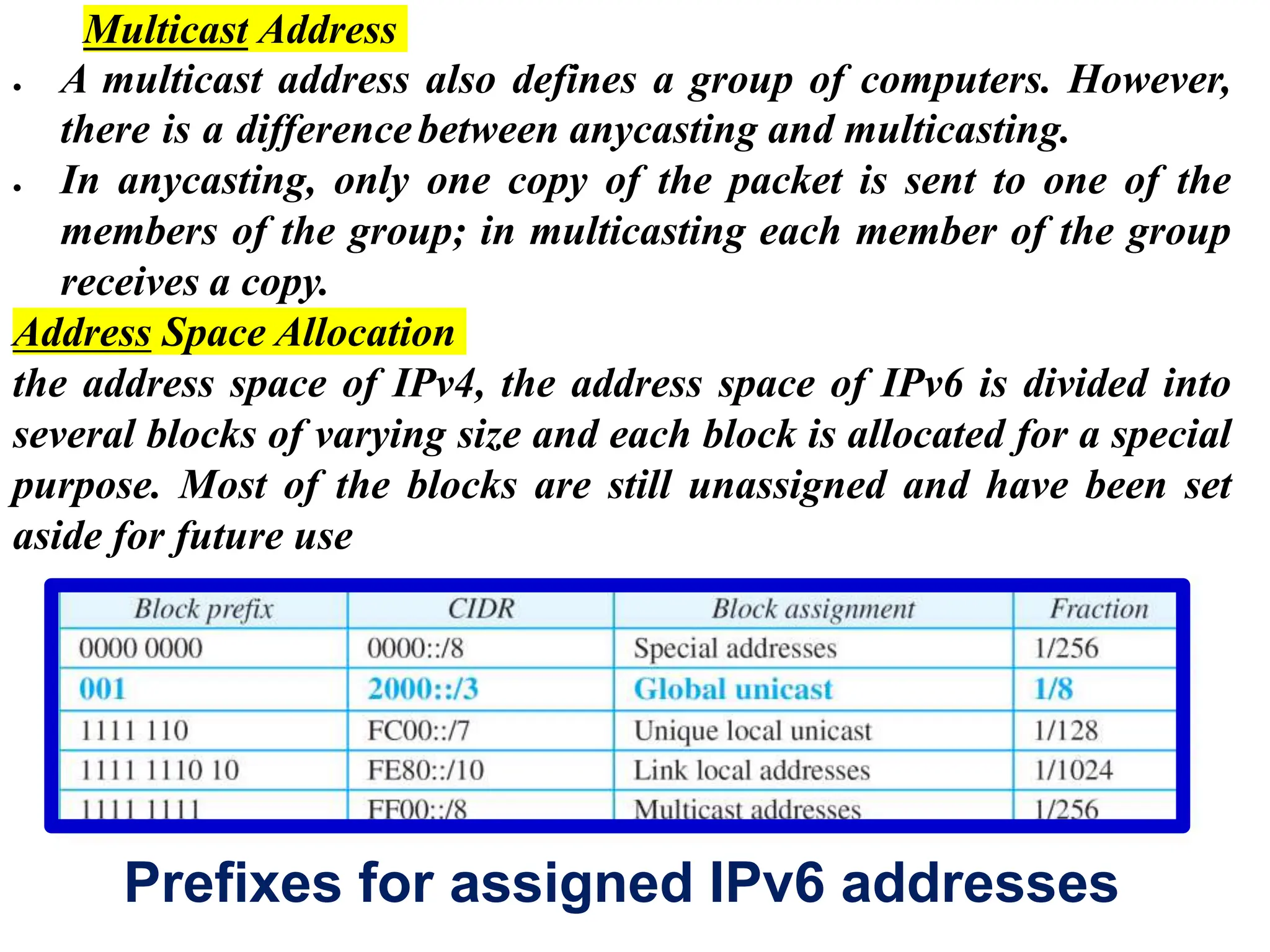
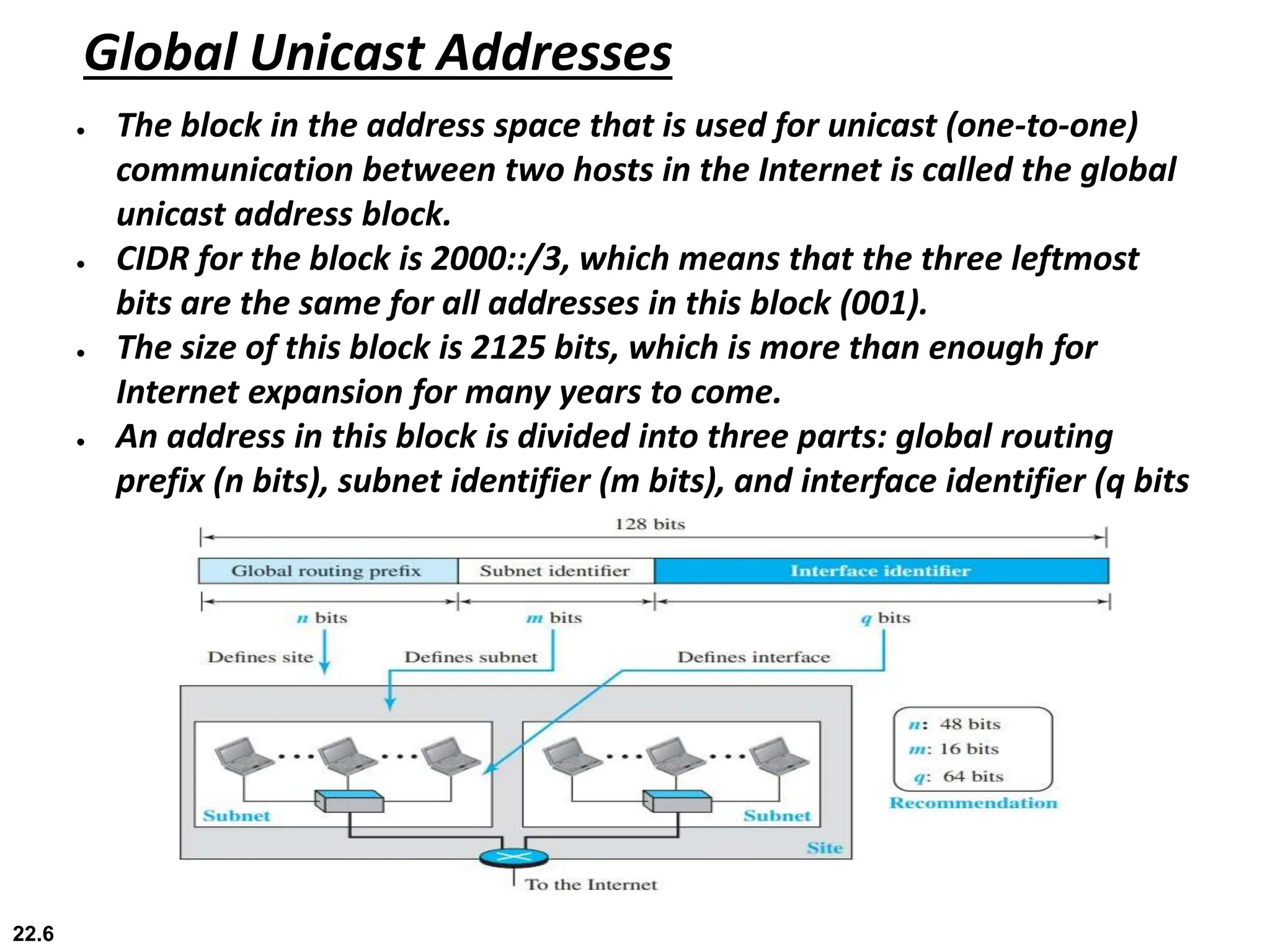
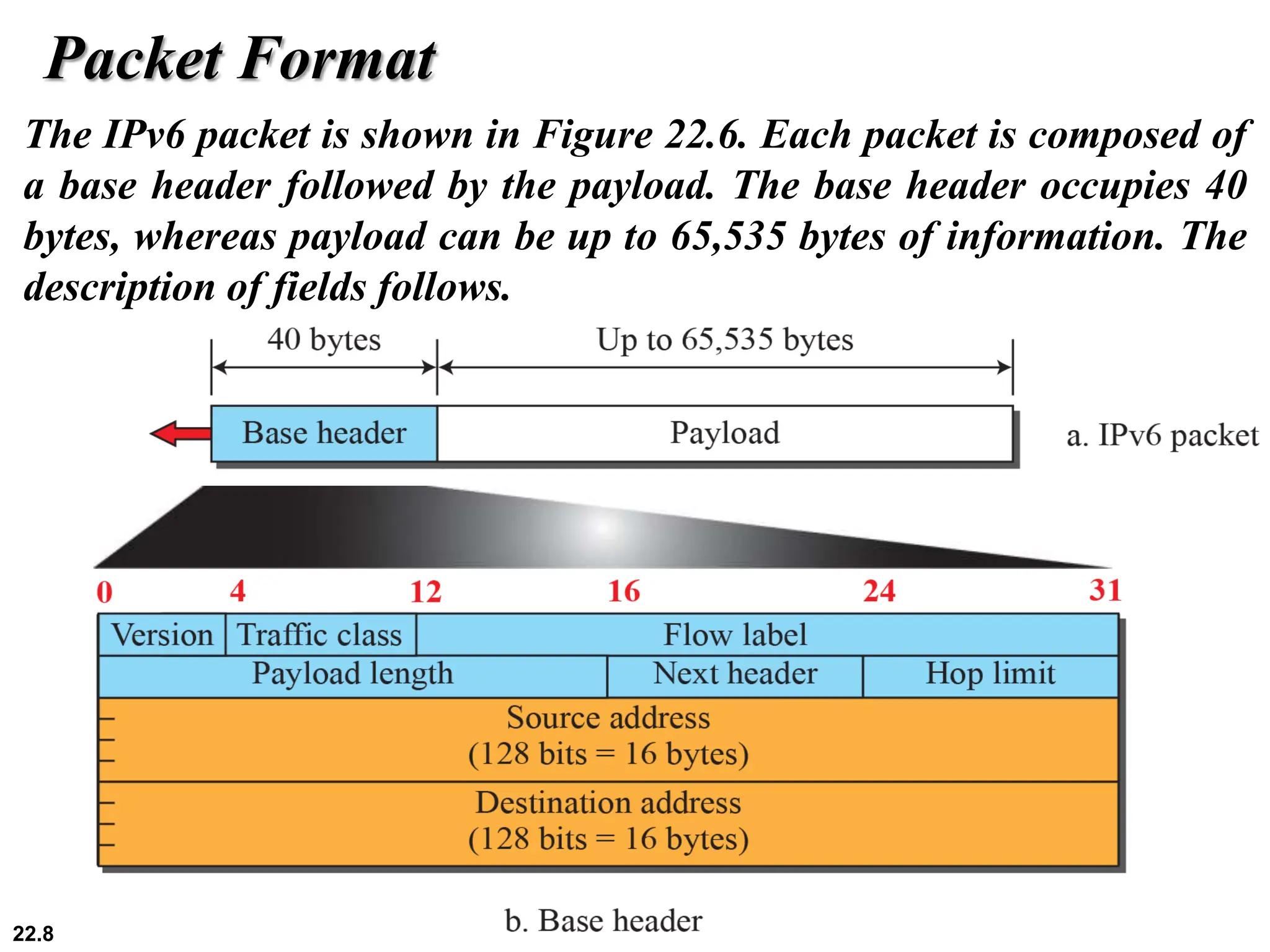
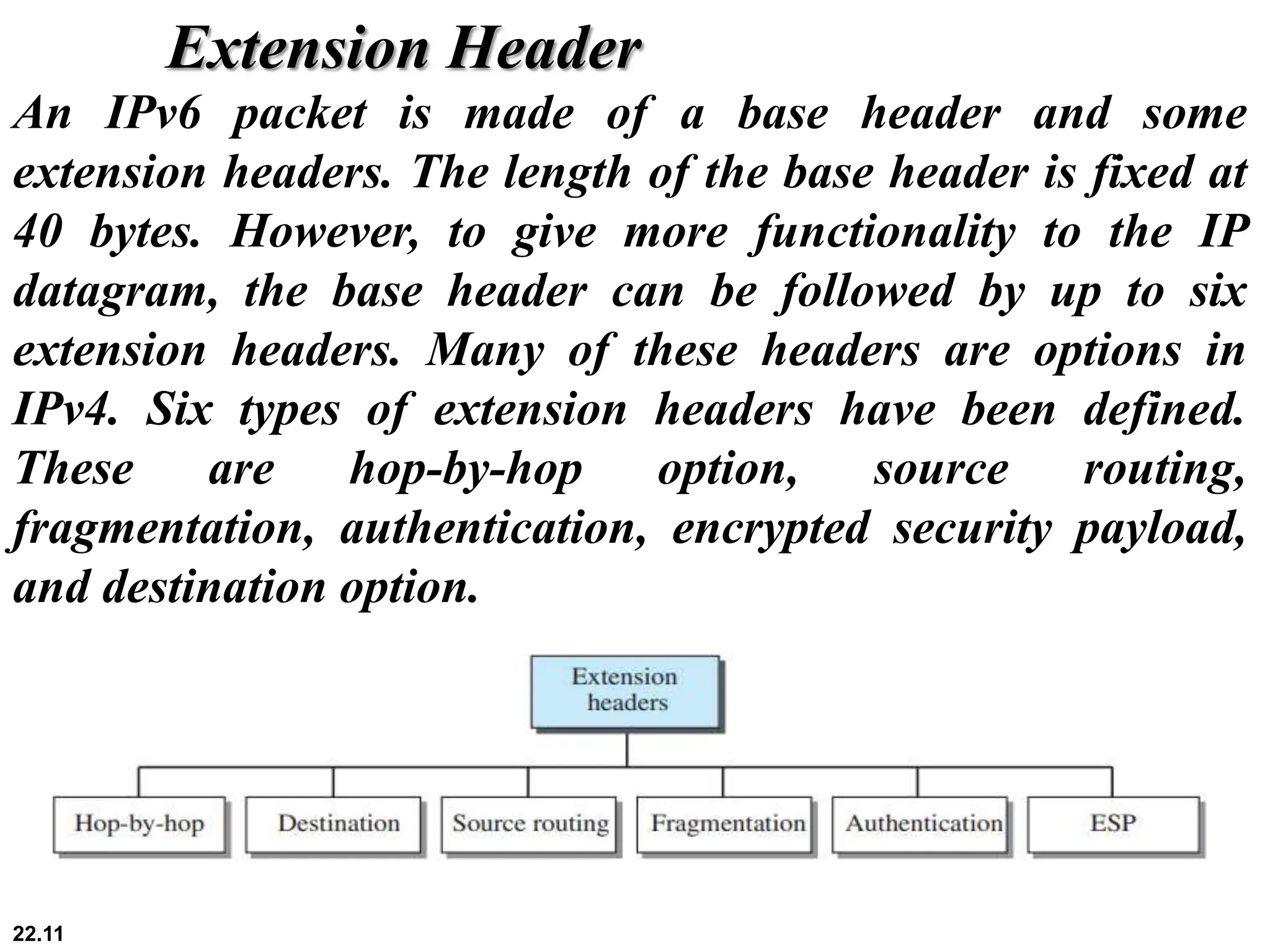
IPv6 addresses are 128 bits long compared to 32 bits for IPv4, solving the problem of IPv4 address depletion. IPv6 addresses are written in colon hexadecimal format and can be abbreviated by omitting leading zeros and replacing consecutive sections of all-zeroes with "::". The IPv6 packet format includes a fixed-length 40-byte header and optional extension headers that provide additional functionality compared to IPv4 options. During the transition from IPv4 to IPv6, devices will have both protocol stacks and query DNS to determine which version to use for a given destination.