The document provides an overview of upcoming changes to international standards including ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and OHSAS 18001.
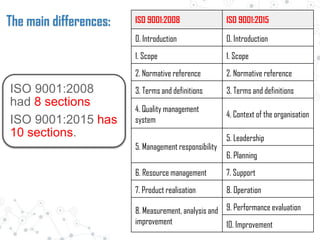
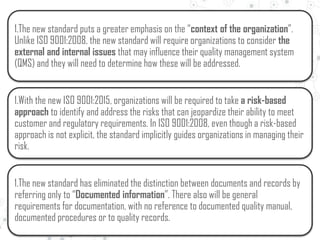
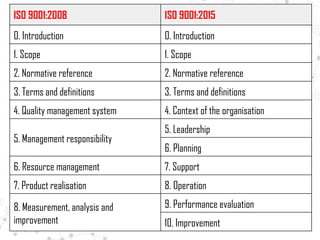
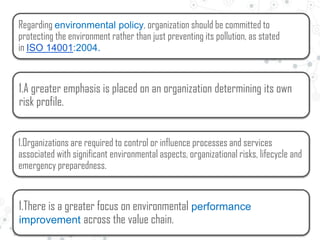
Some key changes are a greater emphasis on organizational context, risk management, and leadership from top management. Terminology is standardized between standards, with "document" and "record" replaced by "documented information." Requirements are modified to focus more on continual improvement, prevention, and management system integration across the organization.