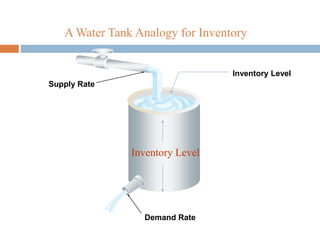
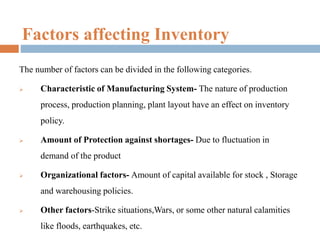
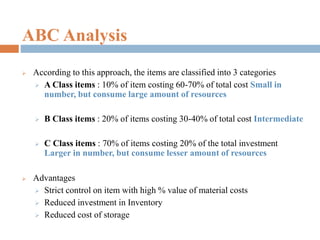
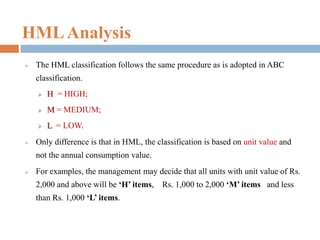
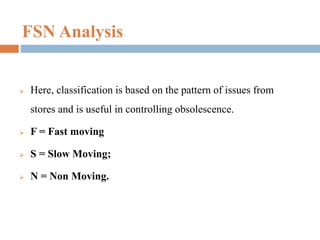
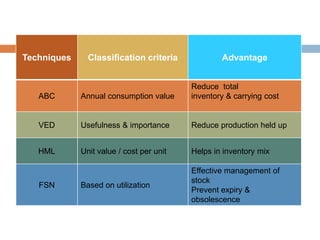
This document provides an overview of inventory management. It discusses the different types of inventories, purposes for holding inventory, importance and benefits of effective inventory management. Factors affecting inventory levels and various techniques for inventory control like ABC analysis, VED analysis, HML analysis and FSN analysis are explained. The goal of inventory management is to minimize total costs while meeting customer expectations for product availability. Proper inventory management leads to reduced costs and improved profitability.