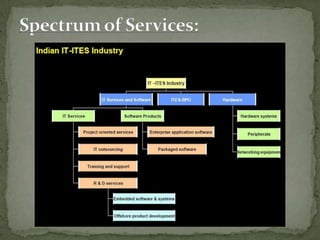
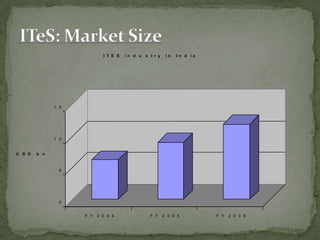
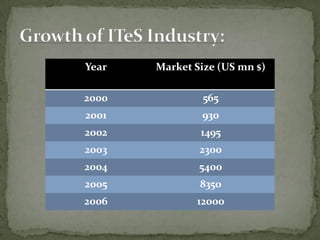
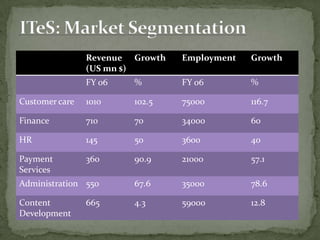
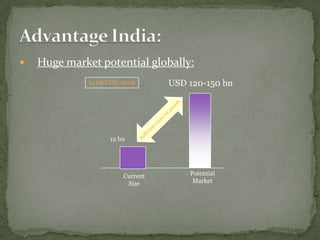
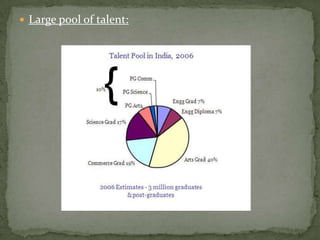
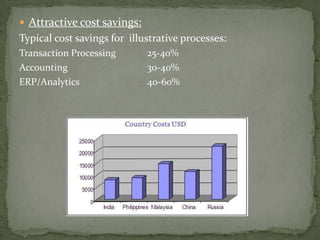
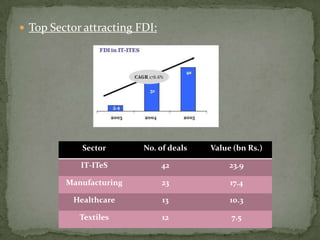
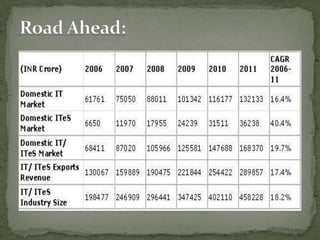
The document discusses the growth of the ITES (IT Enabled Services) industry in India. It notes that the industry has grown significantly over the past decade and continues to experience double-digit growth. It attributes the success of the industry to factors like large talent pool, attractive cost savings compared to developed countries, supportive infrastructure and regulatory environment, and the huge global market potential for outsourced ITES. The document also outlines the evolution of the industry through various phases and identifies some emerging areas for future growth.