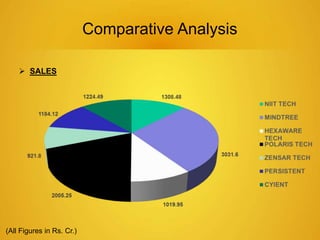
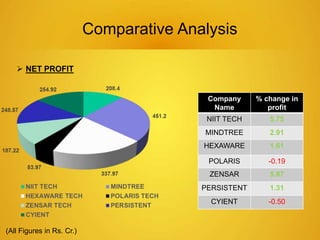
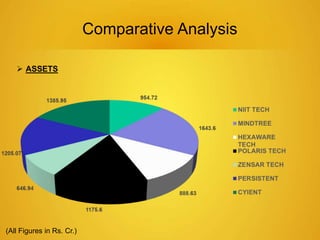
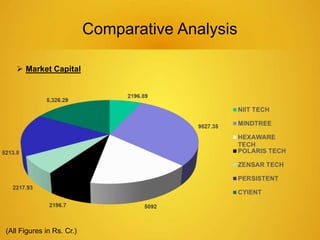
This document provides an overview of the IT sector in India. It discusses how the IT sector has transformed India's image and is now a major driver of the economy, generating millions of jobs. The key players in the Indian IT sector are discussed, including major companies like TCS, Wipro, HCL and Infosys. The document also outlines trends in the sector such as increasing outsourcing, investments and mergers and acquisitions. The future of the IT sector is poised for continued growth, projected to be a $130 billion industry by 2015, fueling the overall economy.