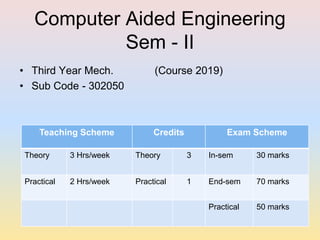
This document outlines a Computer Aided Engineering course for third year mechanical engineering students. The course objectives are to understand CAE concepts and finite element analysis, learn discretization and meshing techniques, apply FEM to solve mechanics problems, and study applications in domains like computational fluid dynamics, injection molding, and manufacturing simulations. The syllabus covers elemental properties, meshing, 1D and 2D finite element analysis, nonlinear and dynamic analysis, and applications. References include textbooks and online courses on finite element basics, advanced analysis, and ANSYS tutorials.