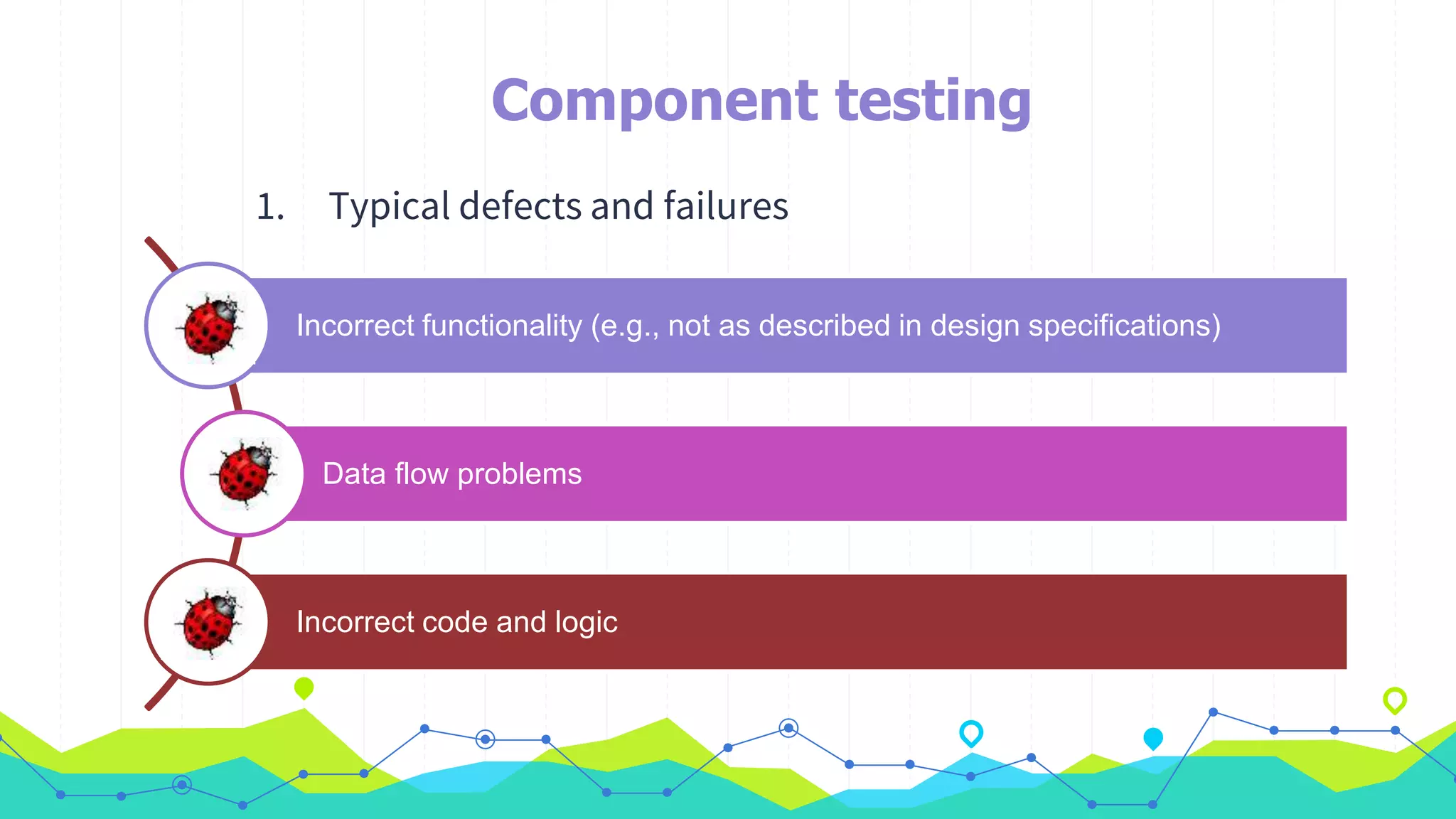
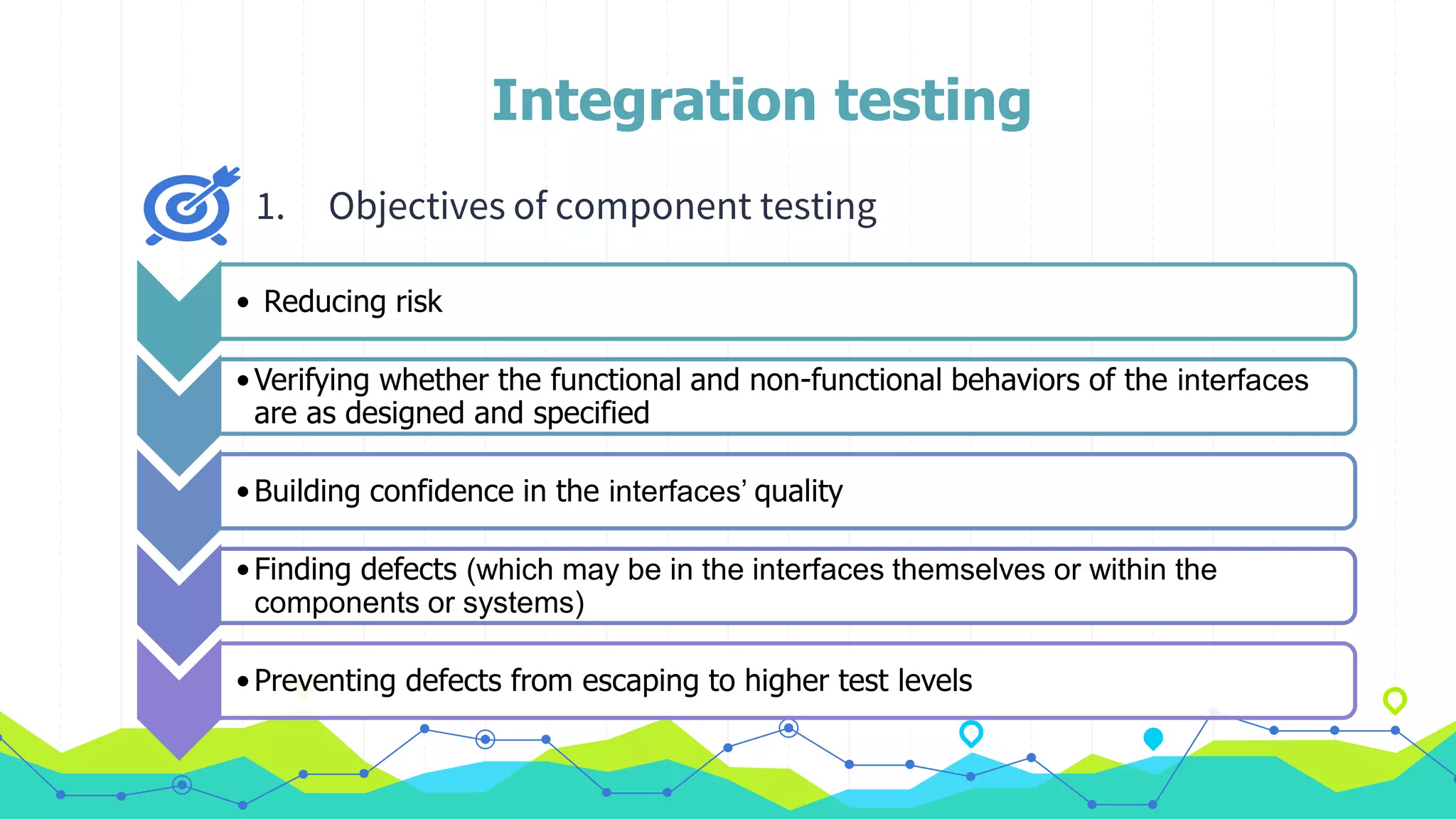
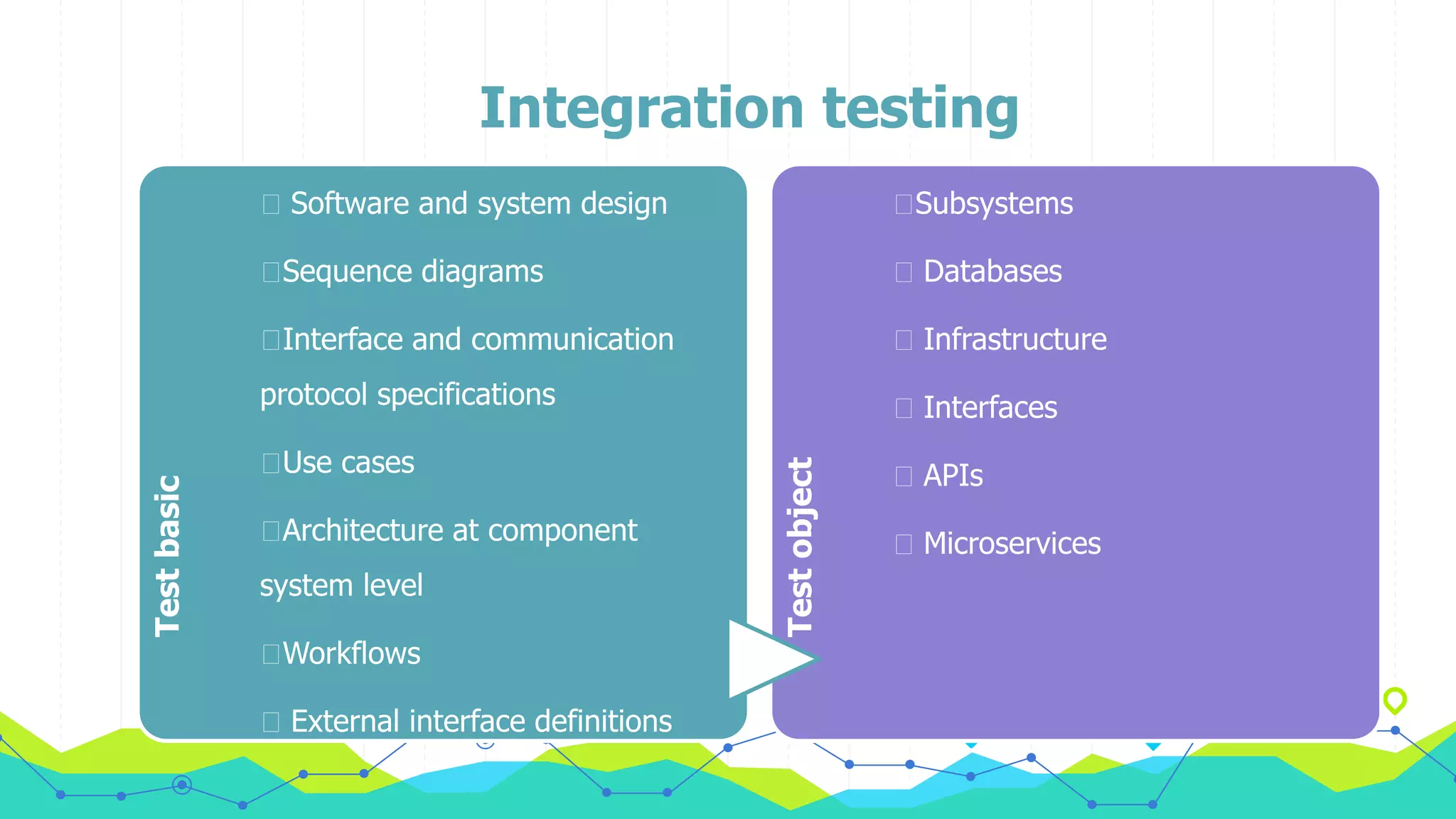
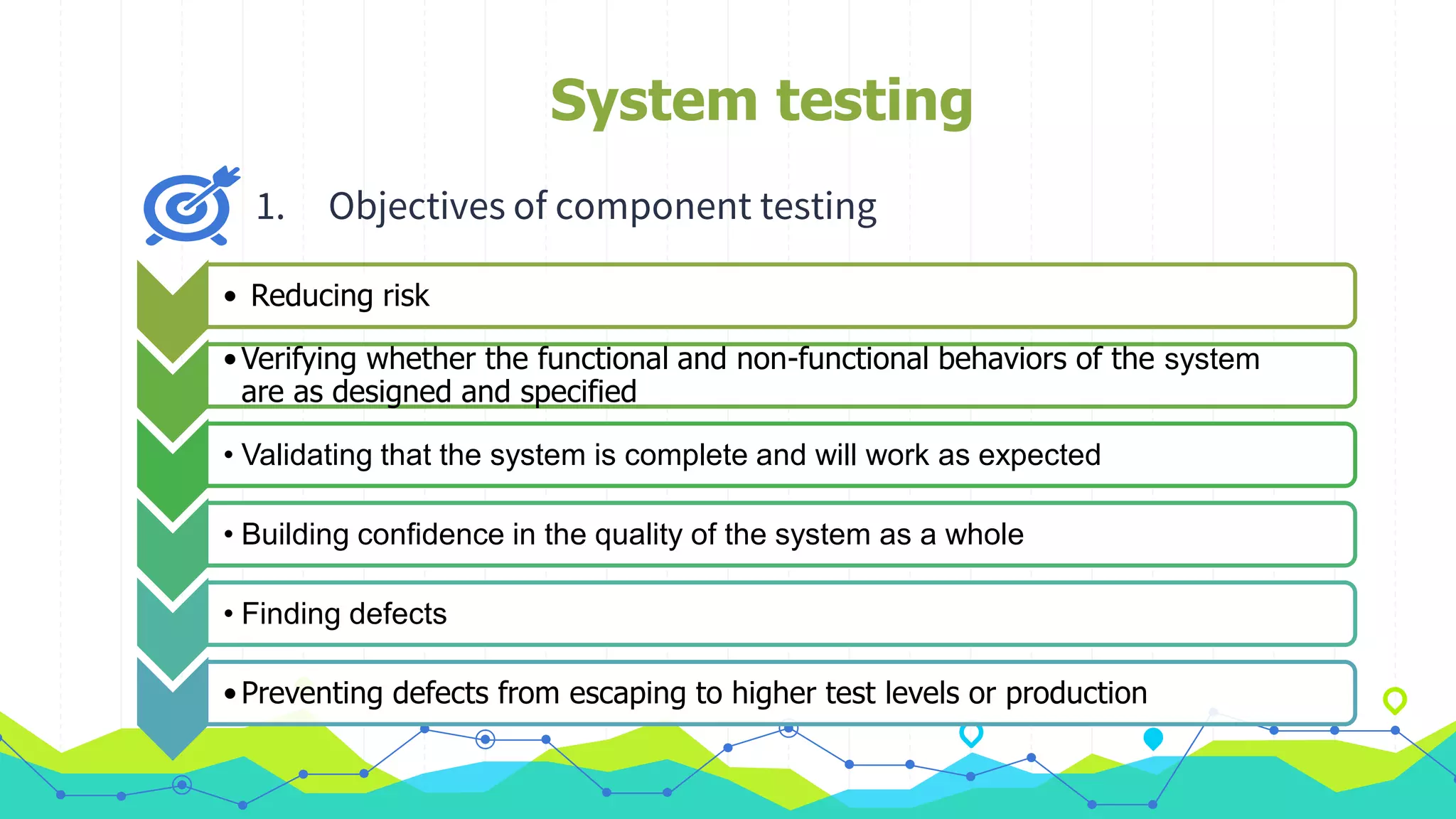
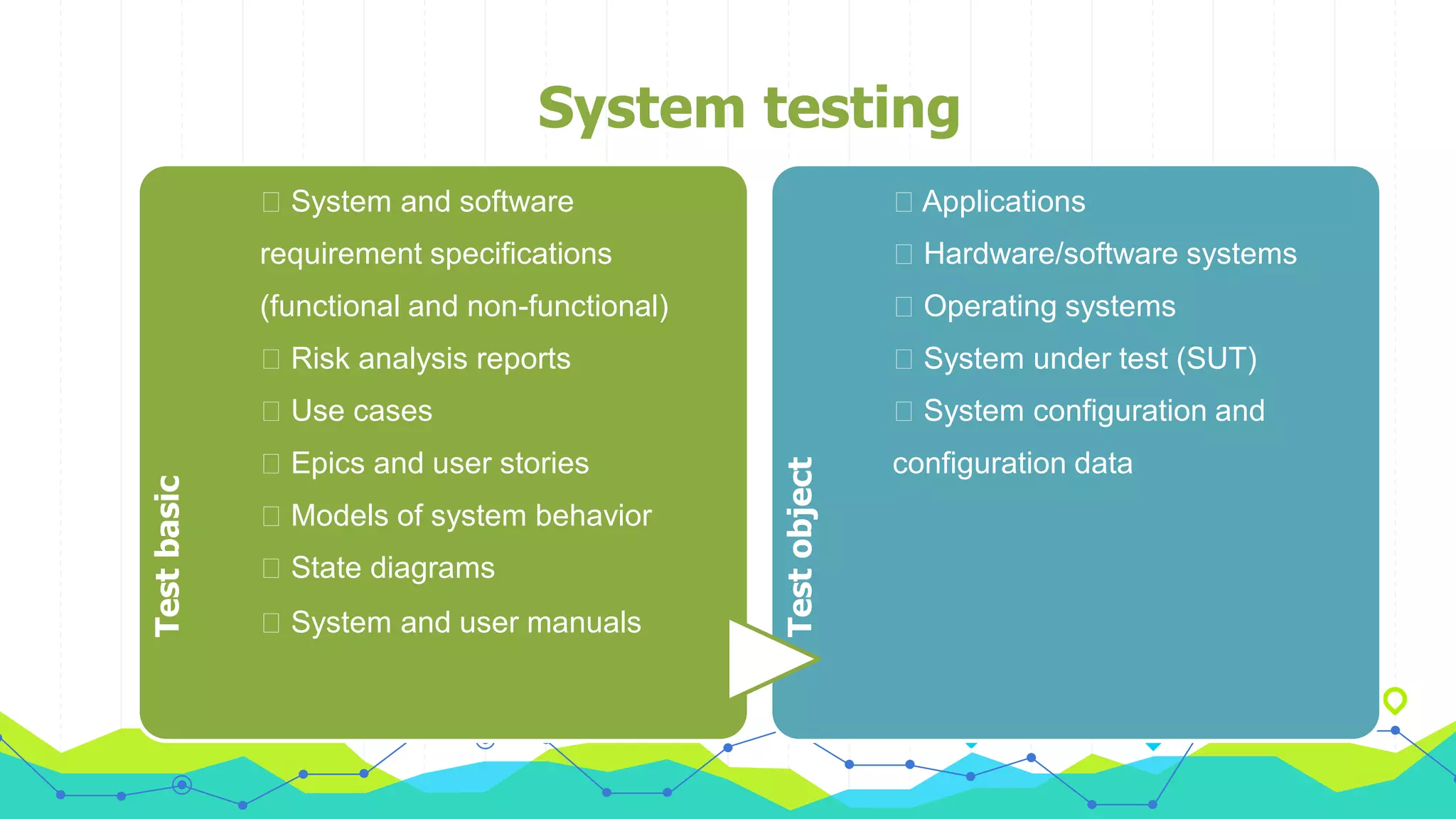
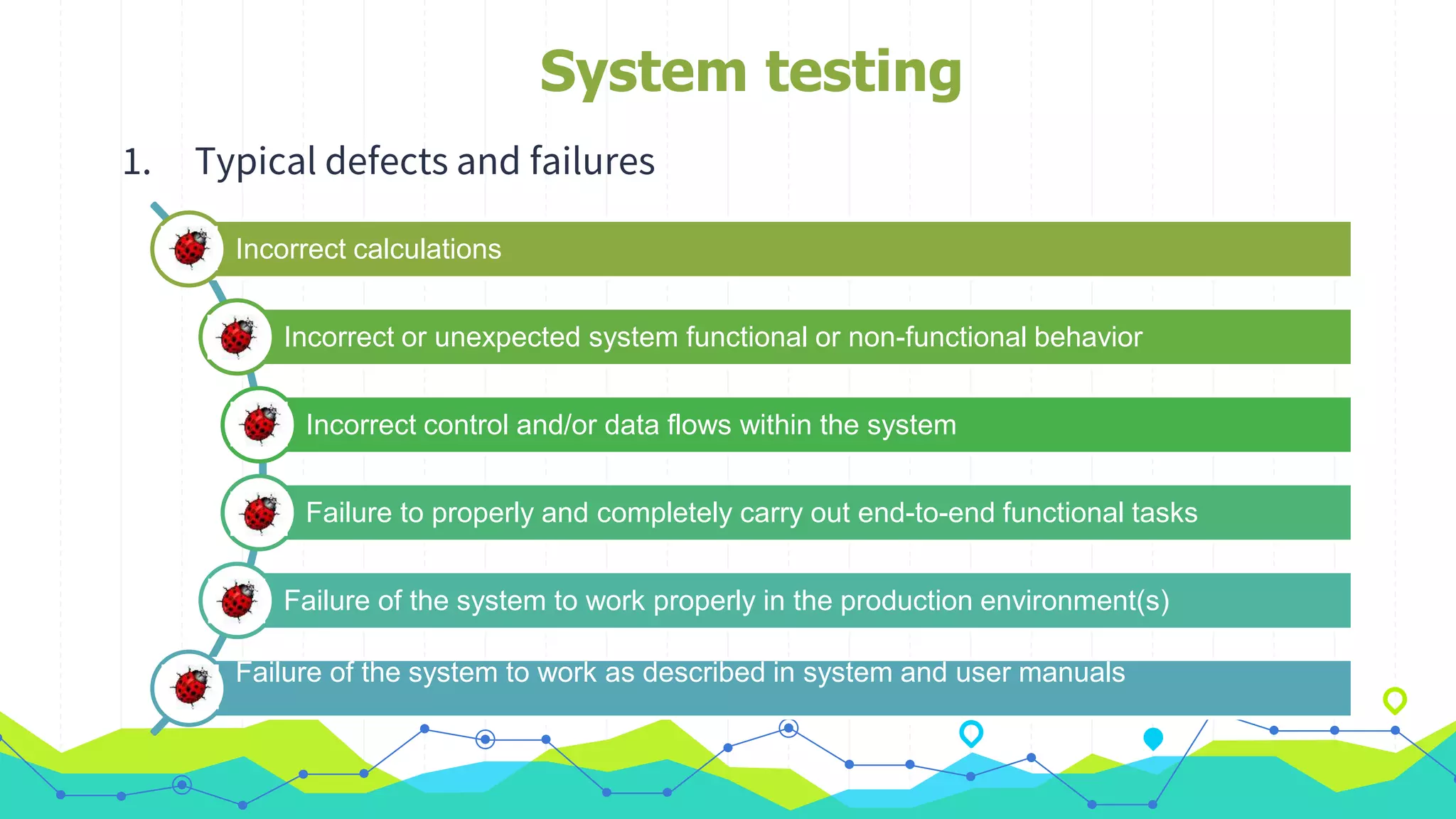
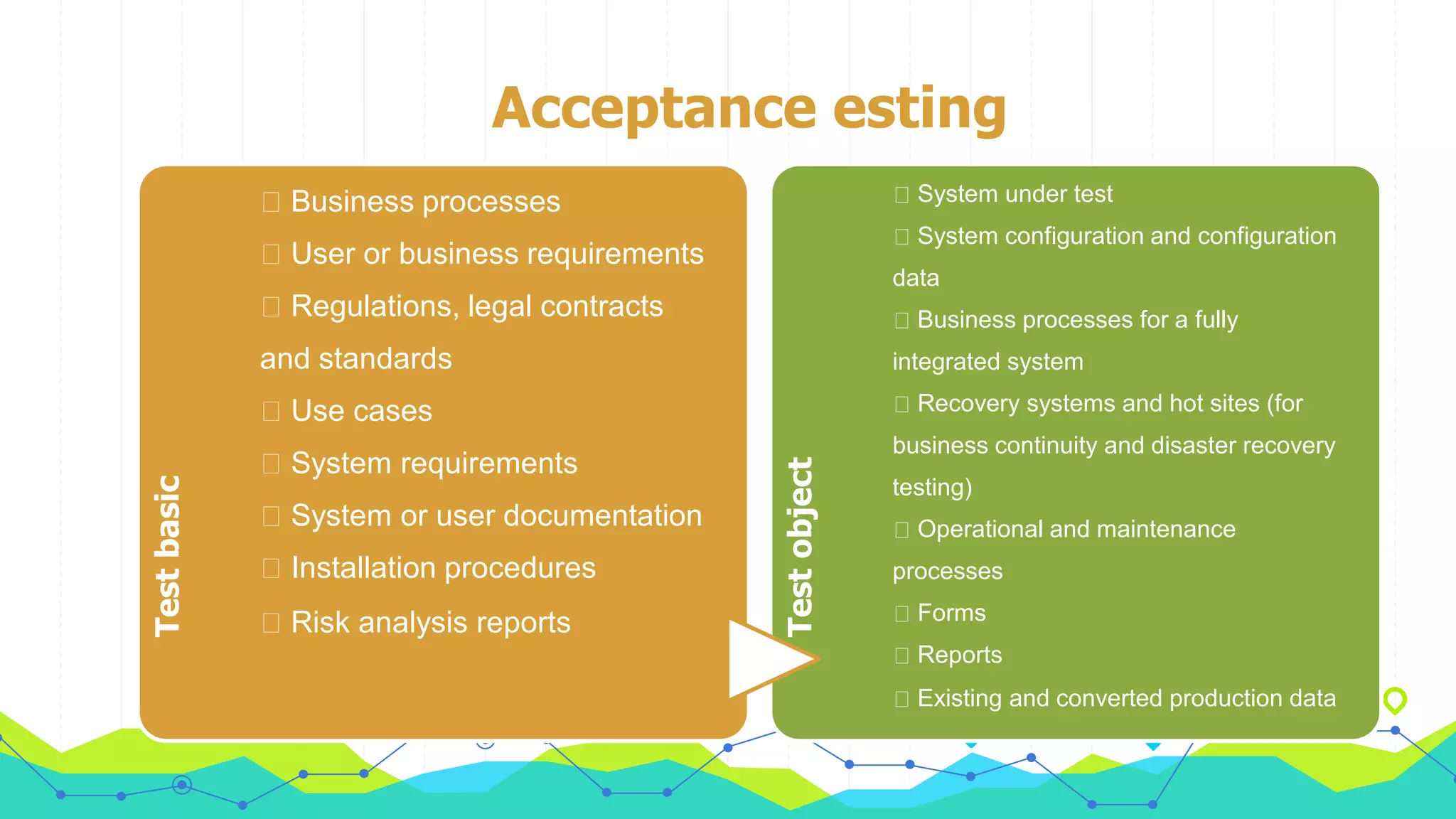
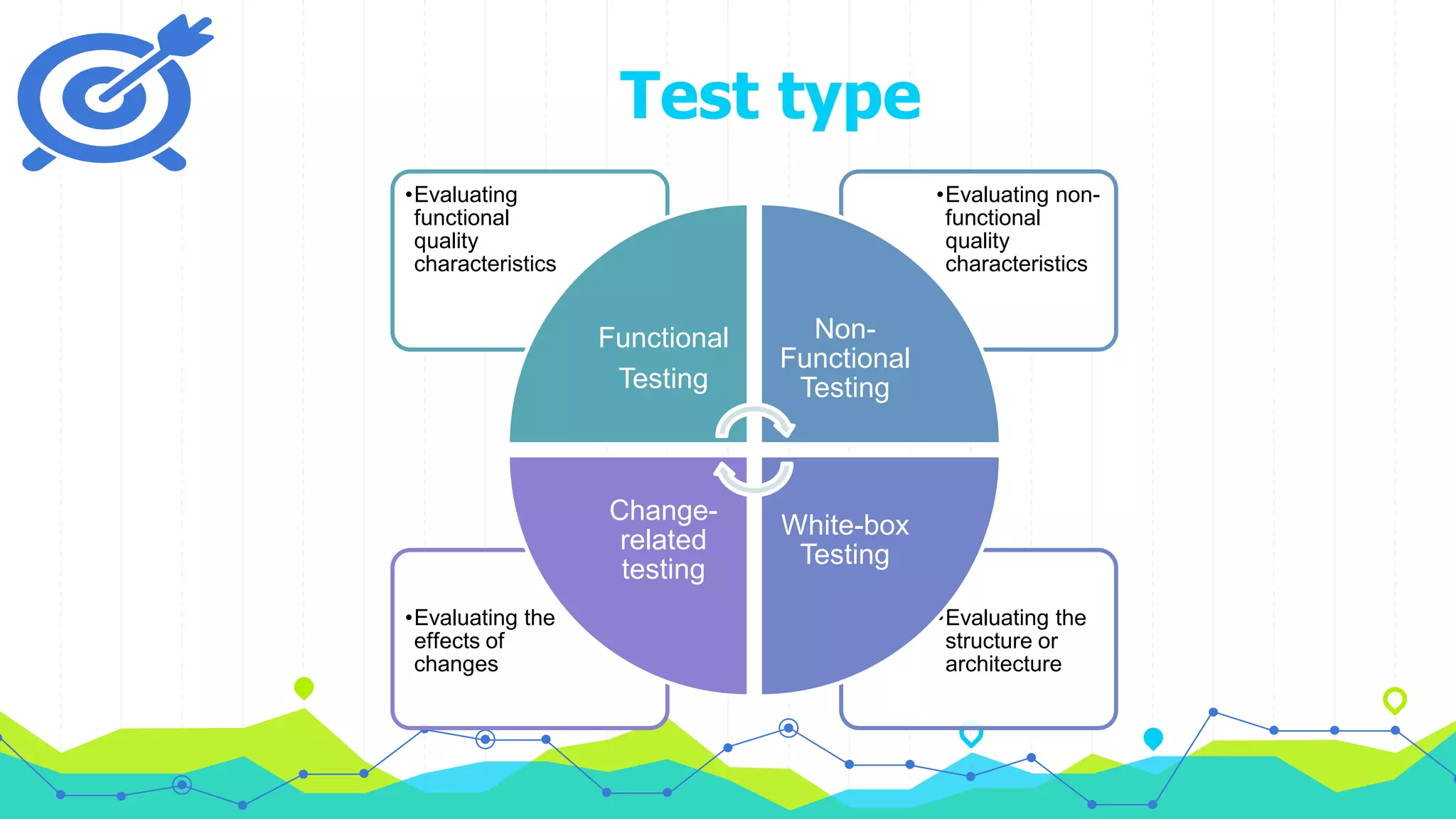
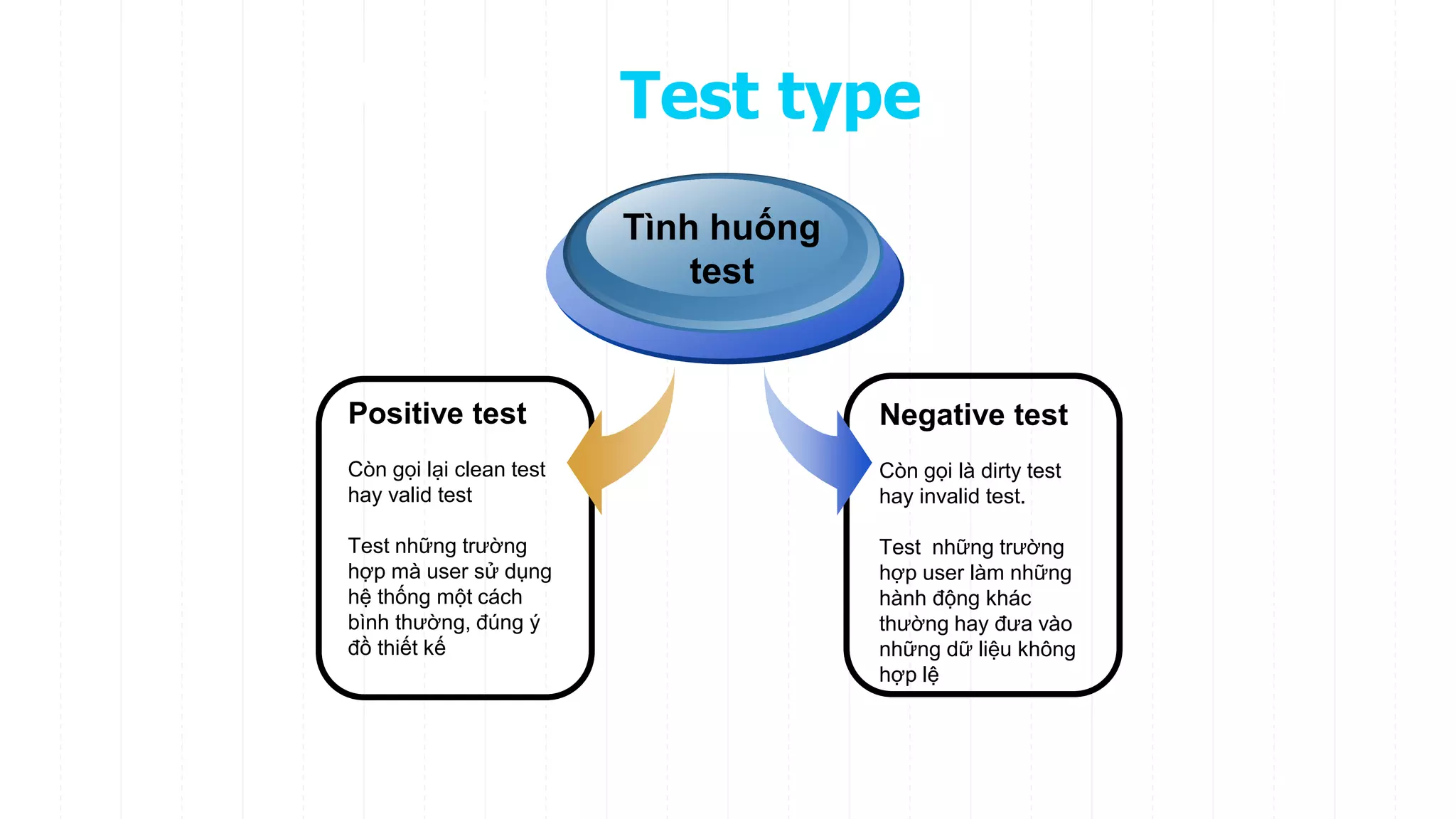
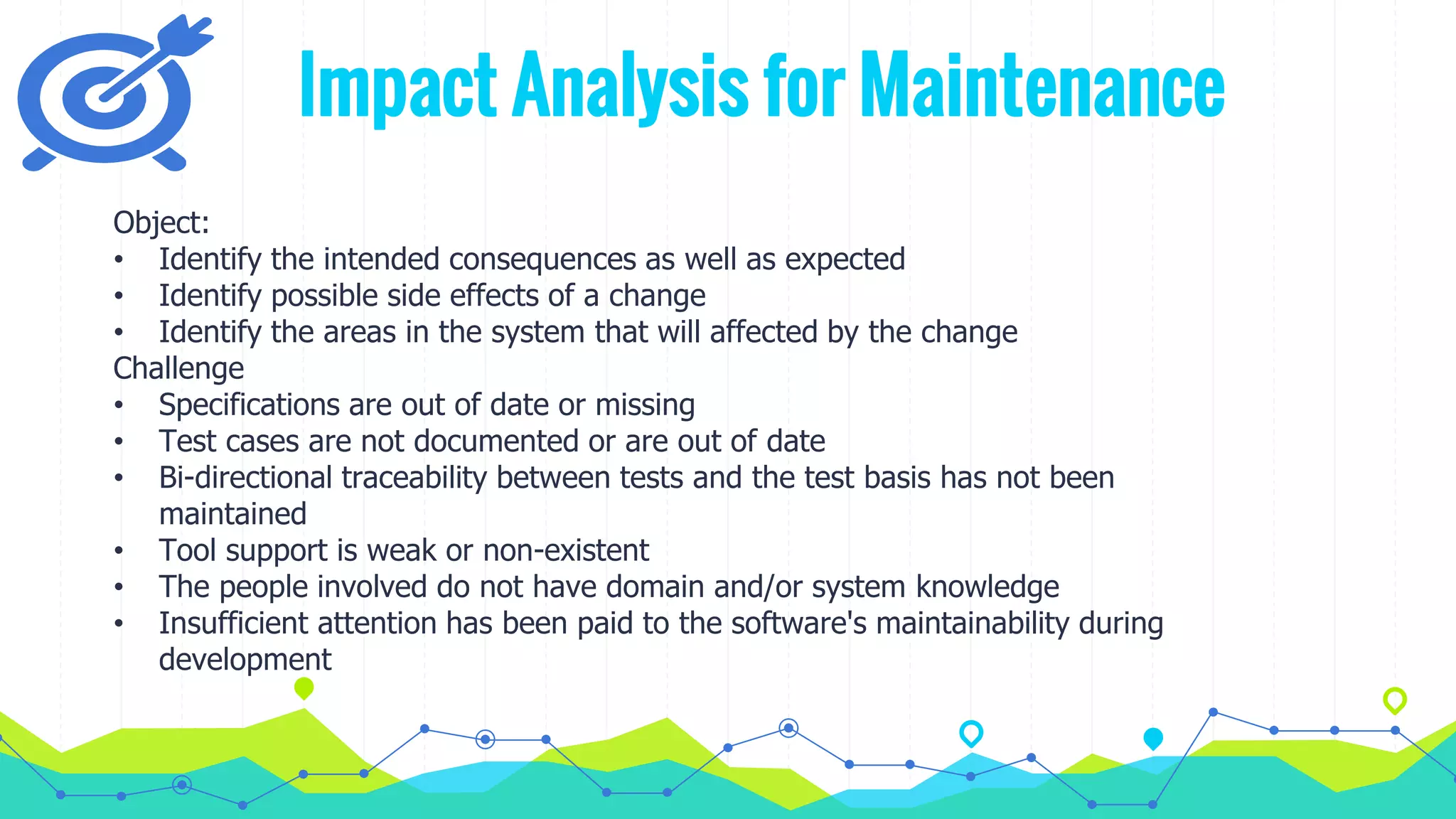
The document discusses different types of testing throughout the software development lifecycle, including component testing, integration testing, system testing, and acceptance testing. It provides objectives and typical defects found for each type. Component testing focuses on individual components/units and verifies functionality and prevents defects. Integration testing focuses on interfaces and prevents interface defects. System testing verifies full system behavior prevents escapes. Acceptance testing validates system meets requirements. Maintenance testing is also discussed and should be done when changes are made to evaluate success and check for side effects.