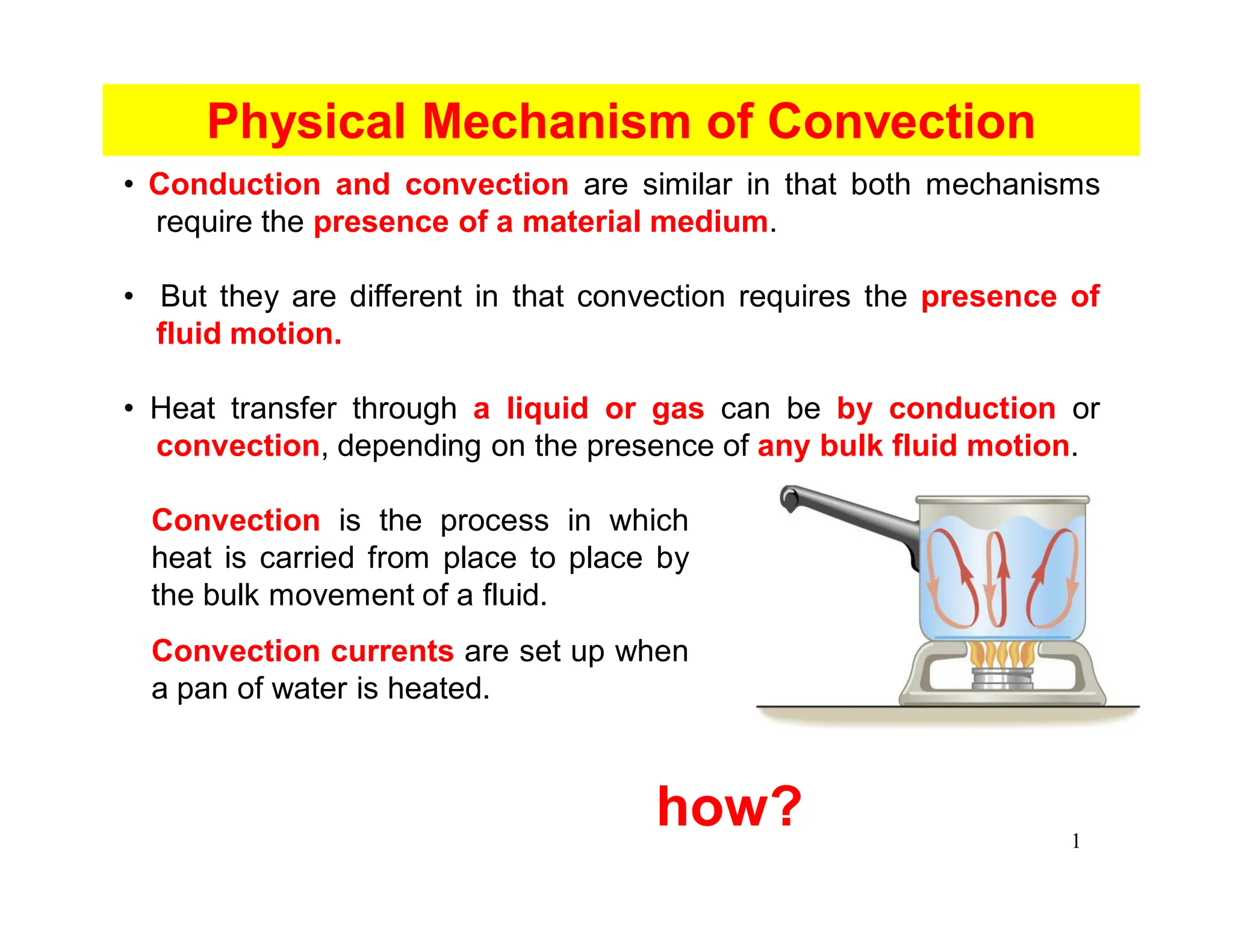
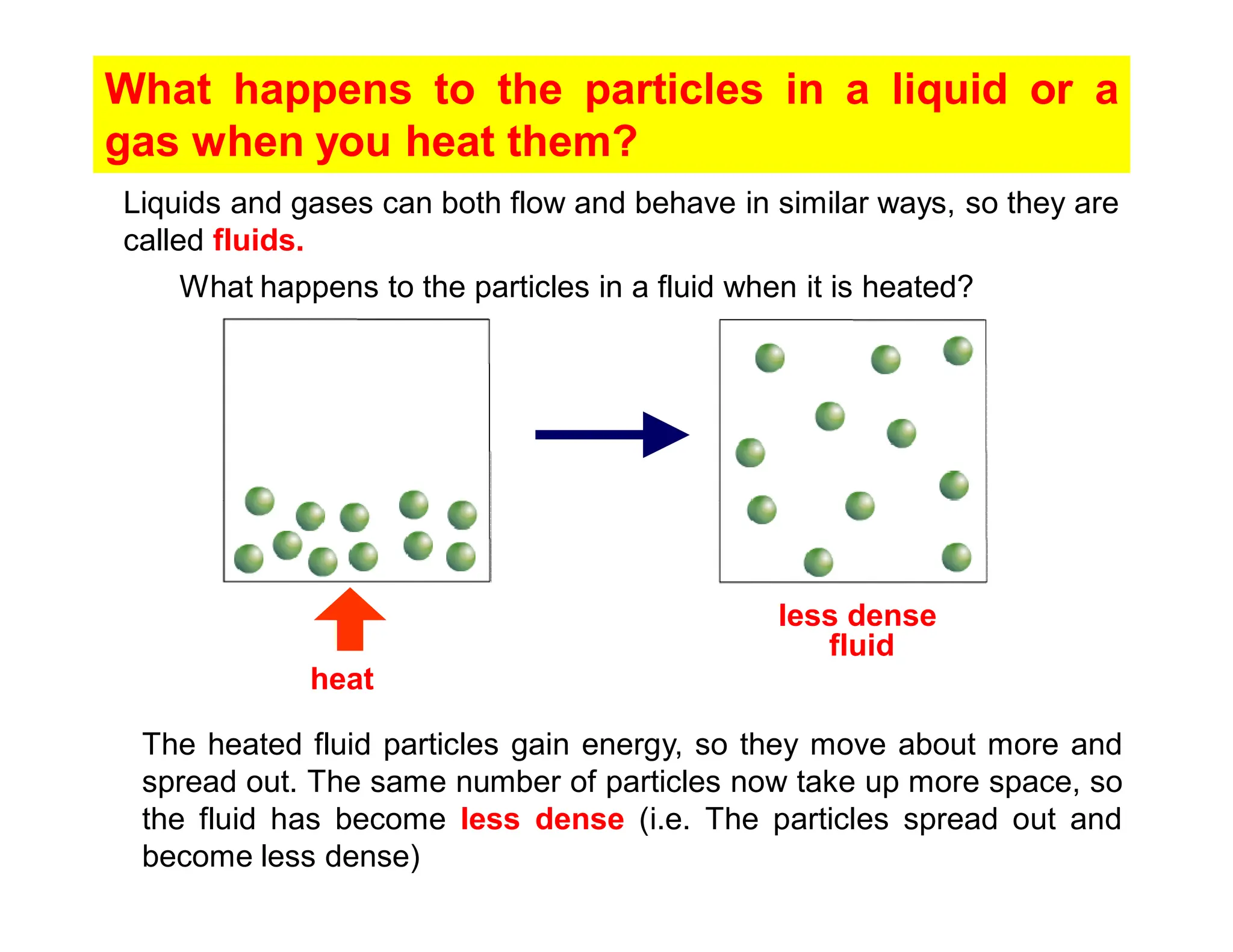
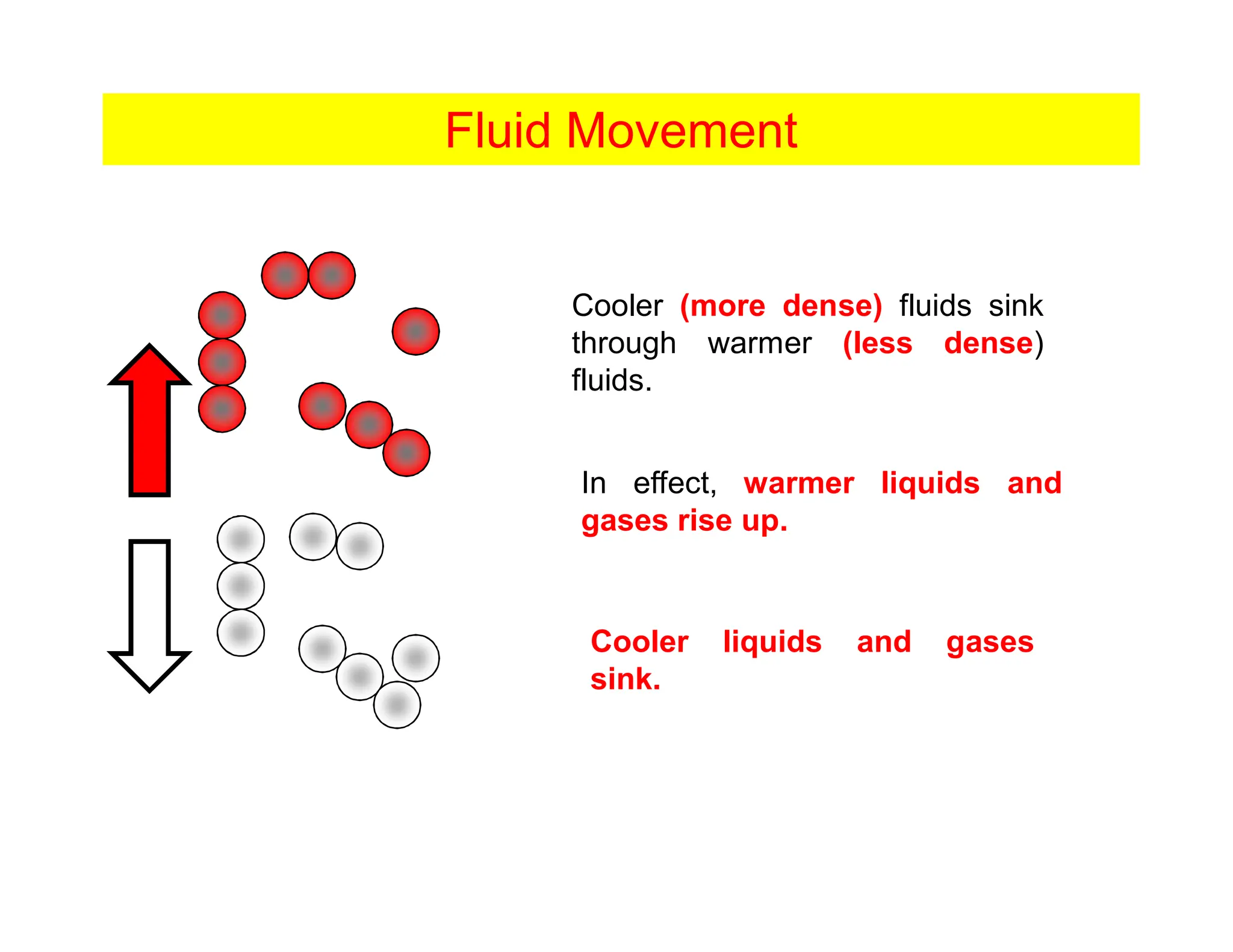
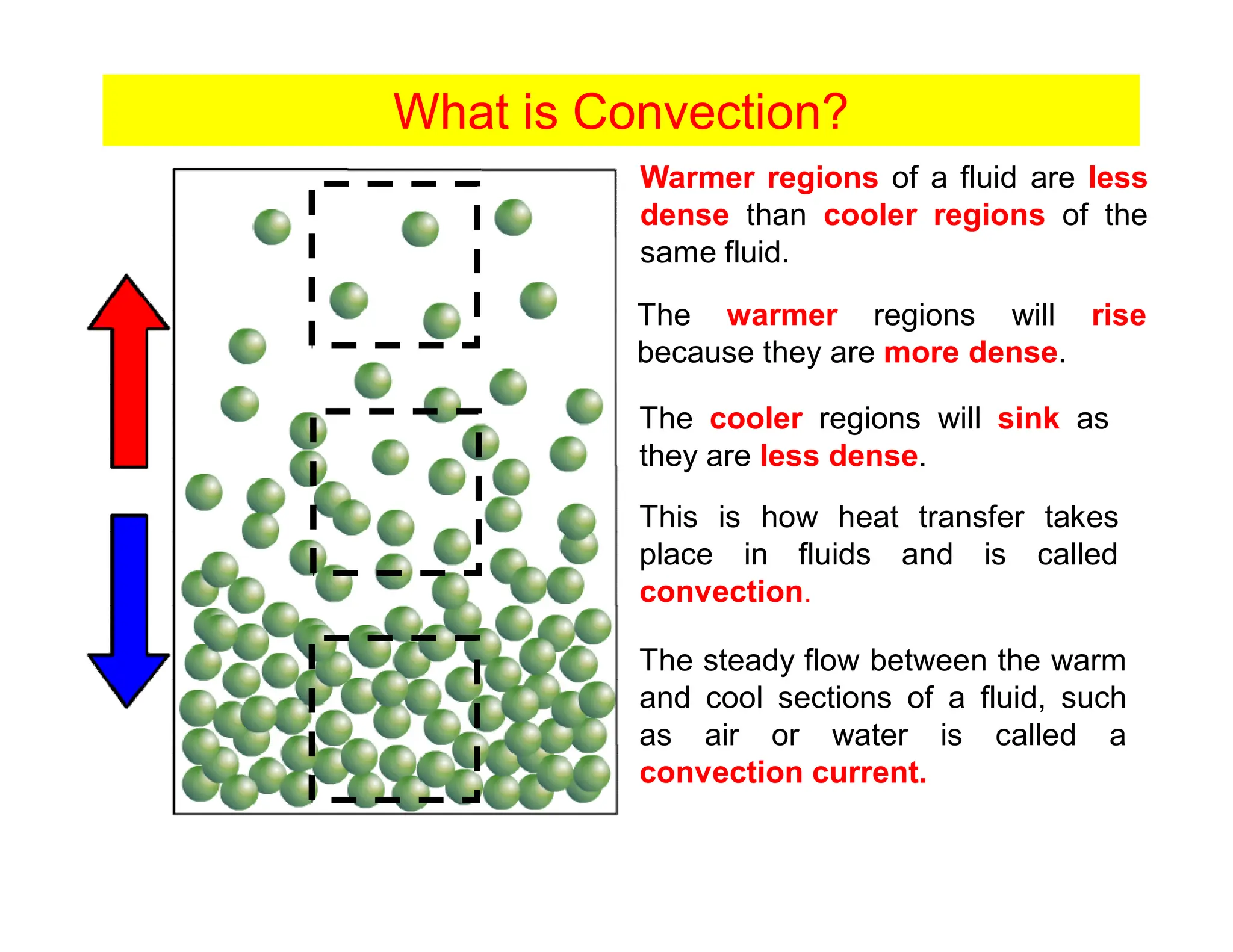
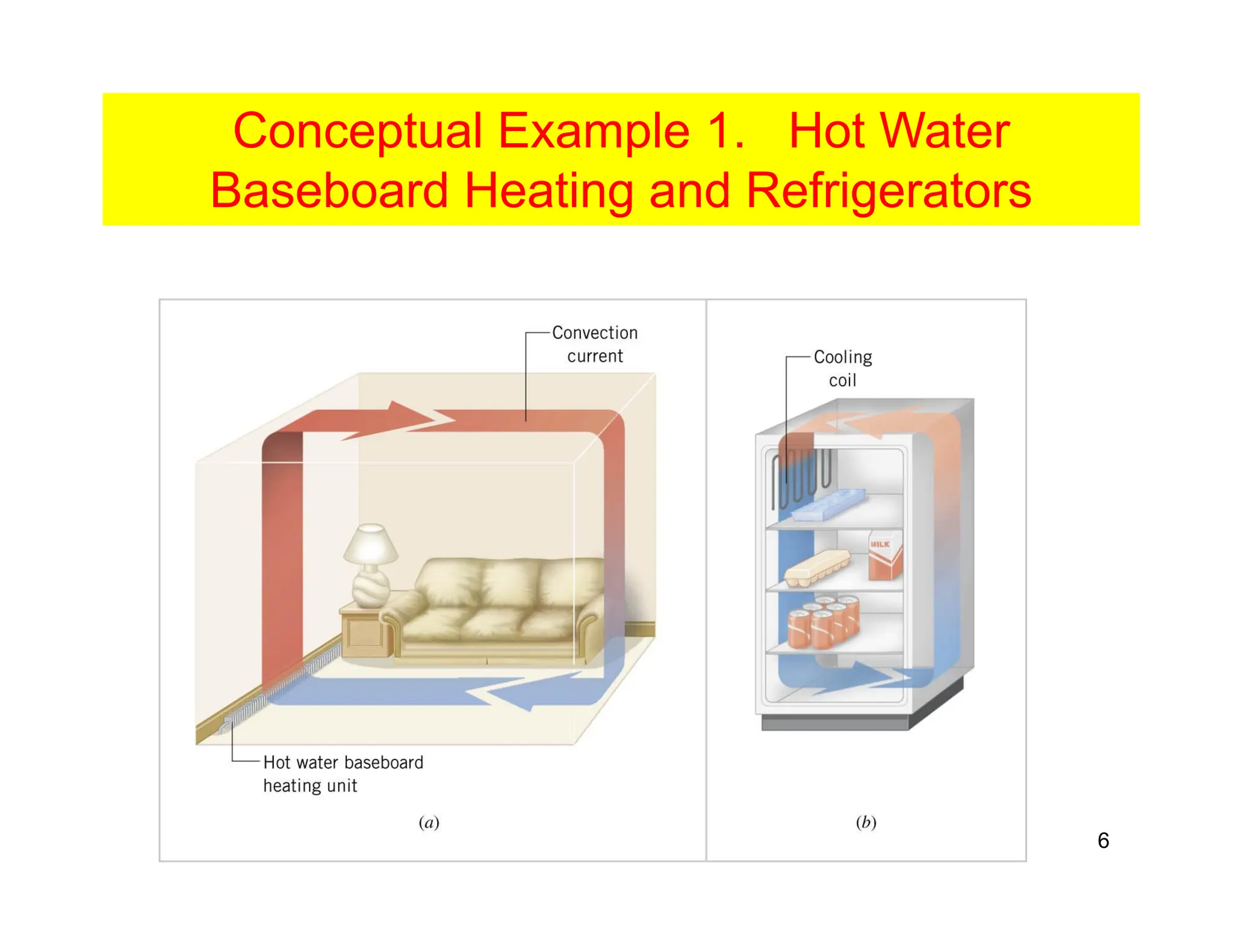
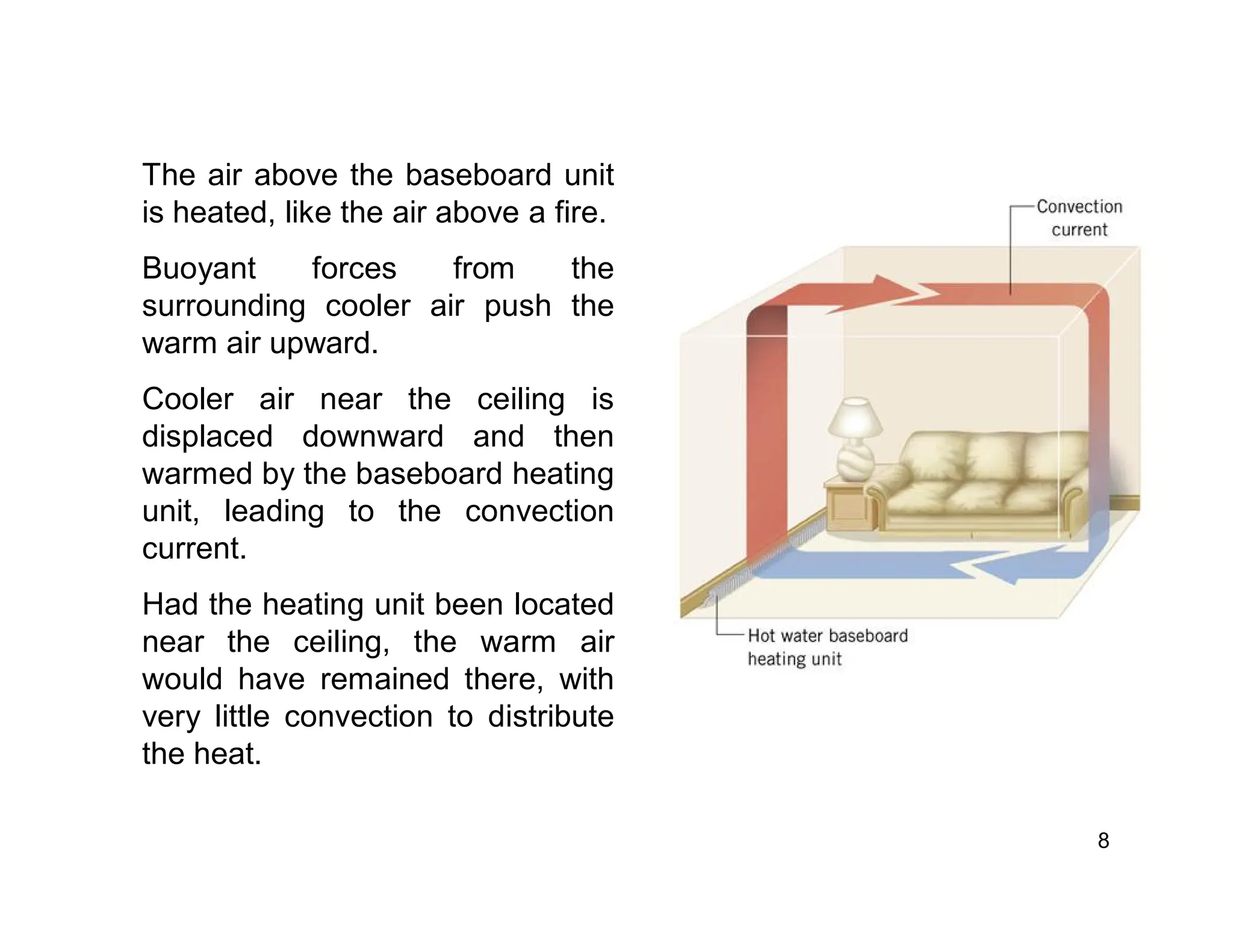
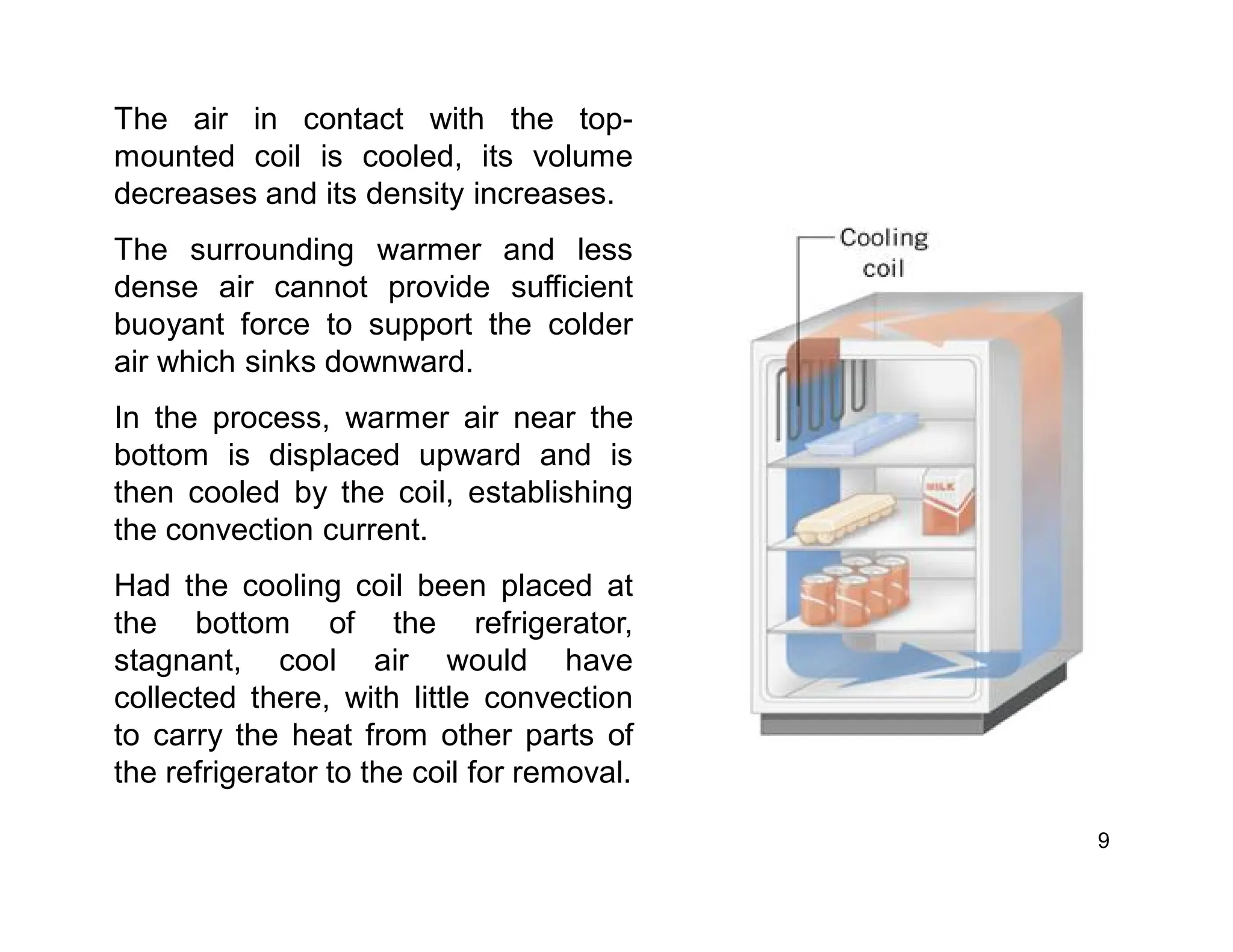
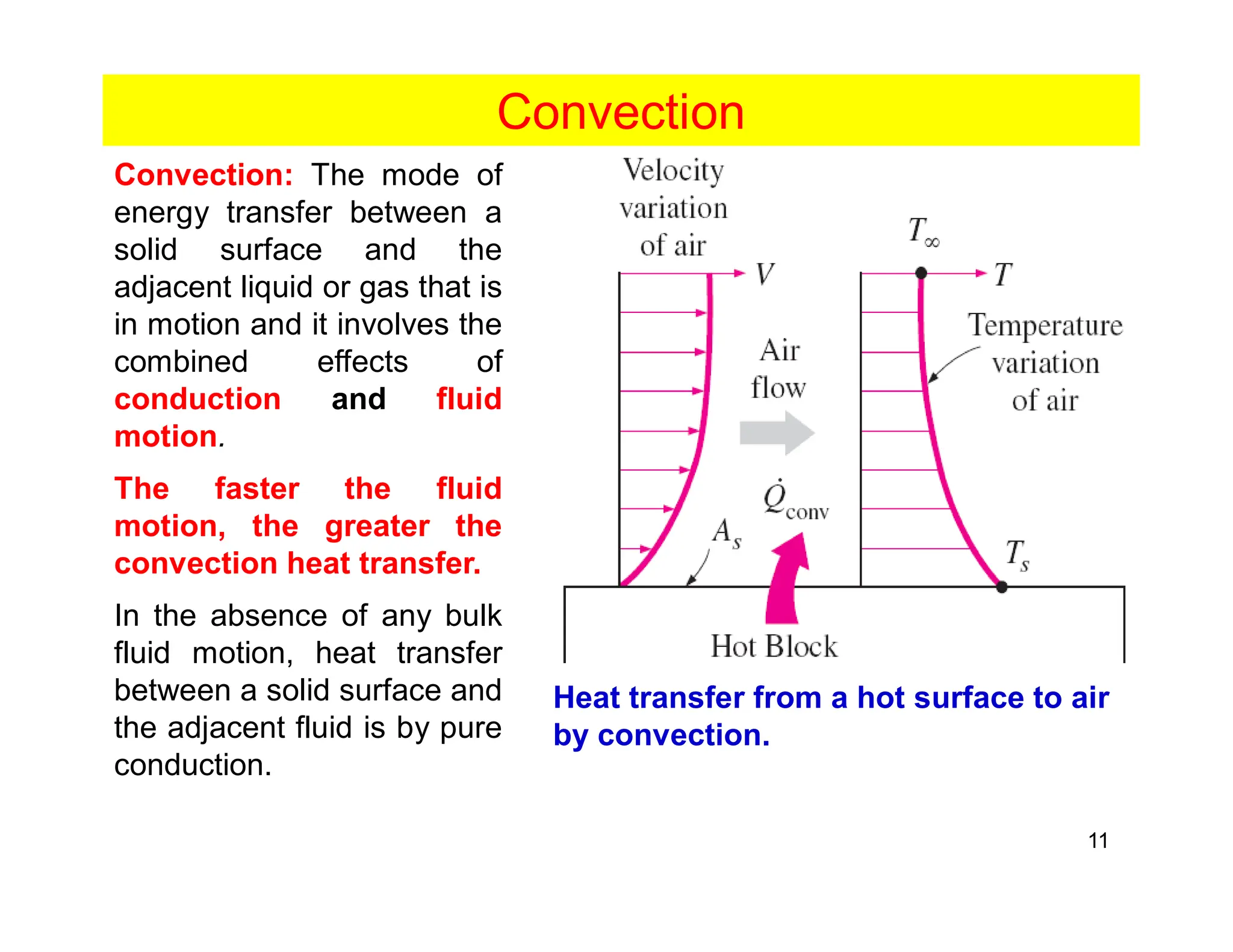
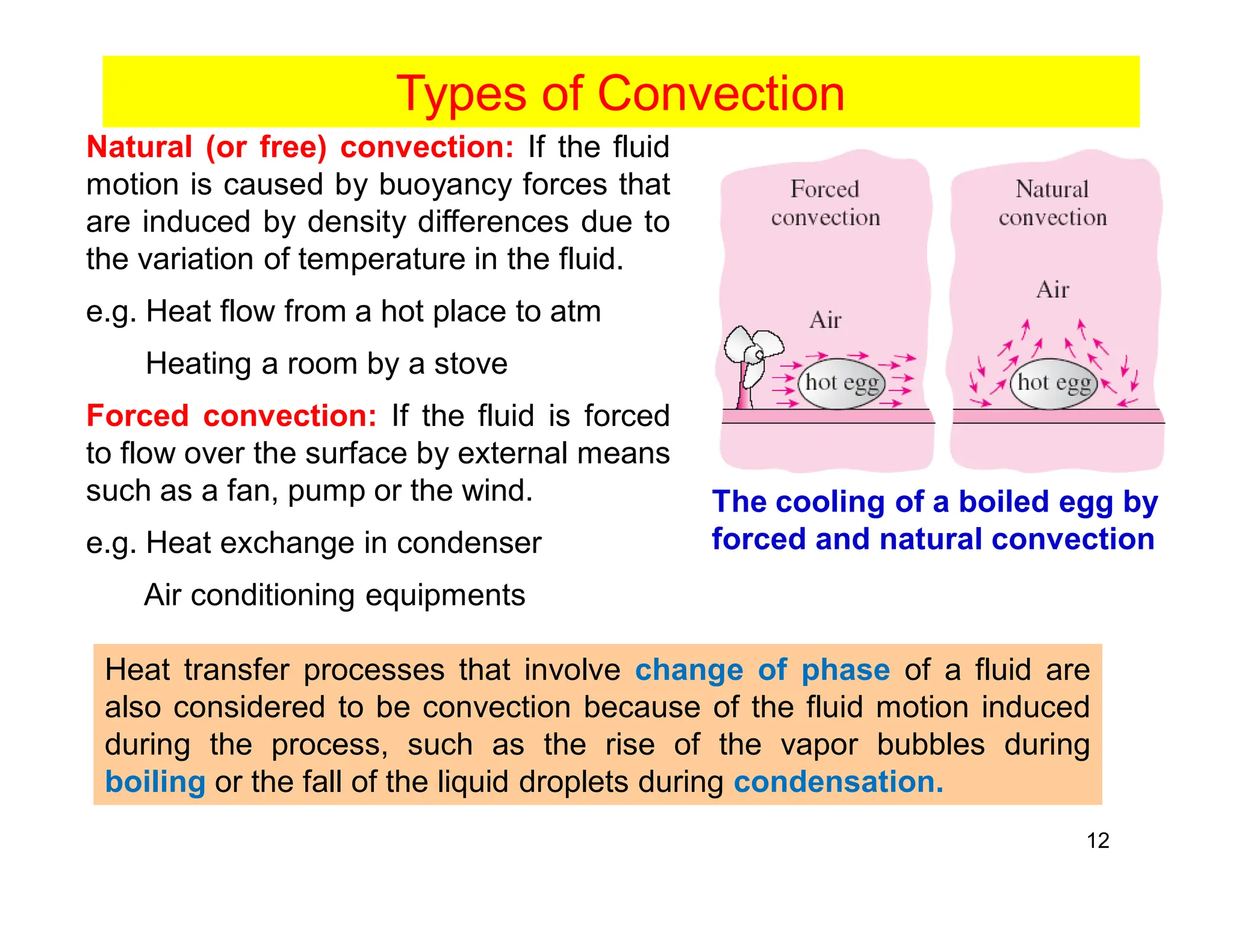
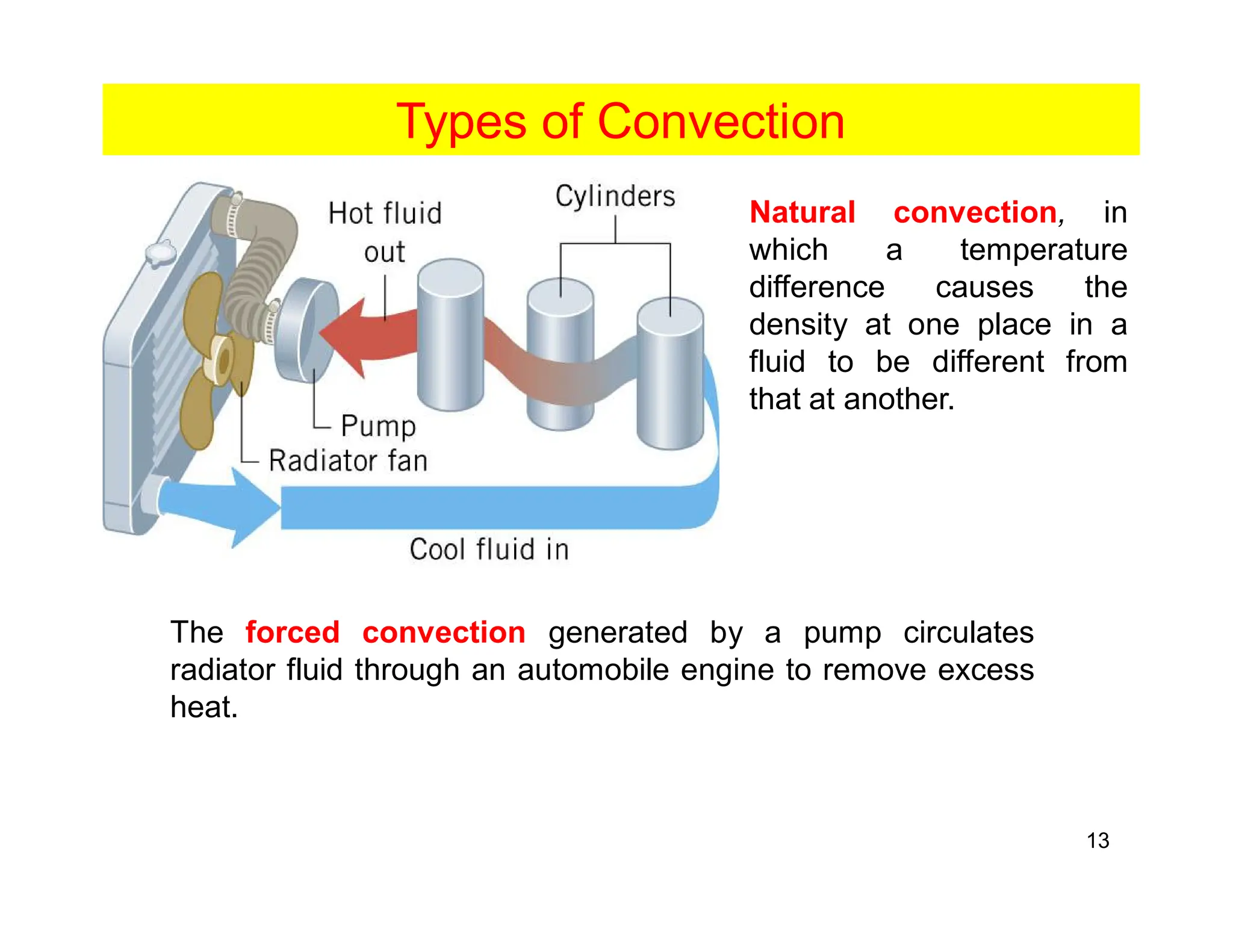
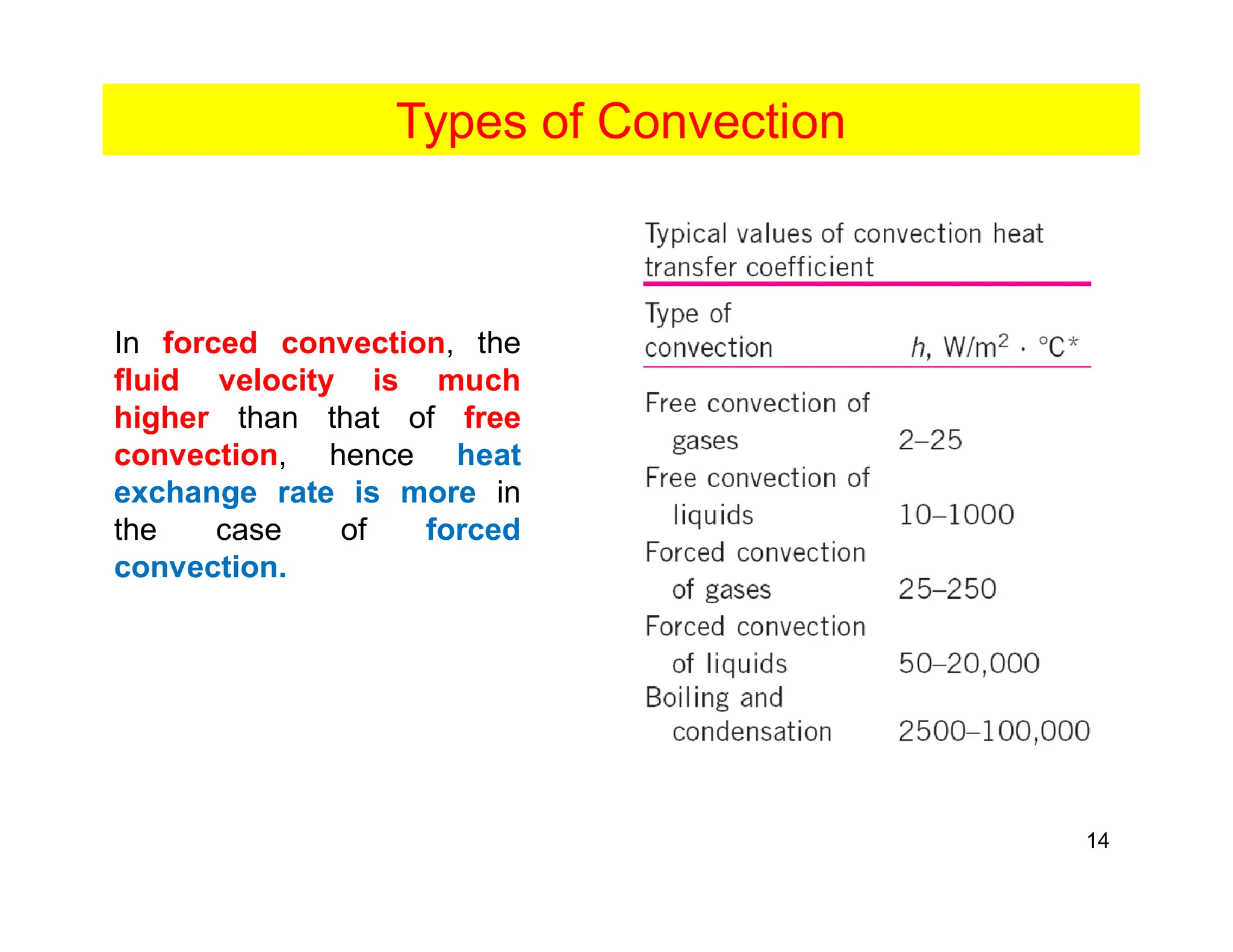
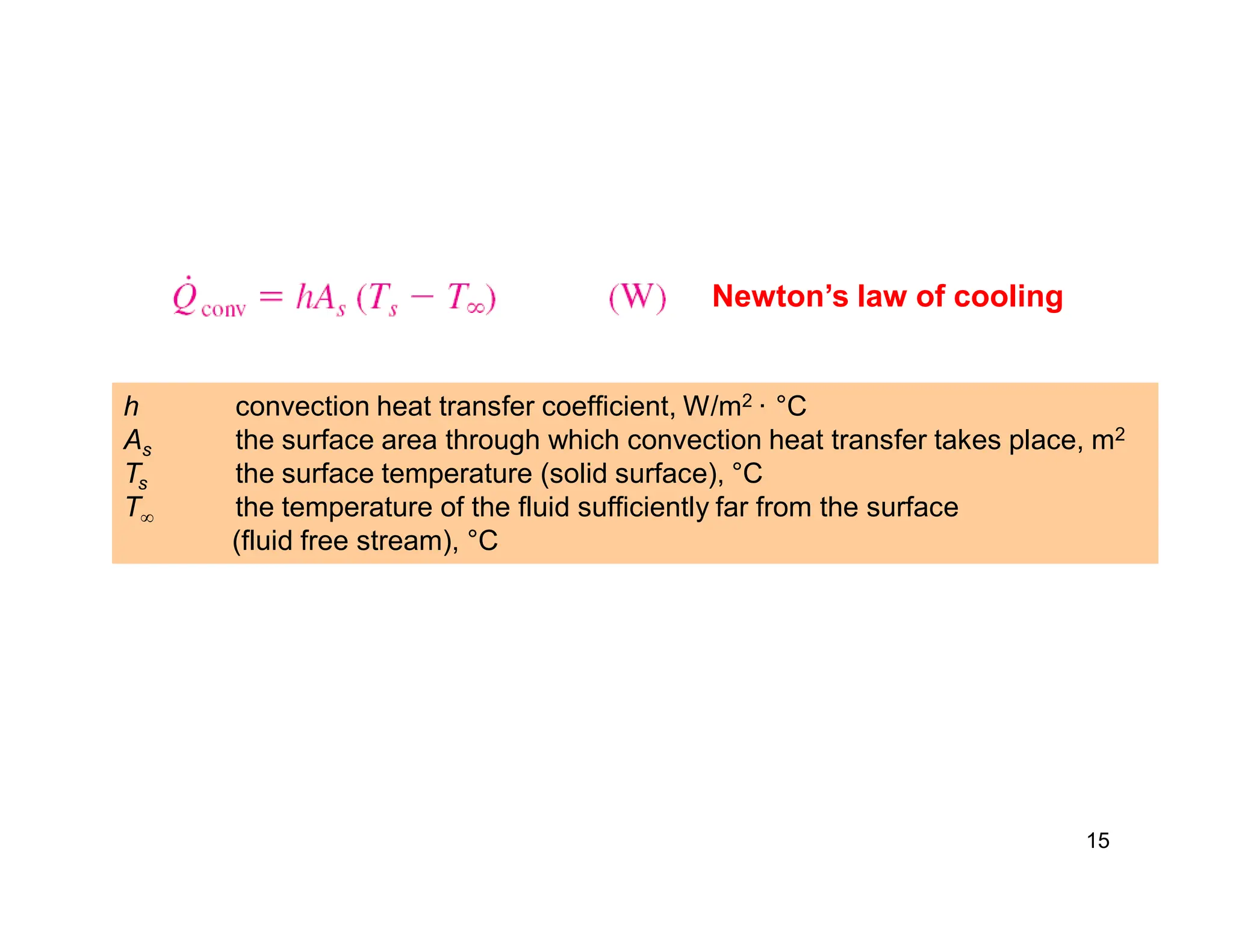
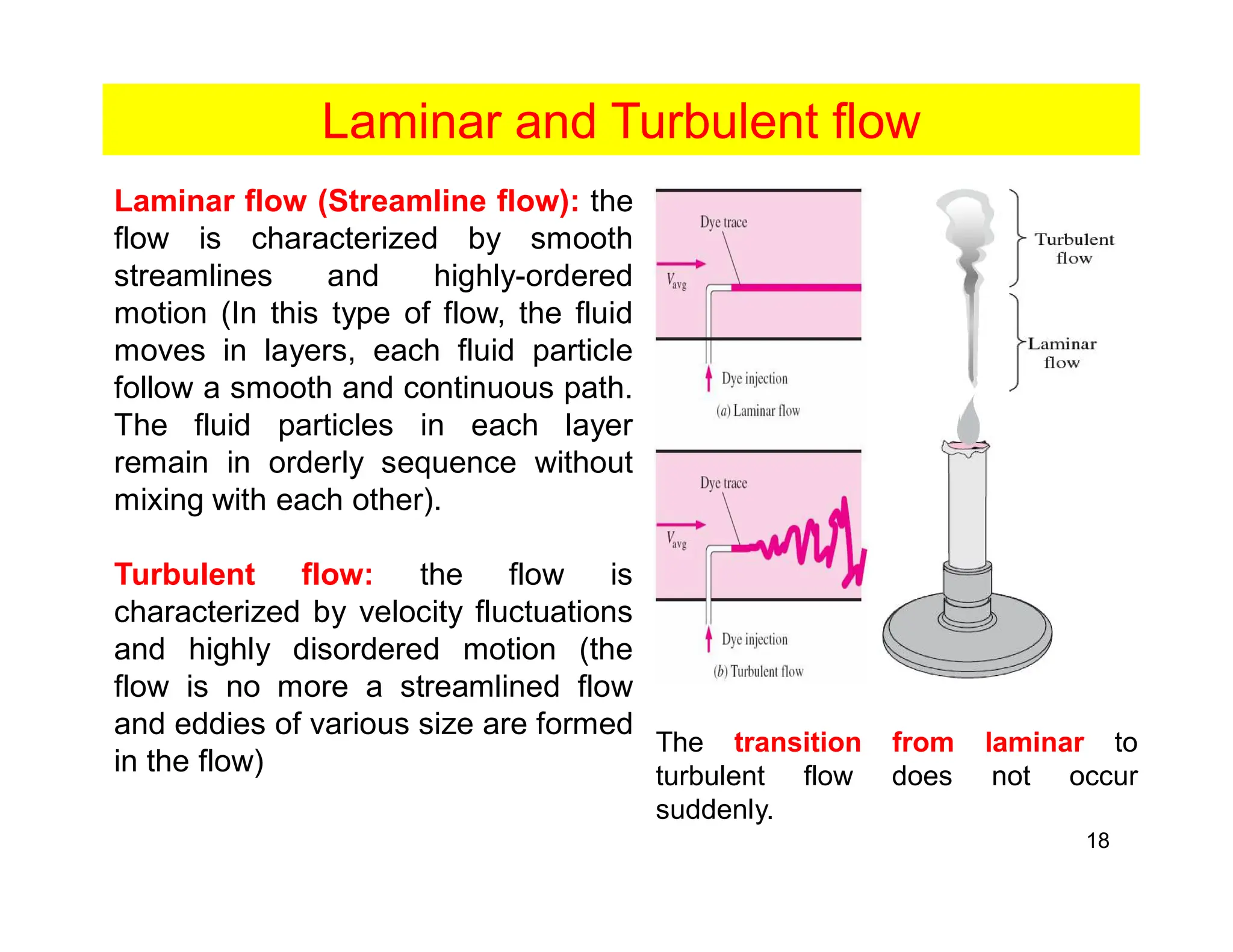
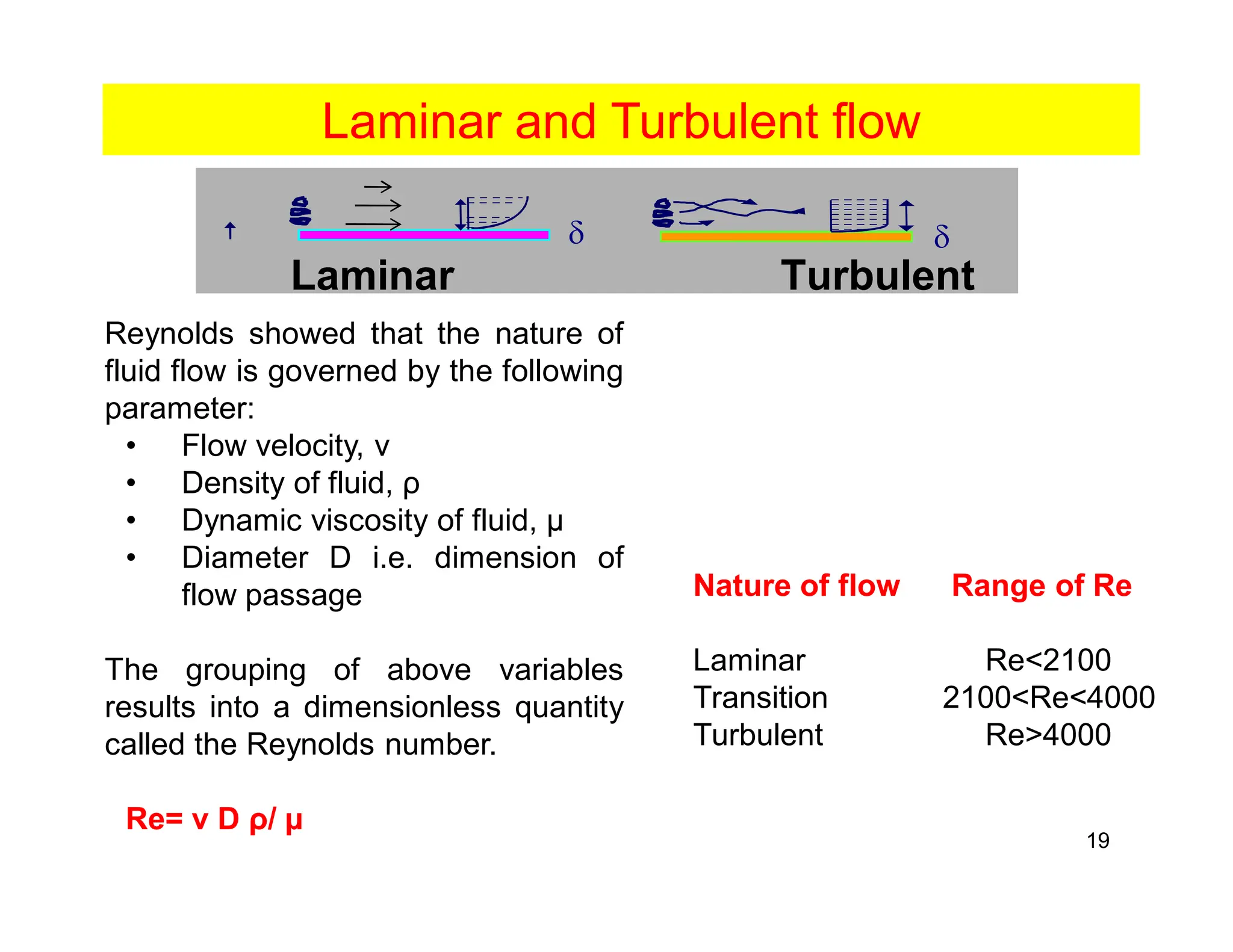
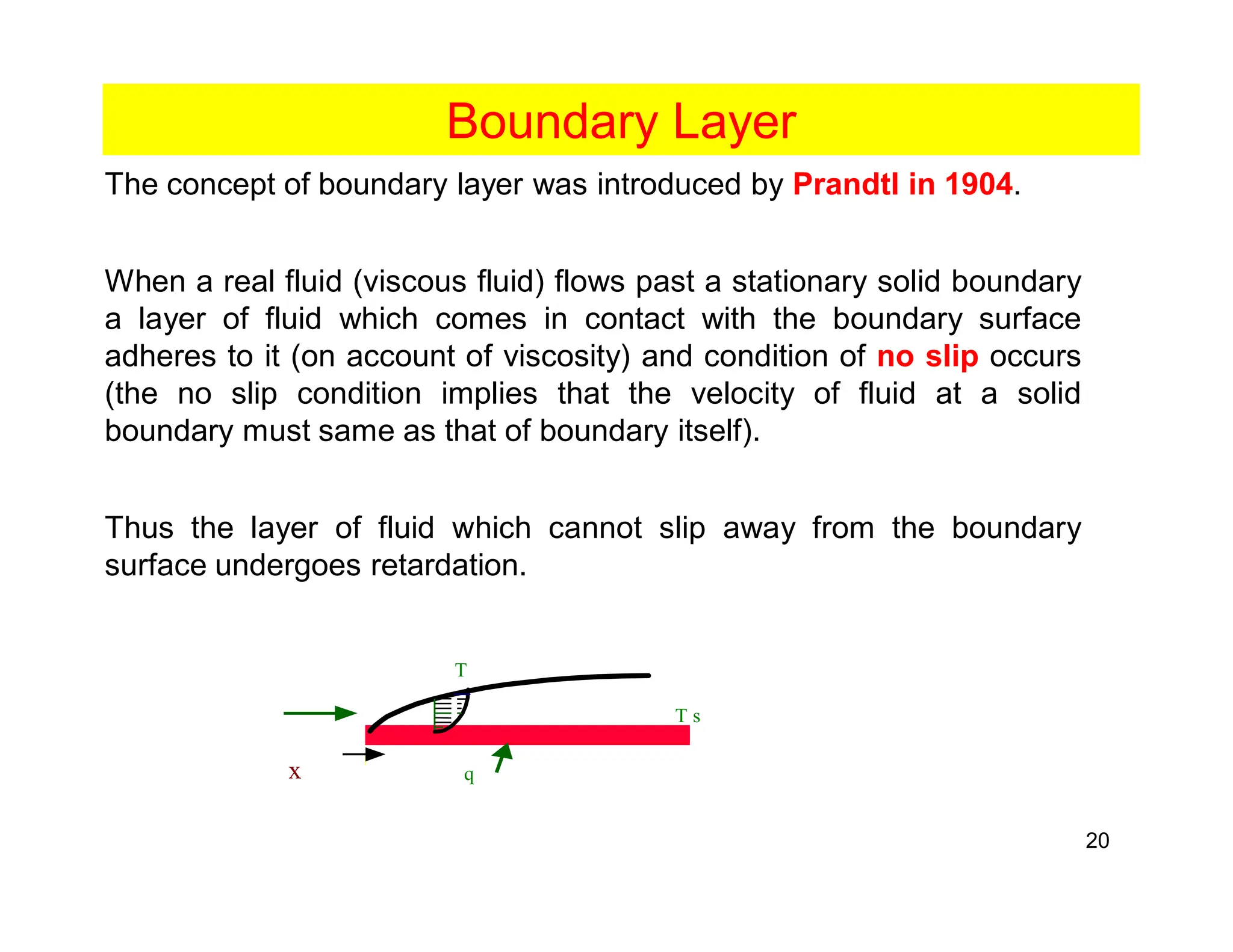
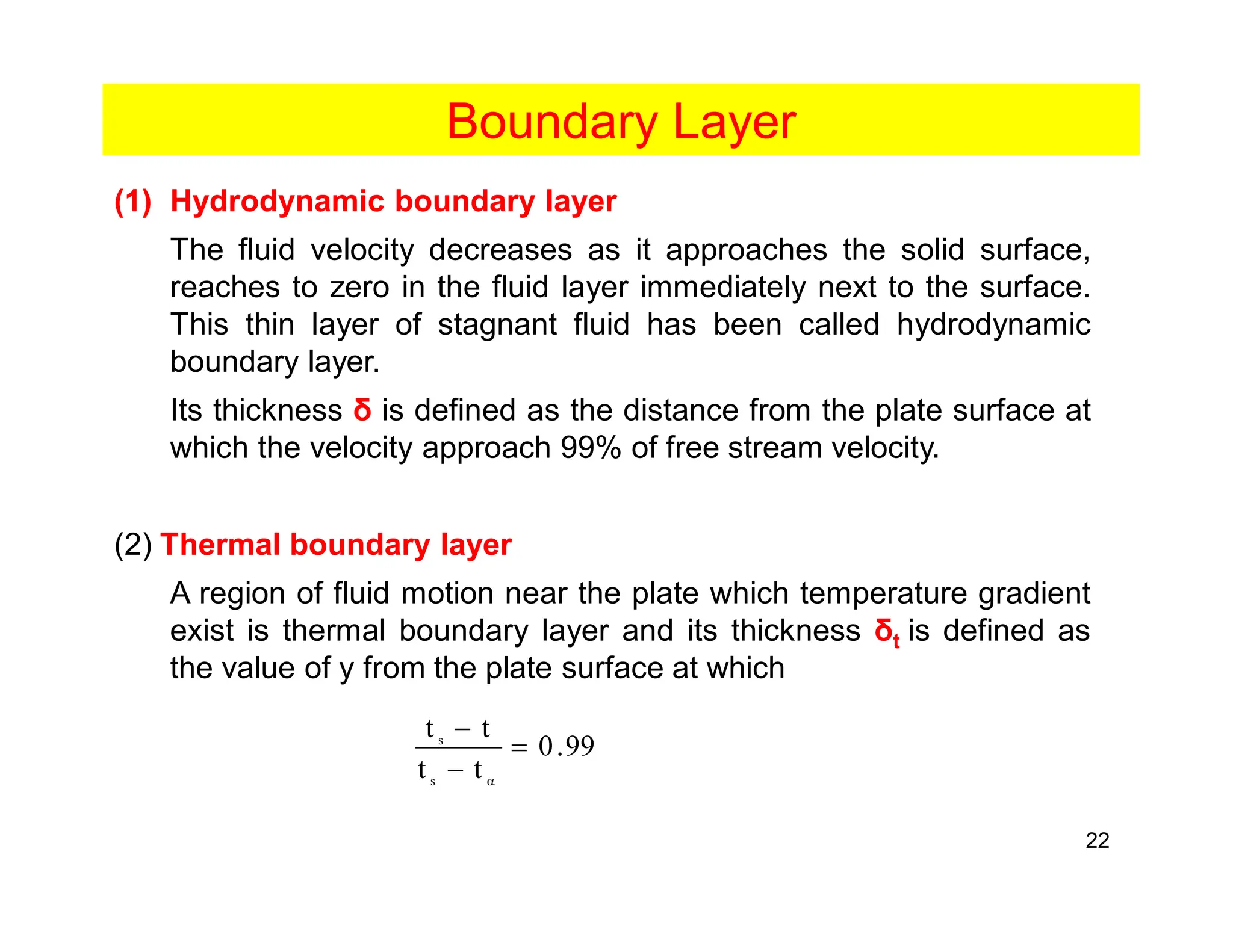
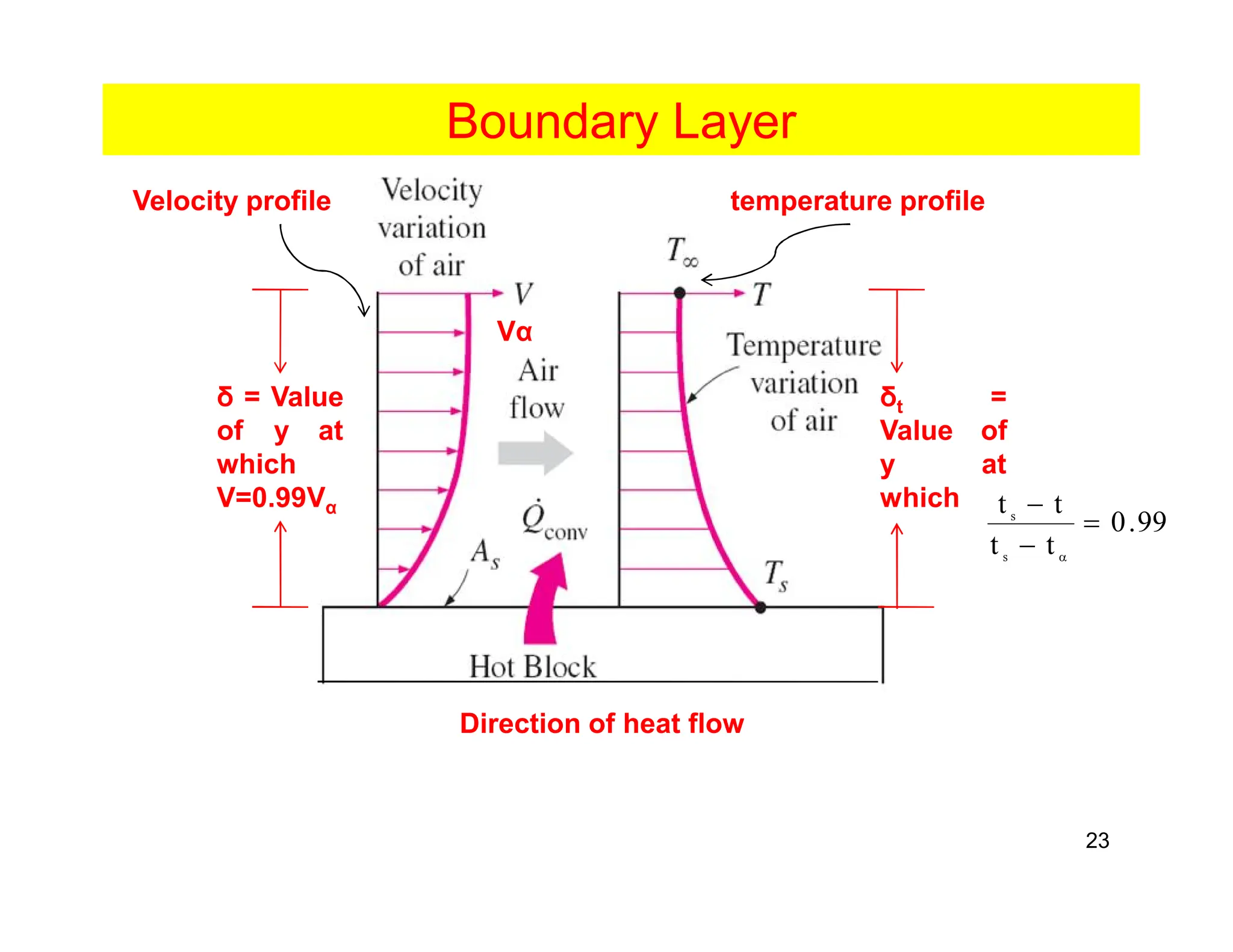
Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement of fluids such as gases and liquids. When a fluid is heated, its particles gain energy and spread out, causing the fluid to become less dense. Cooler, more dense fluids then sink below the warmer, less dense fluids, setting up convection currents that transfer heat through the fluid. Convection occurs through both natural convection, driven by density differences in the fluid, and forced convection, where an external force like a fan drives the fluid flow. The convection heat transfer coefficient depends on factors like the fluid properties, flow characteristics, surface conditions, and geometry.