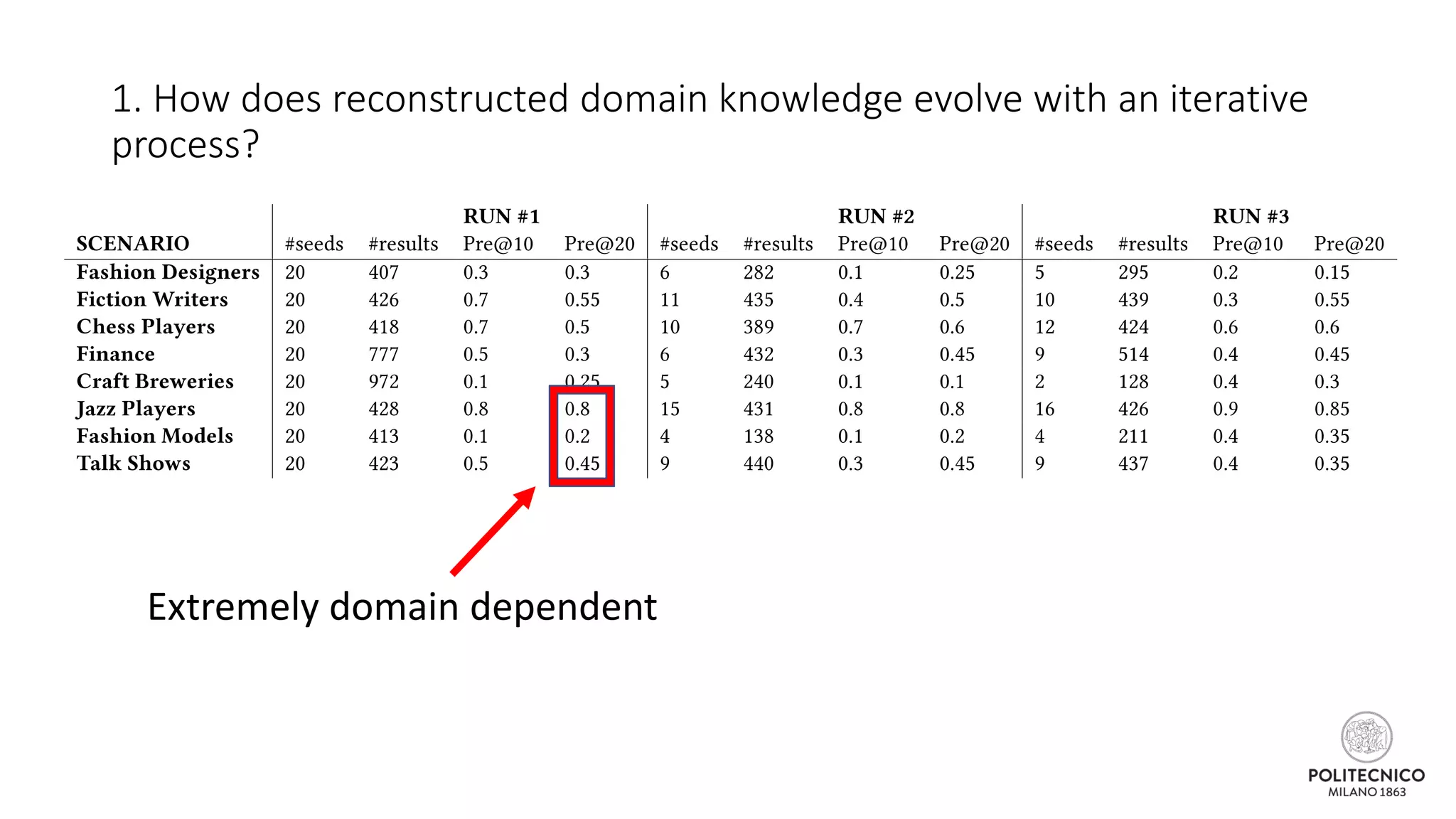
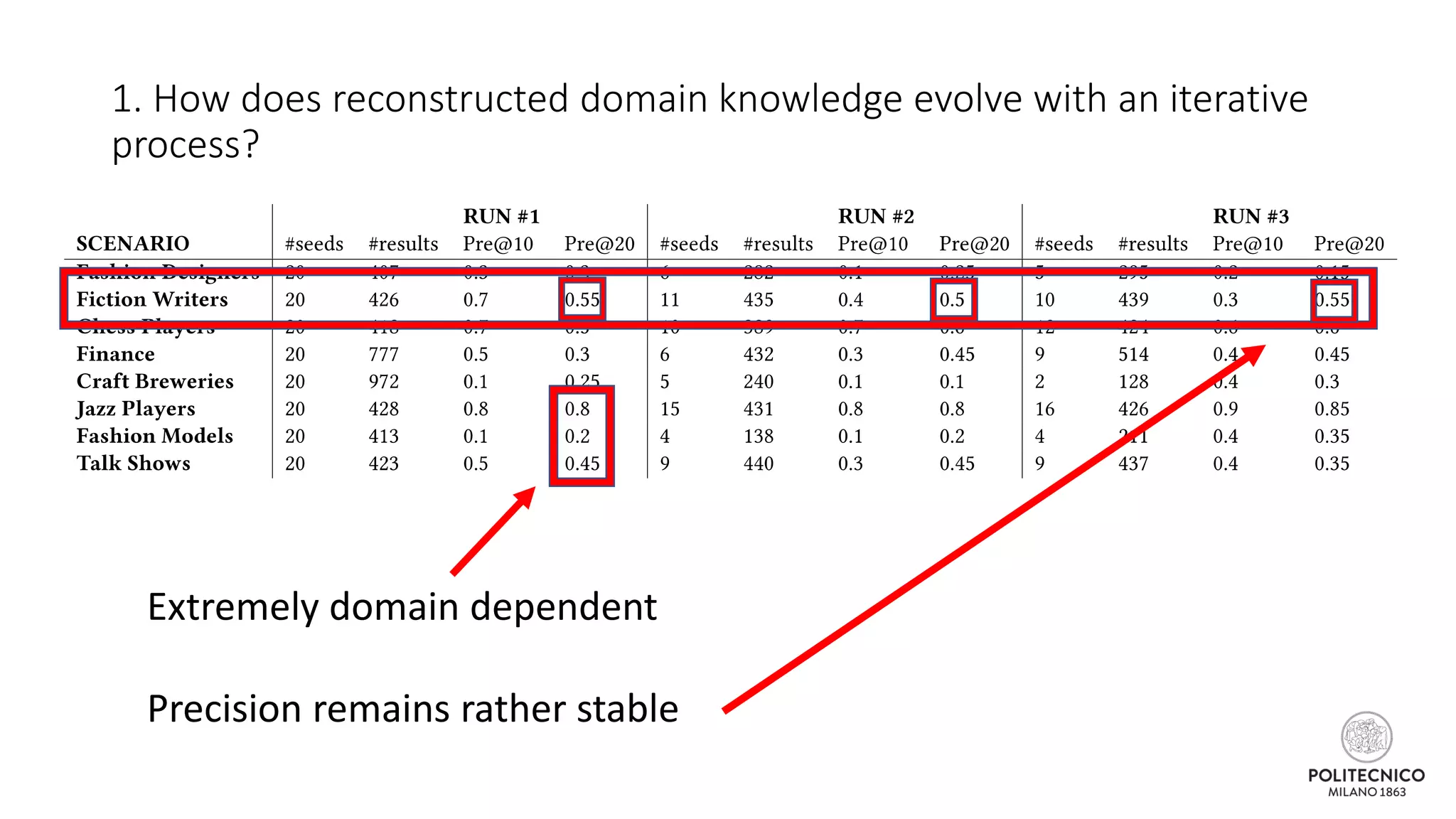
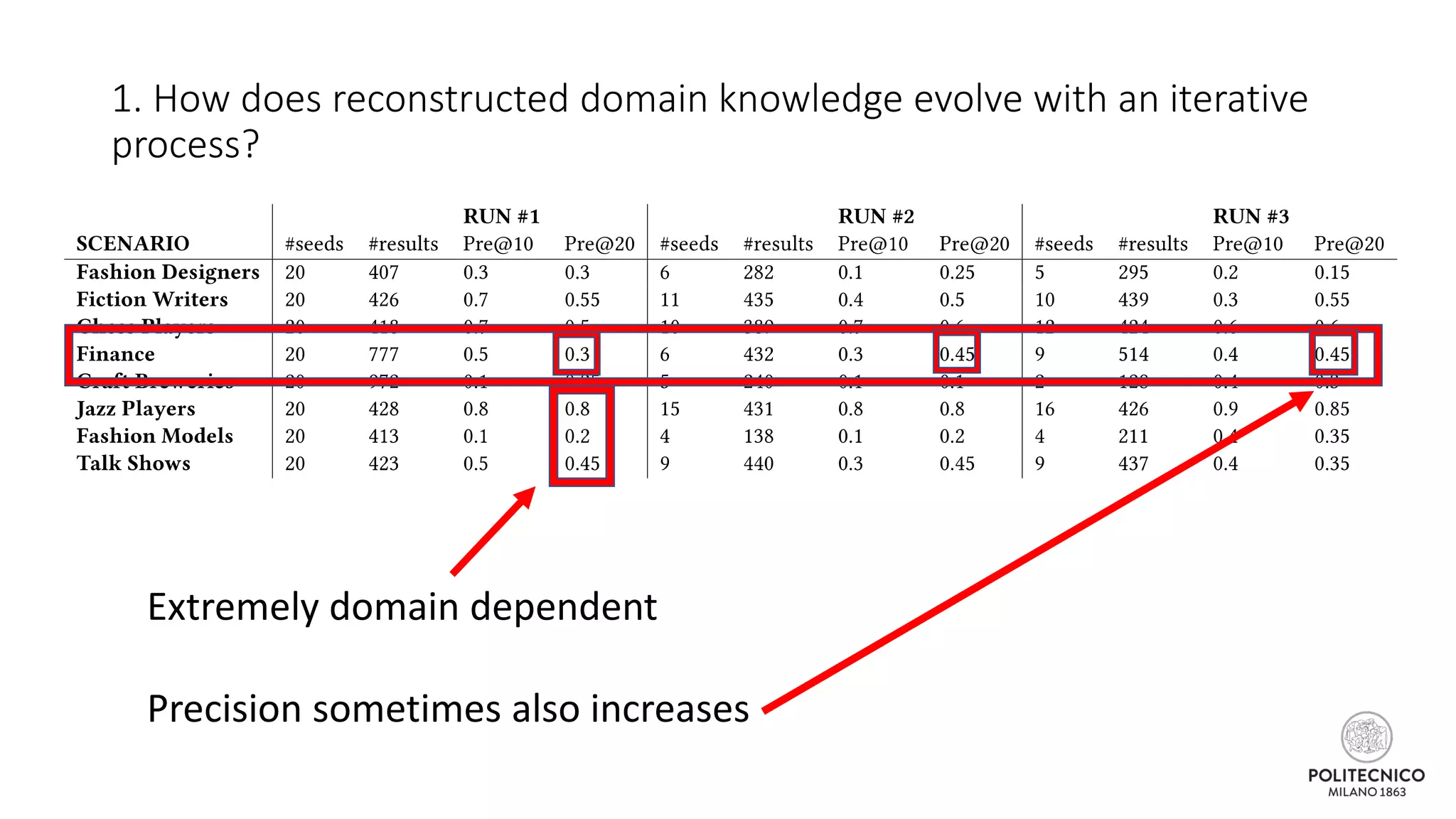
The document discusses an iterative process for extracting emerging knowledge from social networks, focusing on the evolution and geographic spread of this knowledge. It presents methods for retrieving knowledge related to various domains, demonstrating good precision despite multiple iterations. Future work aims to enhance the domain model by analyzing additional social media features.


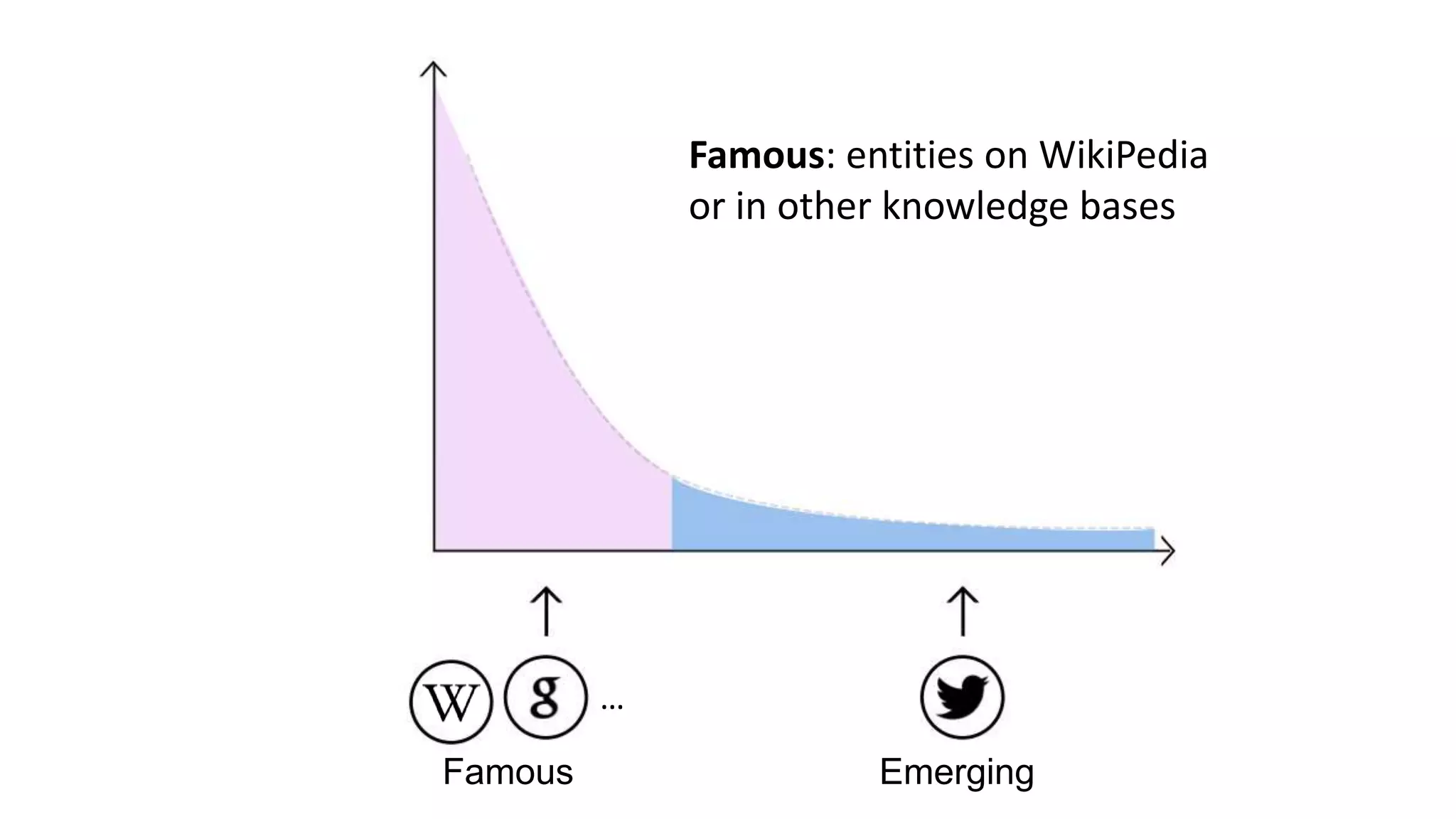
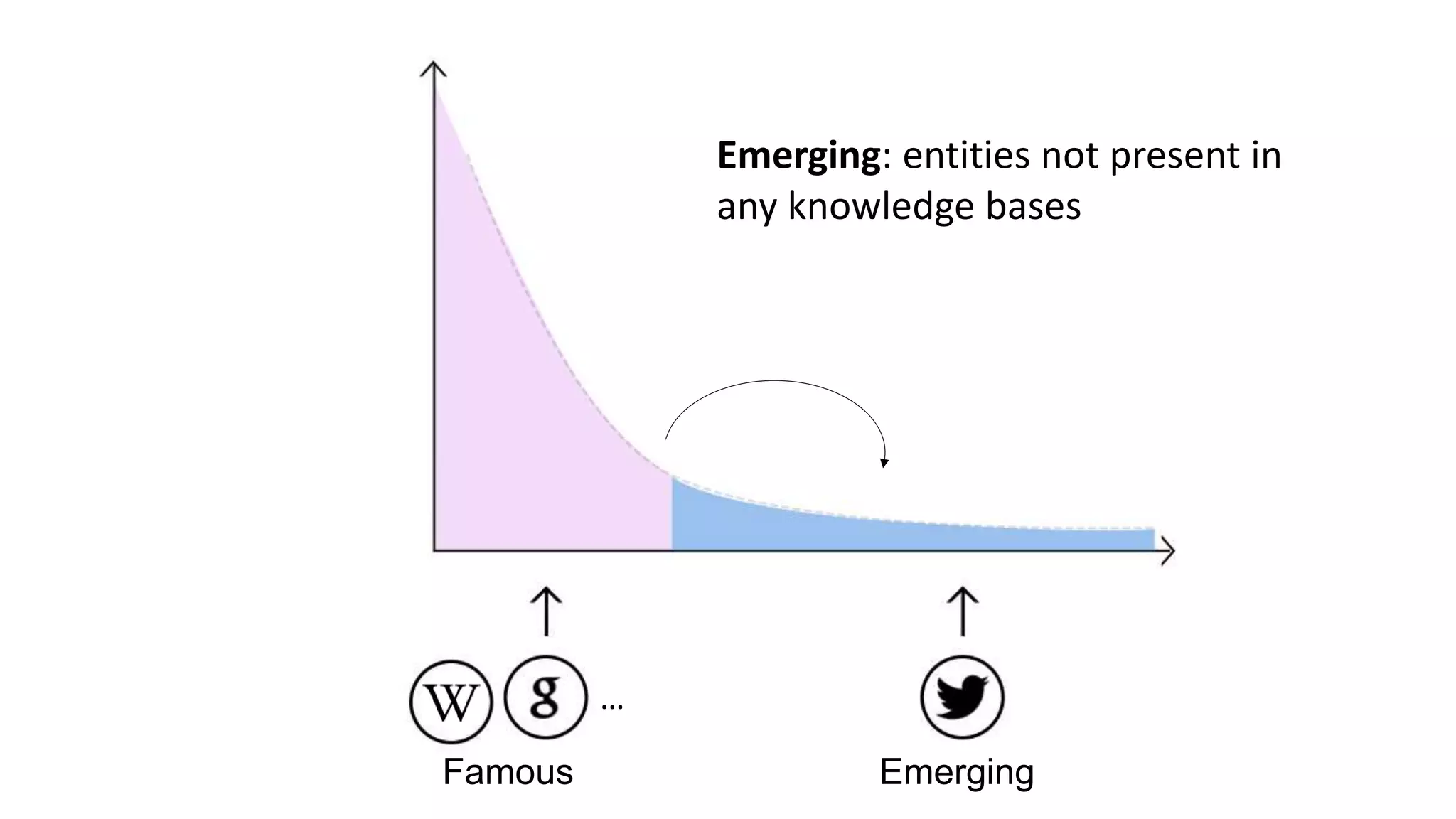
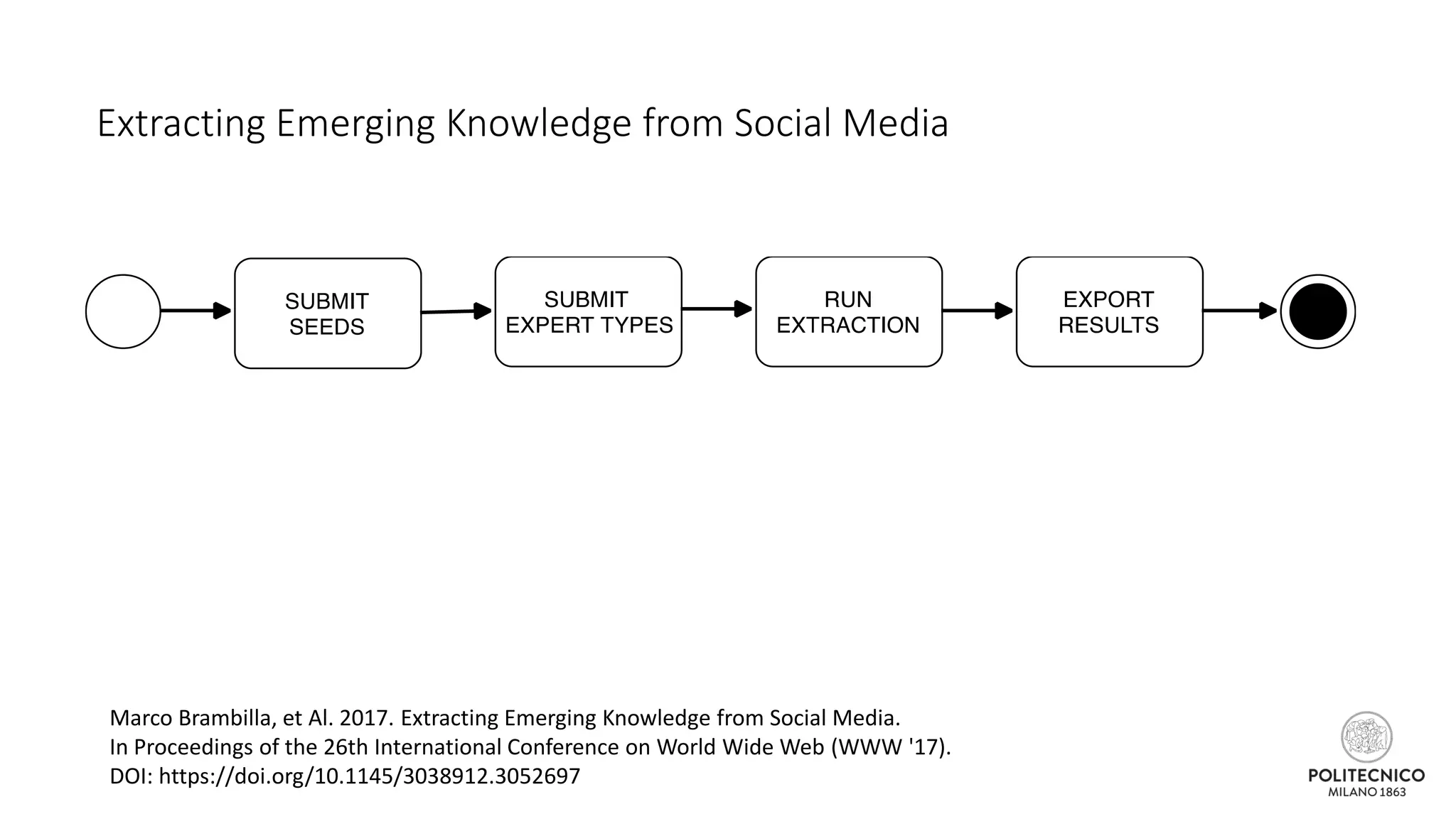
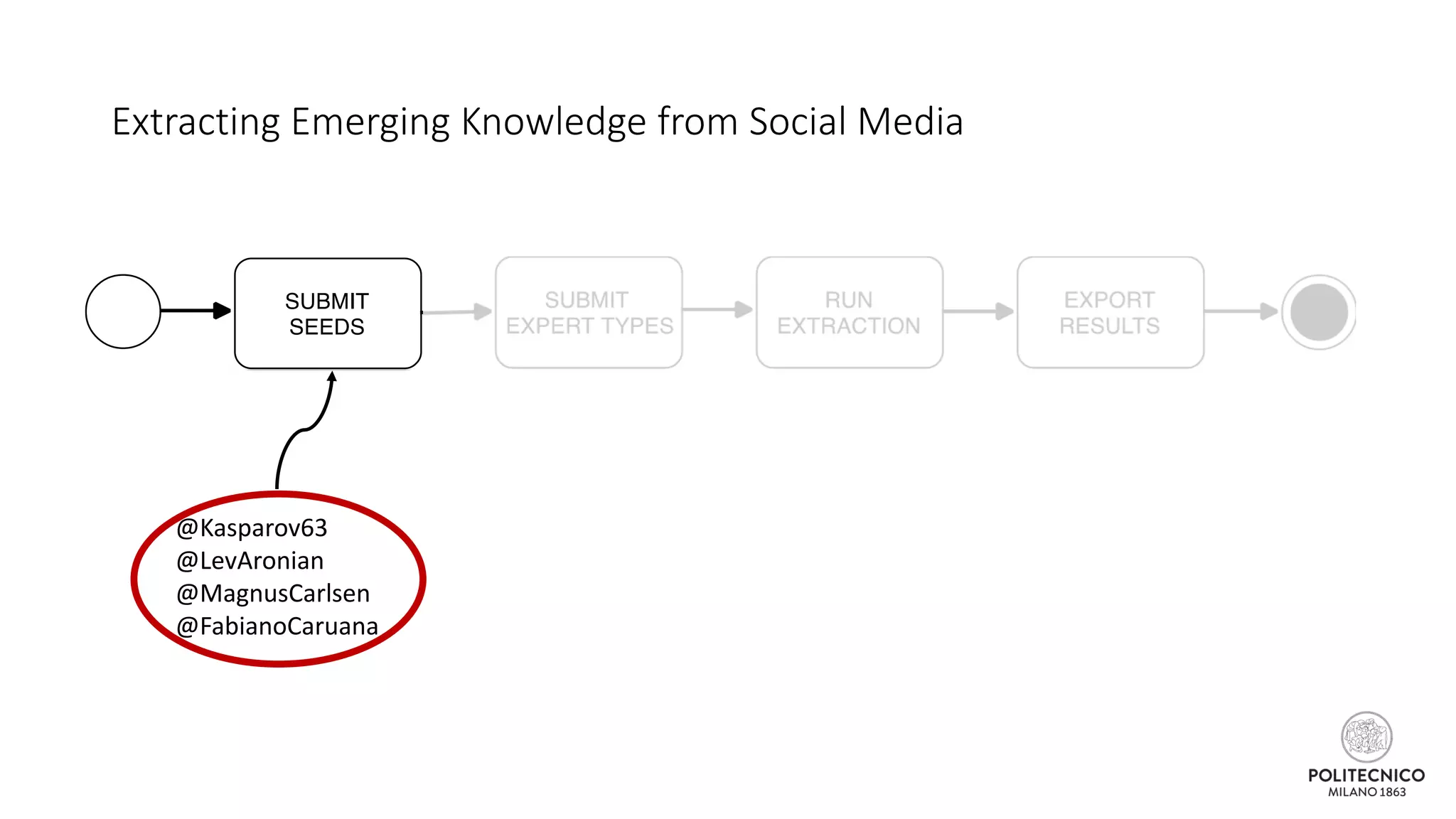
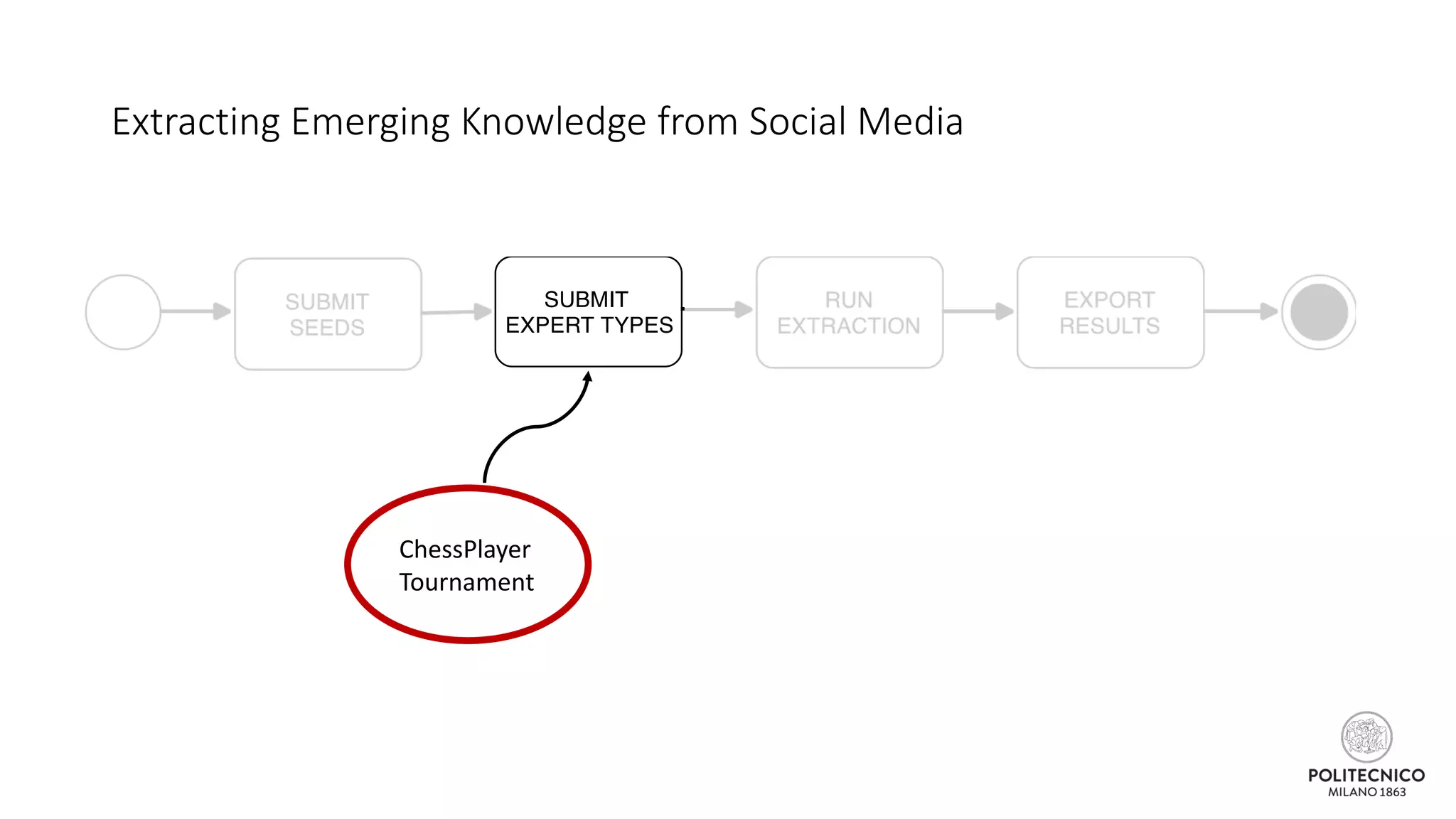
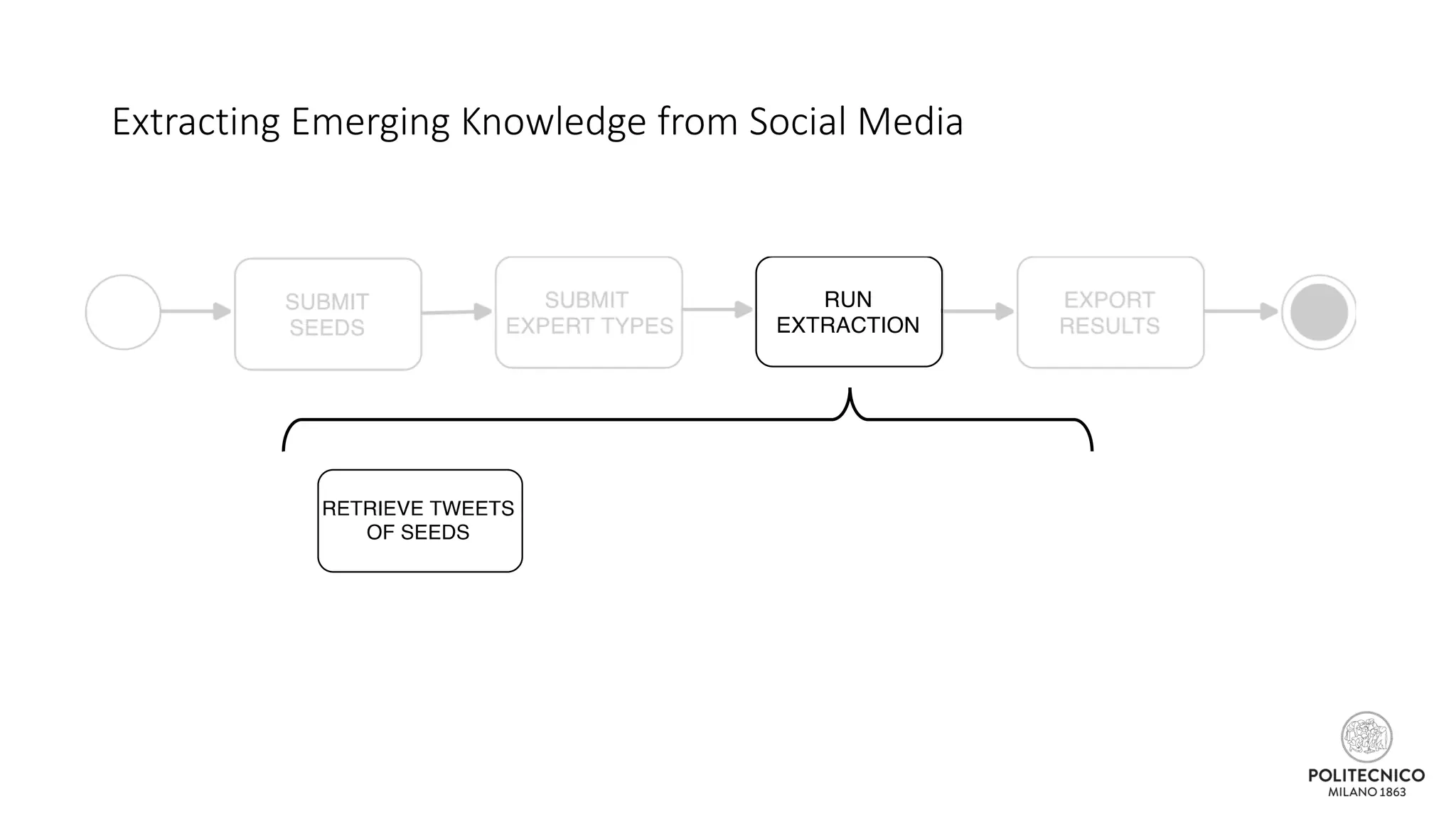
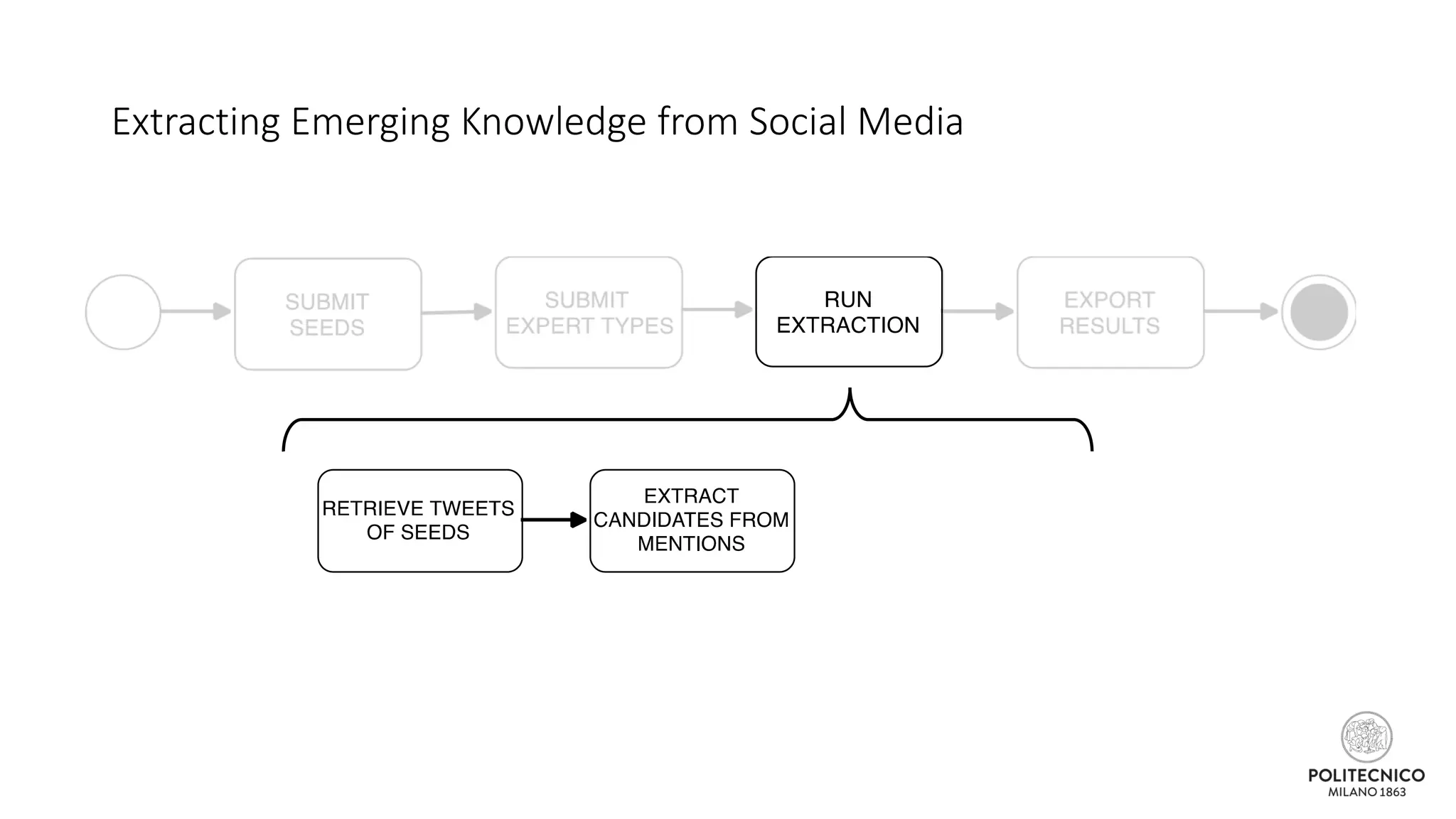
![Extracting Emerging Knowledge from Social Media
Feature vector: [𝑡1, 𝑡2, 𝑡3,..,𝑖1, 𝑖2, 𝑖3, . . ] where:
• 𝑡𝑖 are DBpedia types
• 𝑖𝑖 are DBpedia instances of Expert Types](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iterativeknowledgeextractionfromsocialnetworkswww2018msmsocialmediaske-180426094454/75/Iterative-knowledge-extraction-from-social-networks-The-Web-Conference-2018-10-2048.jpg)
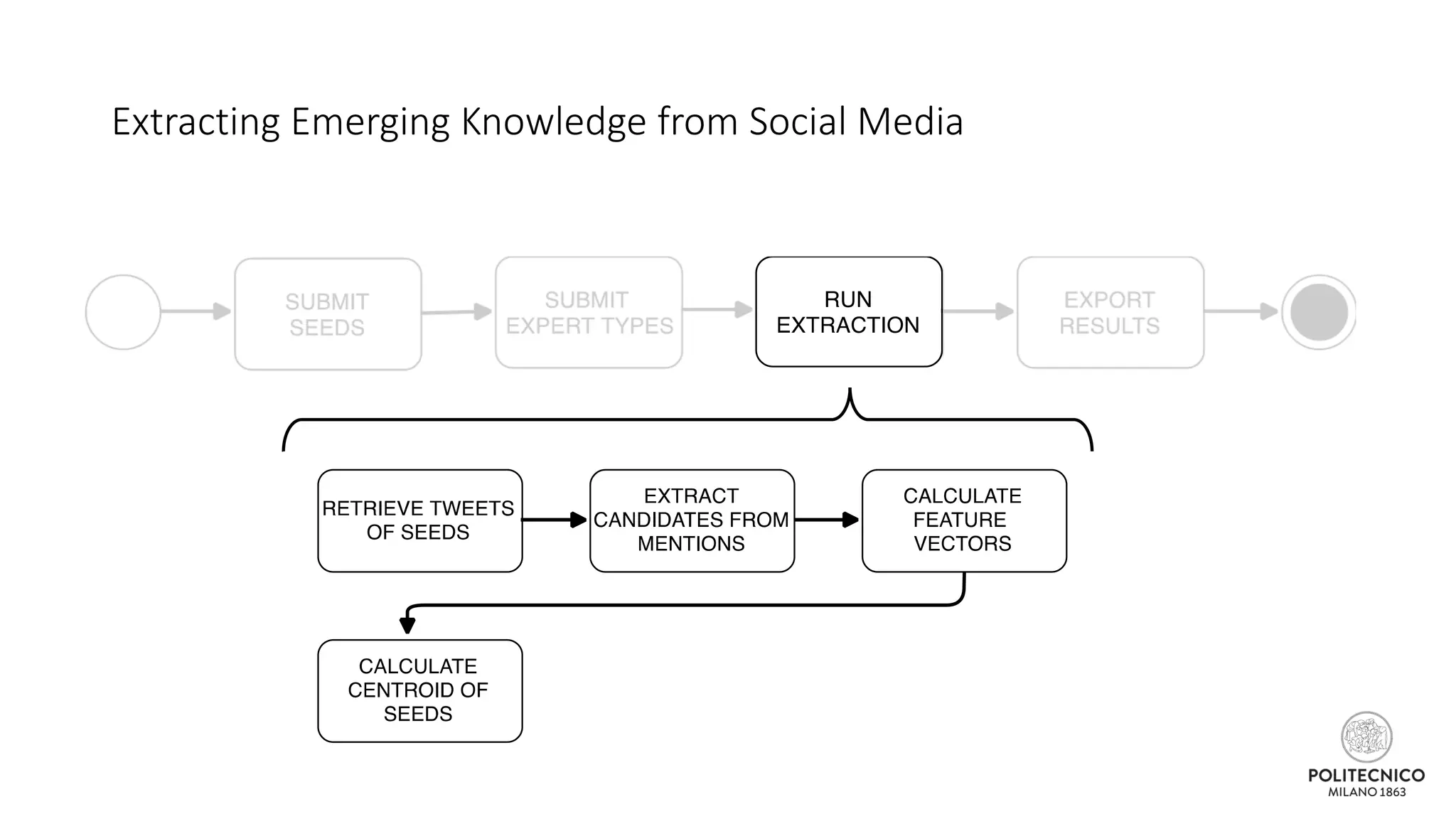
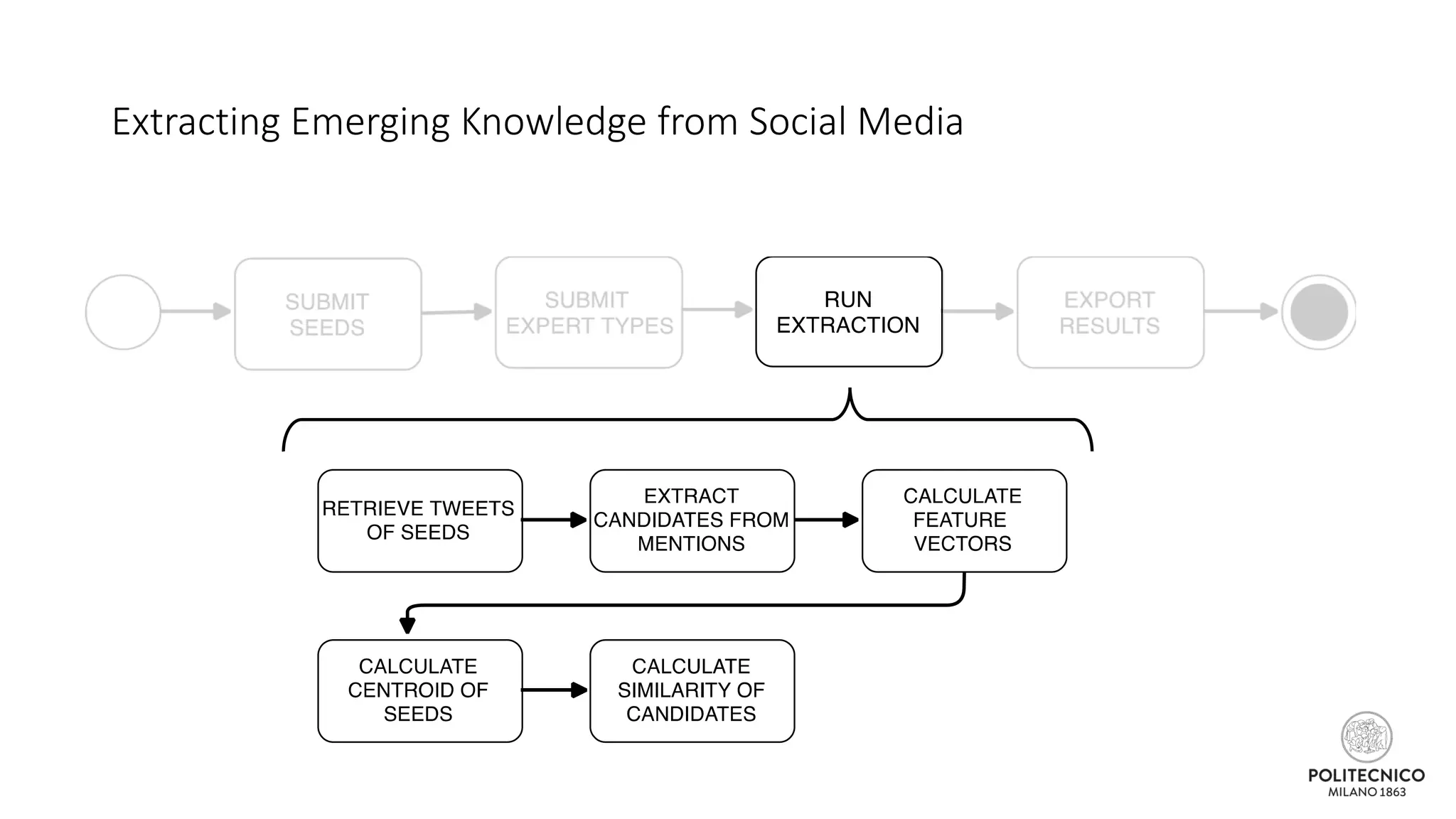
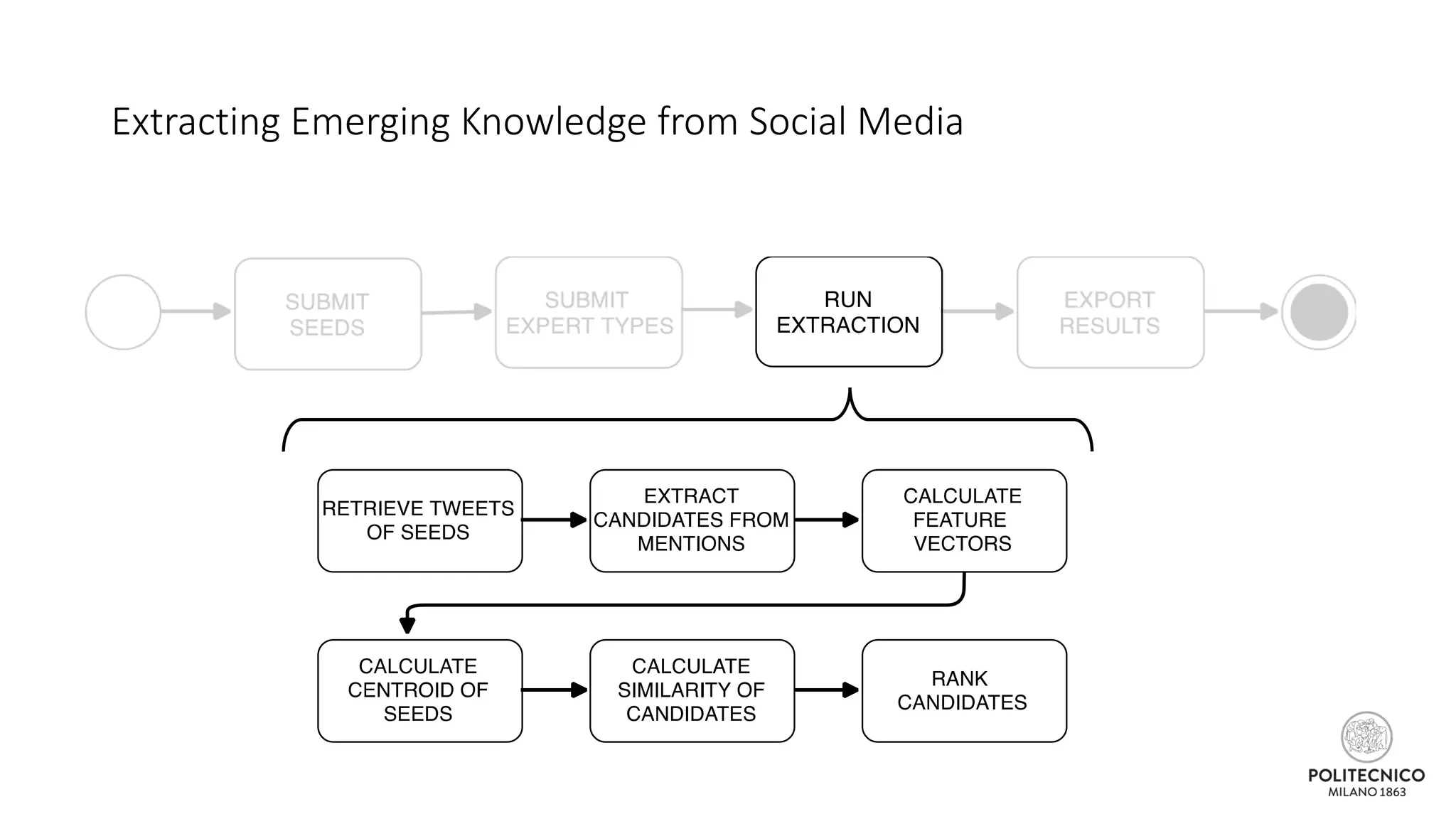

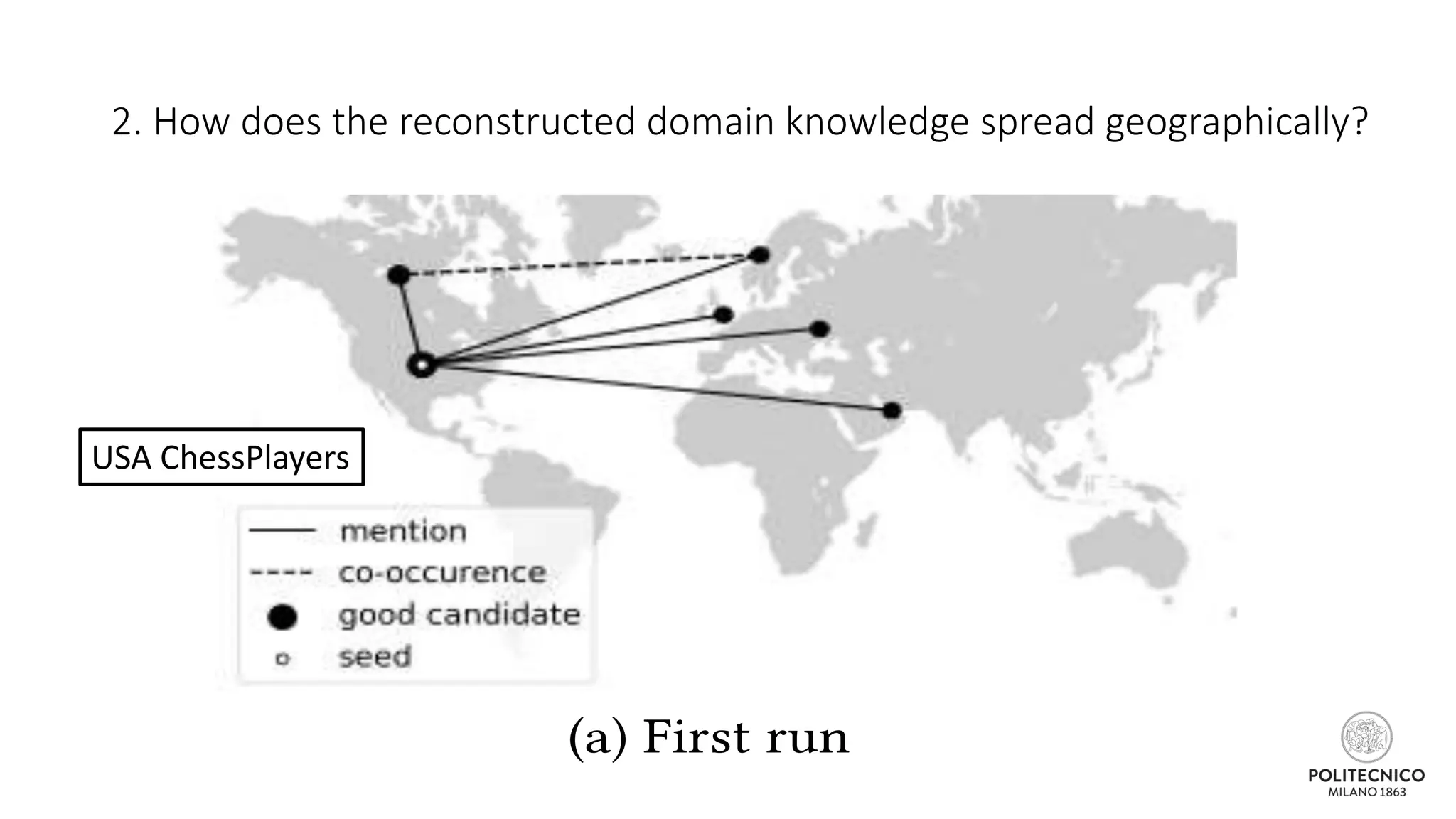
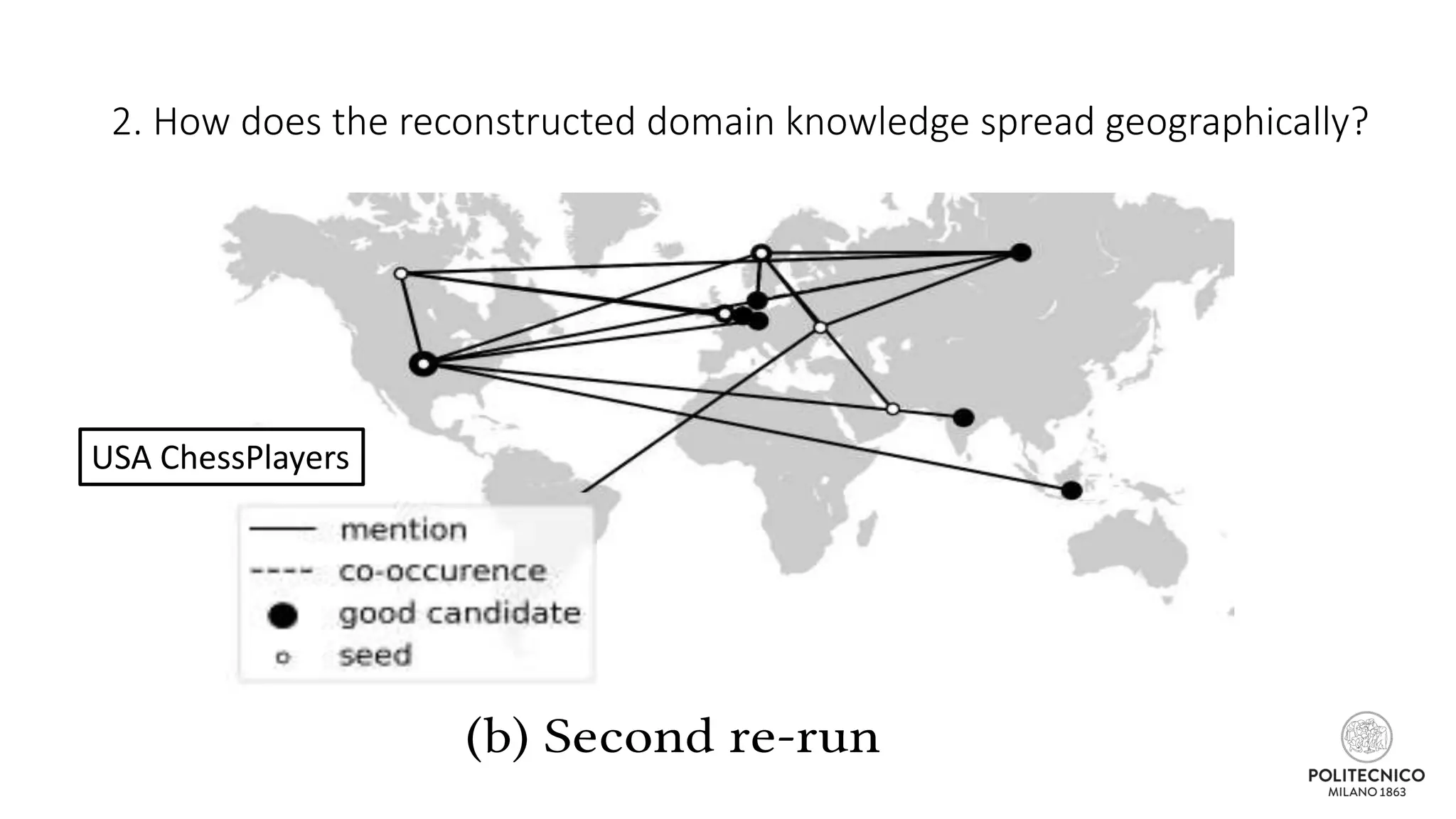
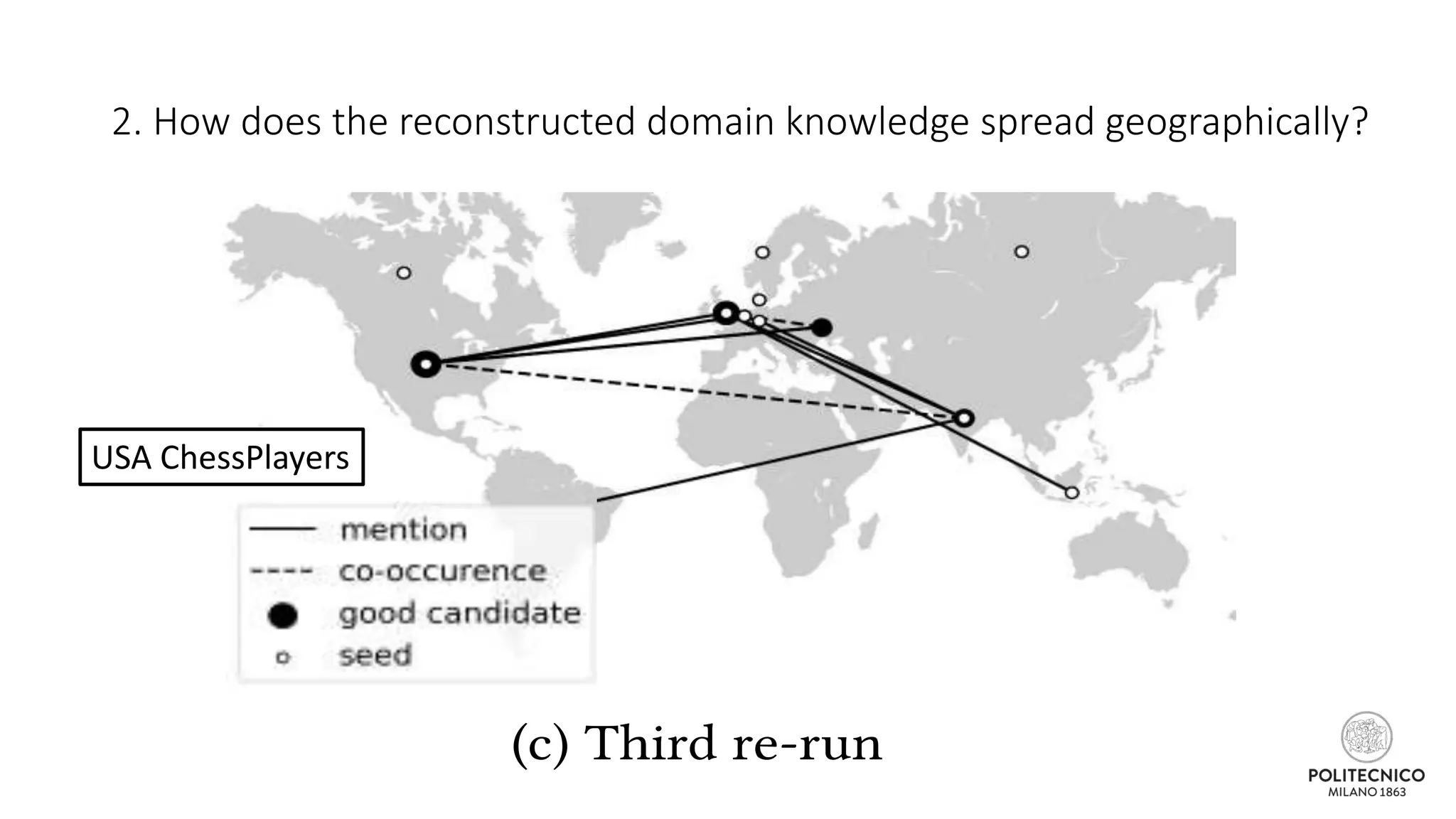
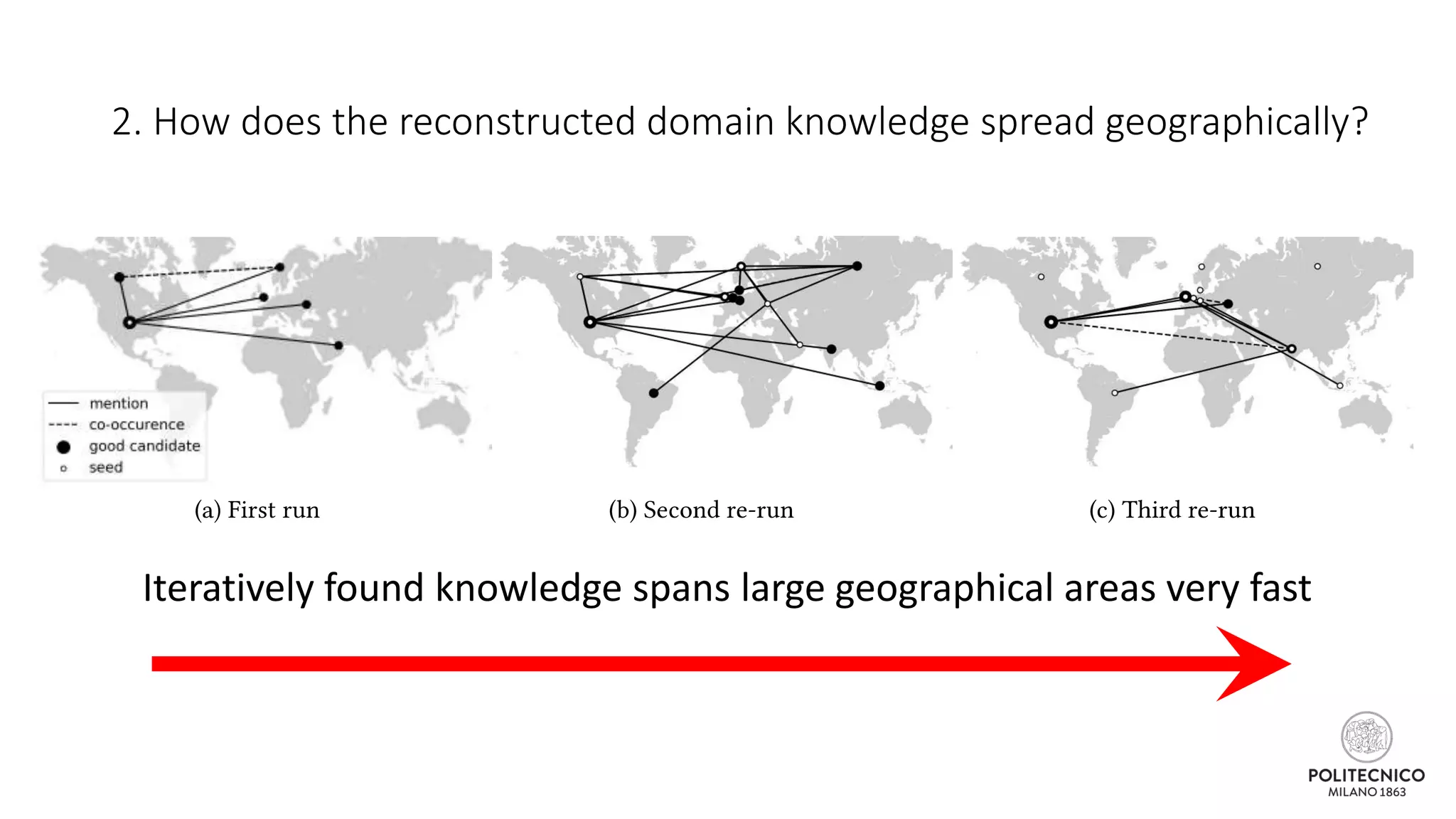
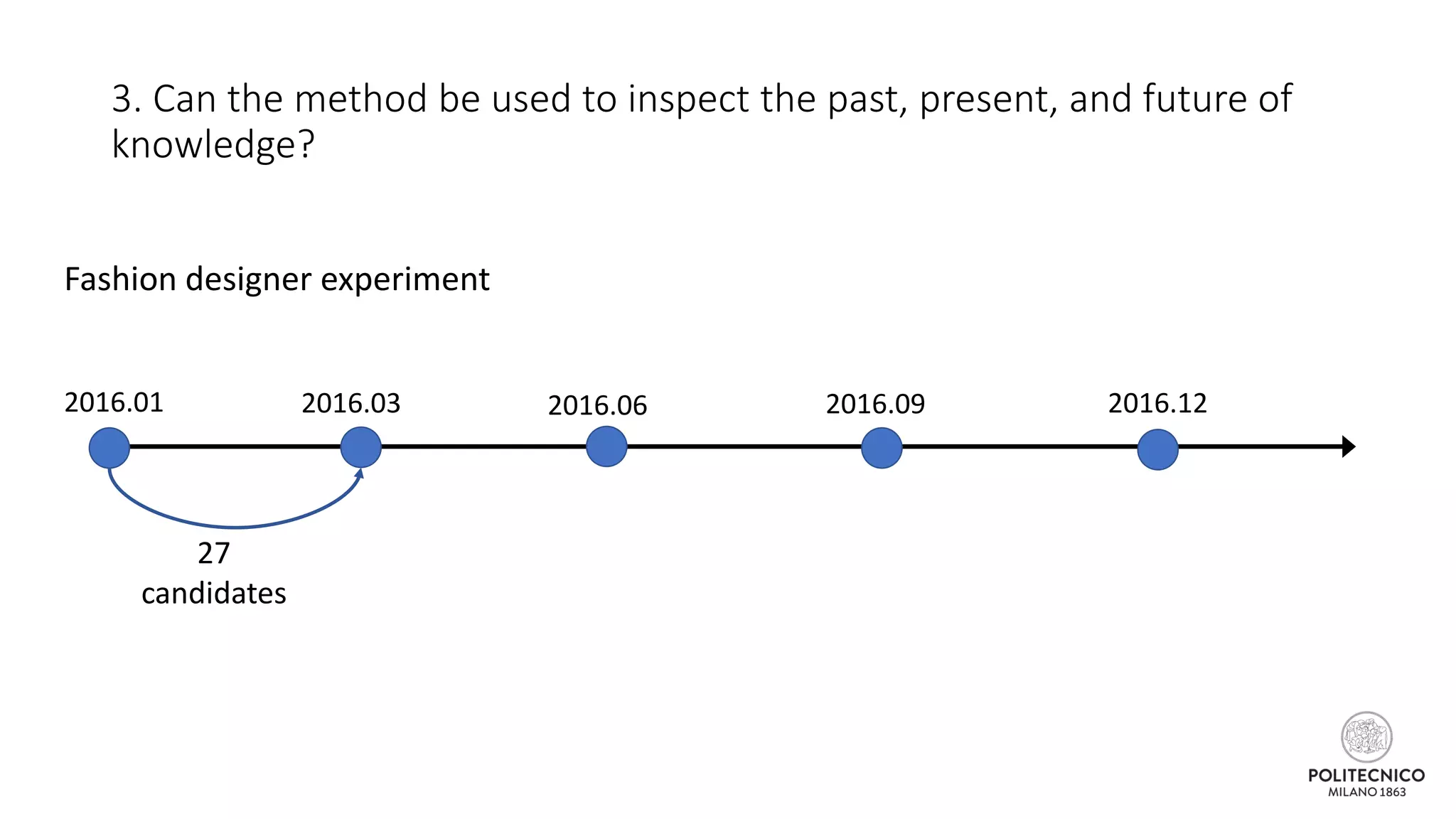
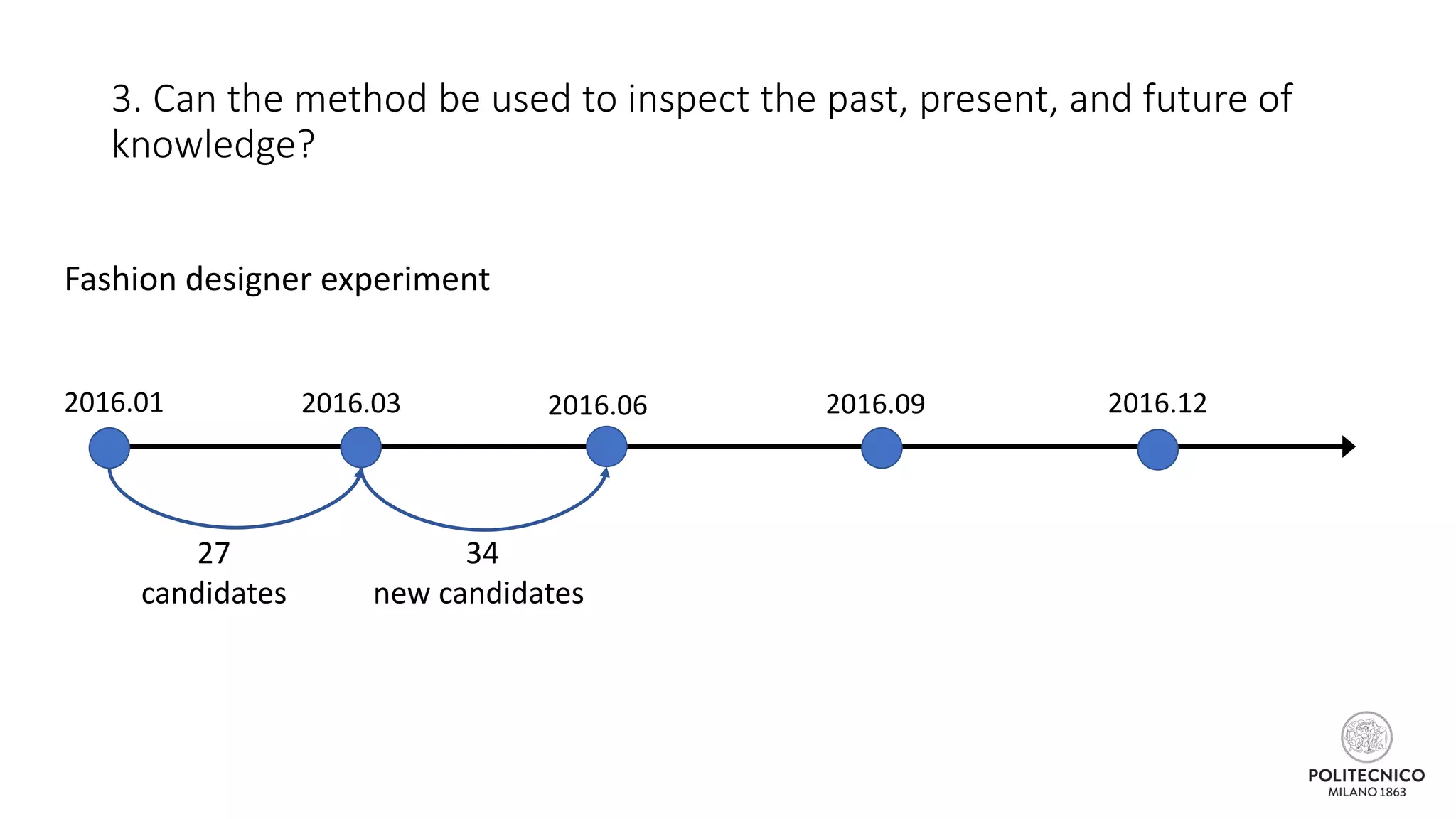
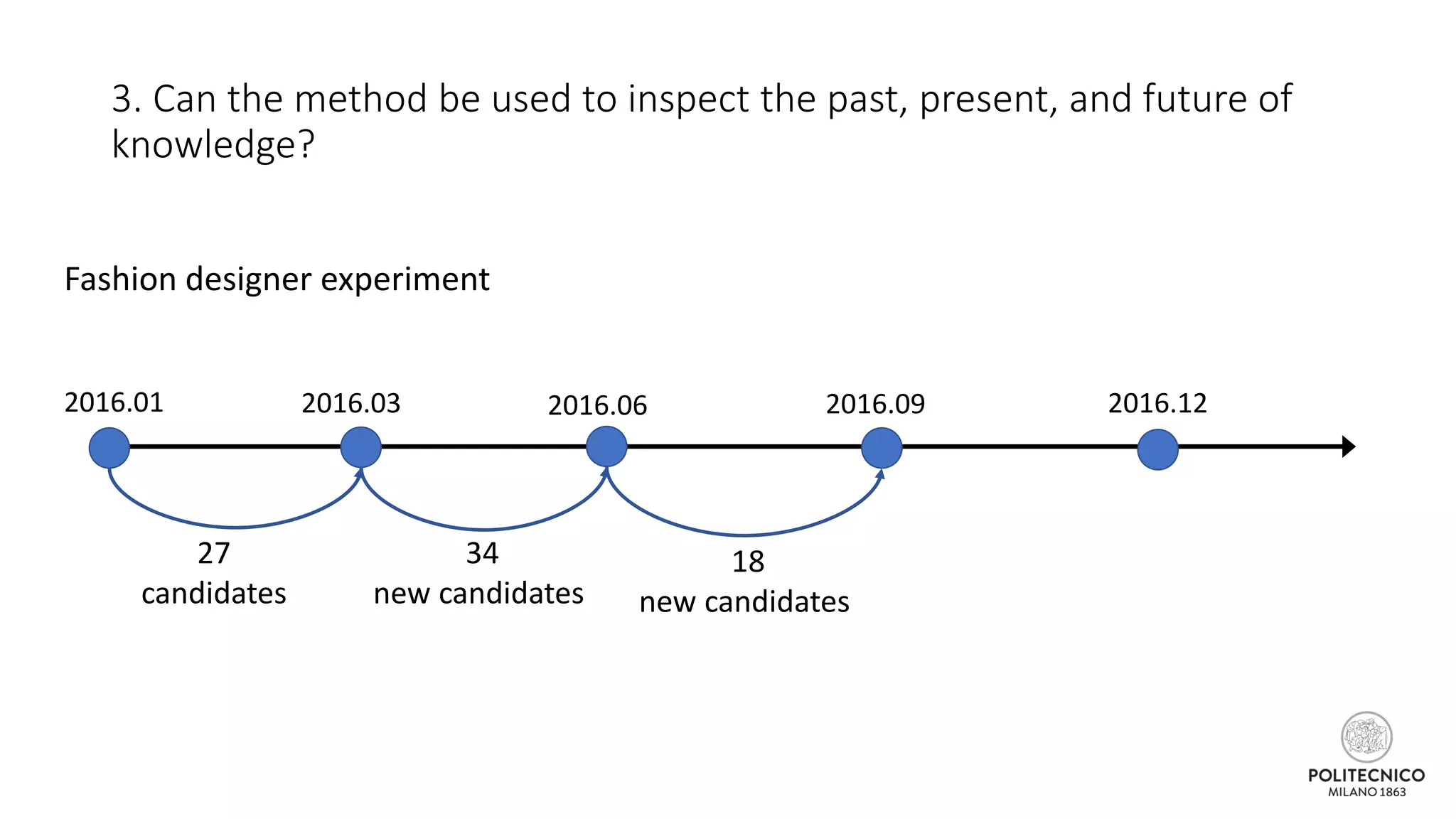
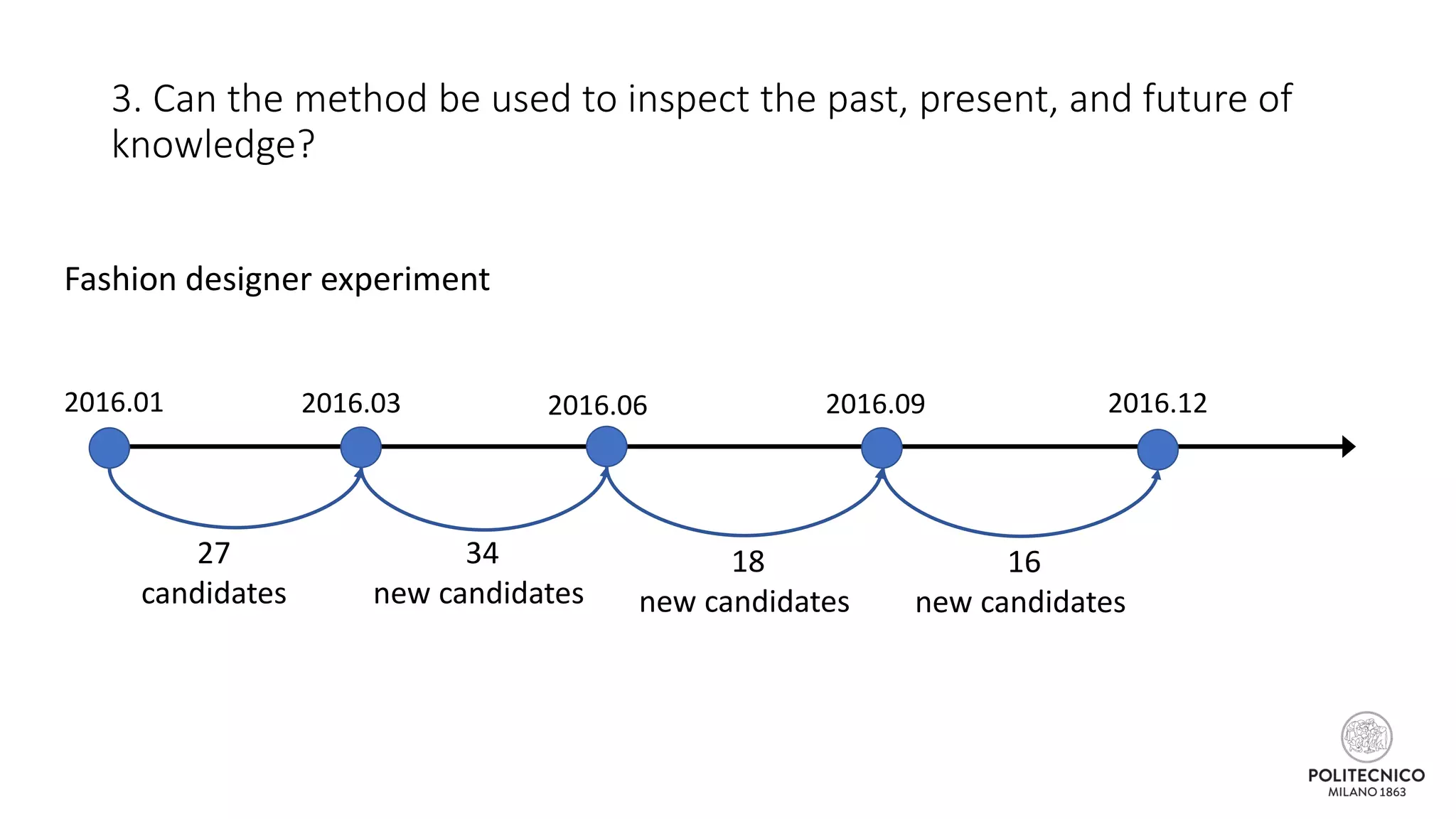
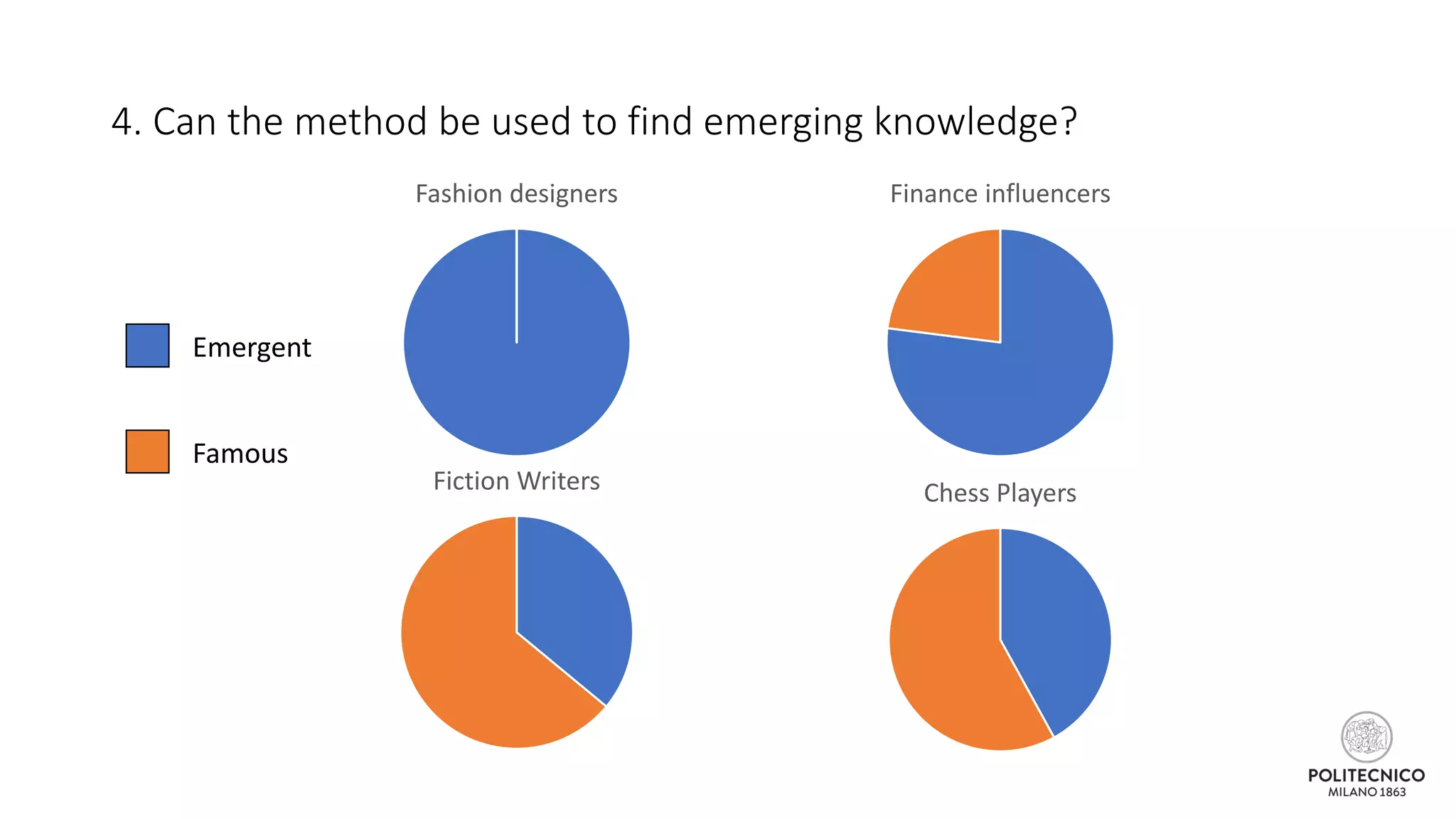

![Some updates..
Feature vector of user u: [𝑛1, 𝑛2, 𝑛3, . . ] where:
• 𝑛𝑖 are nouns/verbs/proper nouns frequencies in user tweets
Syntactic features: verbs, nouns and proper nouns](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iterativeknowledgeextractionfromsocialnetworkswww2018msmsocialmediaske-180426094454/75/Iterative-knowledge-extraction-from-social-networks-The-Web-Conference-2018-30-2048.jpg)
![Some updates..
Feature vector of user u: [𝑛1, 𝑛2, 𝑛3, . . ] where:
• 𝑛𝑖 are nouns/verbs/proper nouns frequencies in user tweets
Syntactic features: verbs, nouns and proper nouns
We consider 𝑛𝑖 as the probabilities that u uses the i-th word in his
tweets.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iterativeknowledgeextractionfromsocialnetworkswww2018msmsocialmediaske-180426094454/75/Iterative-knowledge-extraction-from-social-networks-The-Web-Conference-2018-31-2048.jpg)
![Some updates..
Feature vector of user u: [𝑛1, 𝑛2, 𝑛3, . . ] where:
• 𝑛𝑖 are nouns/verbs/proper nouns frequencies in user tweets
We consider 𝑛𝑖 as the probabilities that u uses the i-th word in his
tweets.
Syntactic features: verbs, nouns and proper nouns
DISTRIBUTION OF WORDS Entropy as metric](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iterativeknowledgeextractionfromsocialnetworkswww2018msmsocialmediaske-180426094454/75/Iterative-knowledge-extraction-from-social-networks-The-Web-Conference-2018-32-2048.jpg)