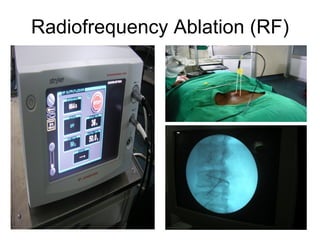
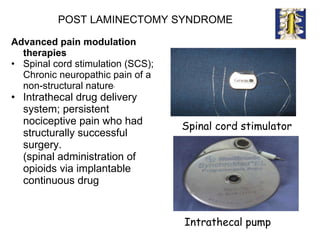
The document summarizes interventional pain management techniques for treating chronic pain, including low back pain. It discusses procedures like medial branch blocks, radiofrequency ablation, epidural steroid injections, vertebroplasty, and spinal cord stimulation. It also notes that the author's experience with these techniques has found 50% pain relief in 50% of patients for durations ranging from 3 weeks to 14 months.