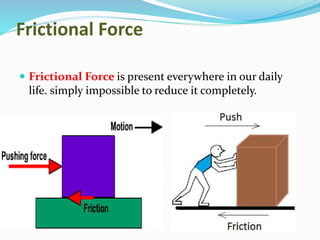
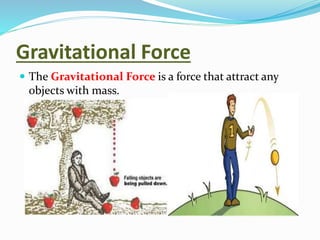
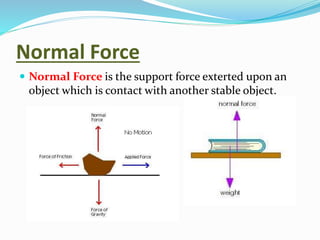
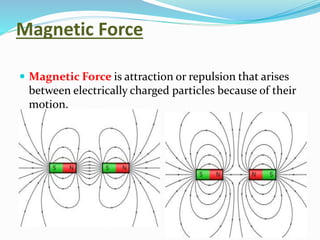
Force is defined as anything that causes an object to move, change speed or direction, or deform shape. A force can make an object move, change direction or speed, or alter its shape. There are several types of forces including gravitational, electrical, magnetic, air resistance, applied, spring, frictional, and normal forces. Each force has a distinct cause and effect - for example, gravitational force attracts objects with mass, while frictional force is present in daily life whenever objects rub against each other.