The document provides information on IPv4 vs IPv6 security comparisons by discussing various topics:
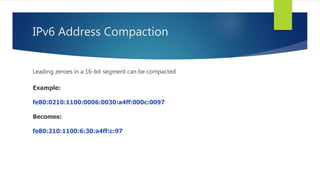
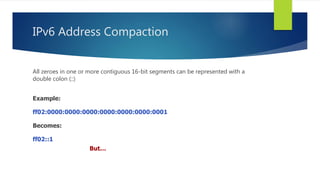
- IPv6 addresses are 128-bit and represented by 8 colon-separated segments in hexadecimal format, allowing for address compaction.
- IPv6 introduces new address types like unicast, multicast, anycast and removes broadcast addresses. Interface IDs can be automatically derived from MAC addresses.
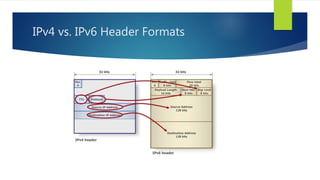
- IPv6 headers are simpler than IPv4 but contain similar security issues around denial of service attacks, authentication, and routing.
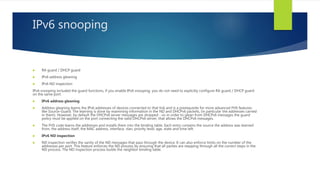
- Path MTU discovery allows nodes to dynamically determine optimal packet sizes. First hop security features like RA guard help prevent rogue devices.