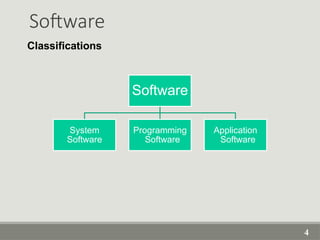
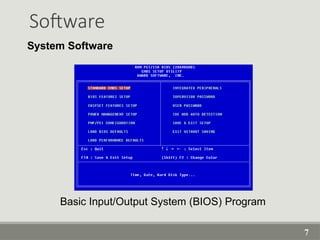
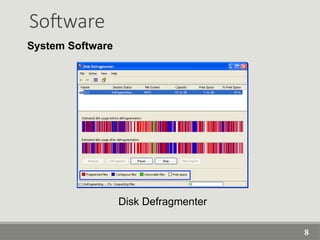
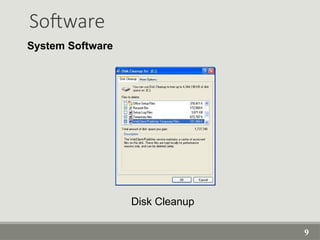
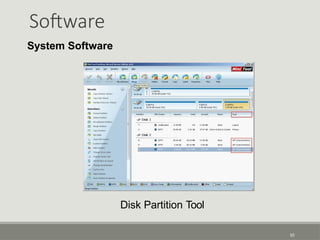
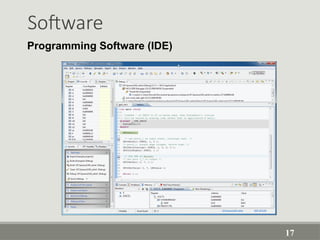
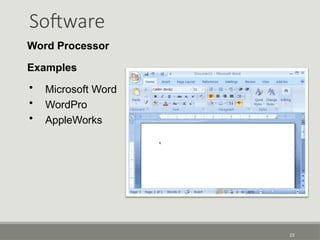
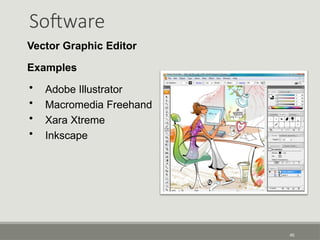
The document provides an overview of computer software, detailing its types, classifications, and specific examples. It distinguishes between system software, programming software, and application software, highlighting their functions and features. Additionally, it covers software licensing types and various forms of software piracy.