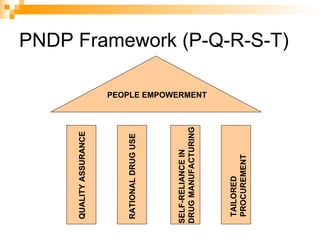
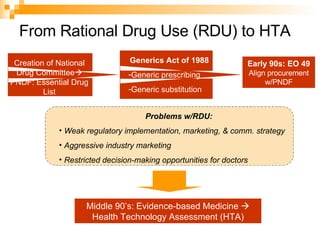
The document summarizes the drug approval process and relevant laws in the Philippines. It describes the 5 phases of clinical trials required to approve a drug, from pre-clinical testing to post-marketing surveillance. It also outlines the country's PNDF framework for ensuring drug quality, rational use, and self-reliance. Key laws discussed include the 1988 Generic Drugs Act promoting generic drug use, the 1997 Traditional and Alternative Medicine Act, and the 2002 Dangerous Drugs Act strengthening penalties for drug crimes.