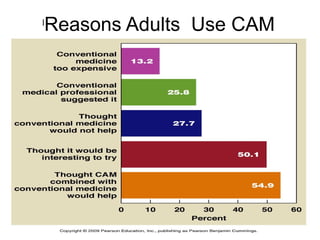
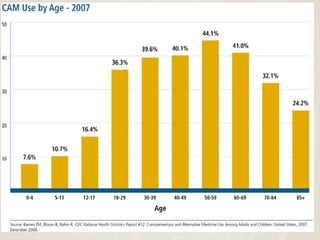
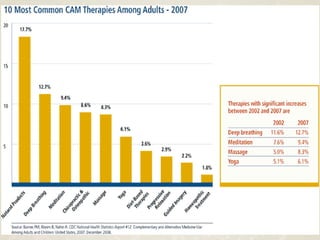
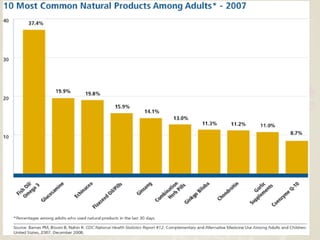
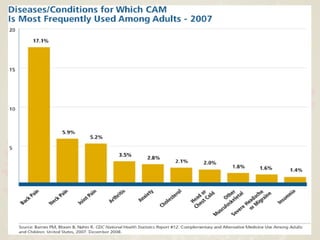
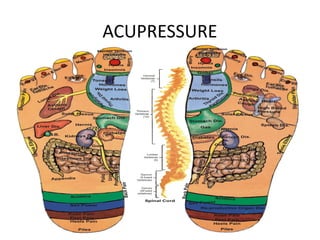
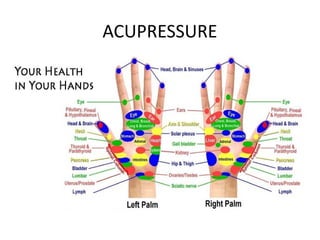
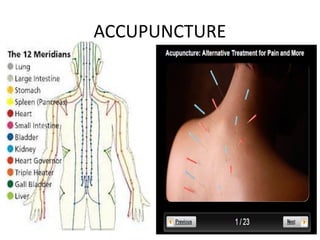
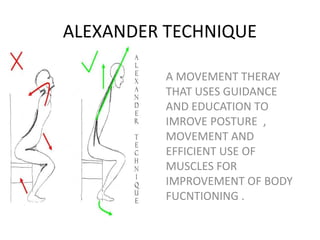
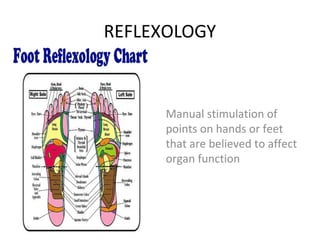
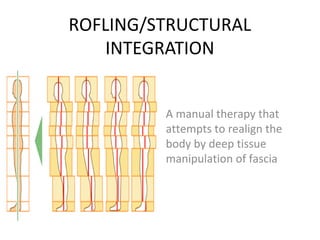
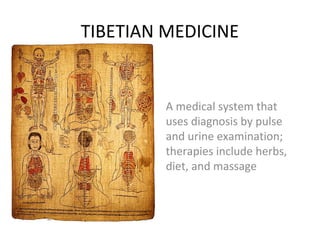
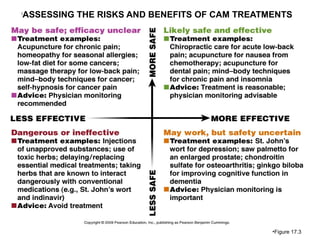
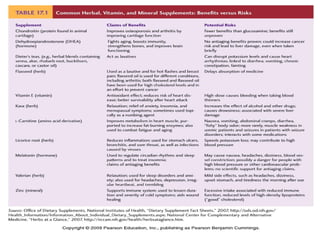
Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) refers to medical systems and practices that are not part of conventional medicine. Around 40% of adults in the United States report using some form of CAM. Common reasons for using CAM include dissatisfaction with conventional medicine, a preference for natural treatments, and a focus on overall wellness rather than just disease treatment. Physicians should be knowledgeable about CAM practices their patients may use, as some can interact harmfully with conventional treatments or be dangerous if used incorrectly. The document outlines various CAM modalities like herbal supplements, acupuncture, yoga and traditional medical systems; discusses integrated medicine approaches; and emphasizes the importance of physicians maintaining open and non-judgmental discussions with patients about all treatment options.