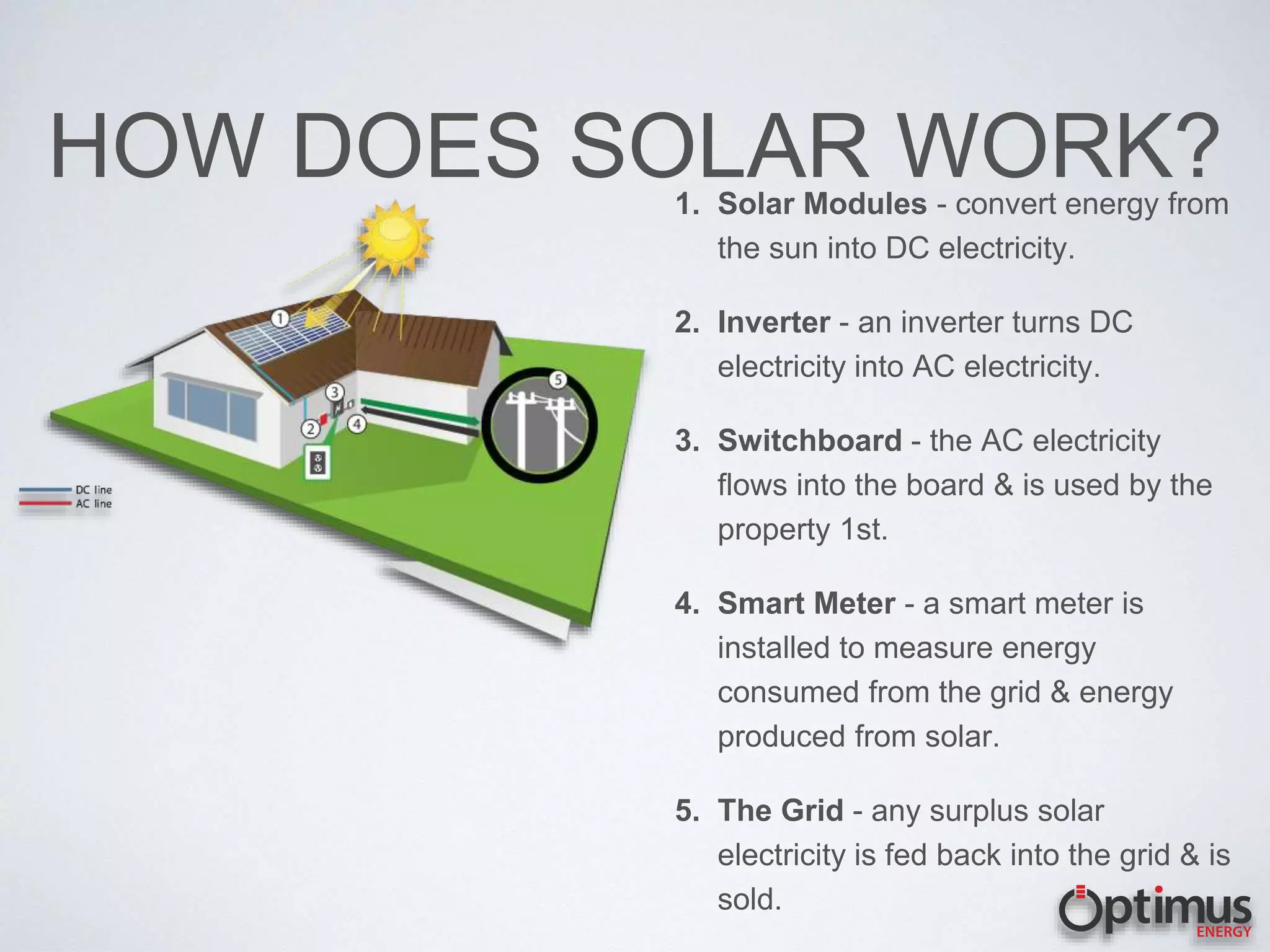
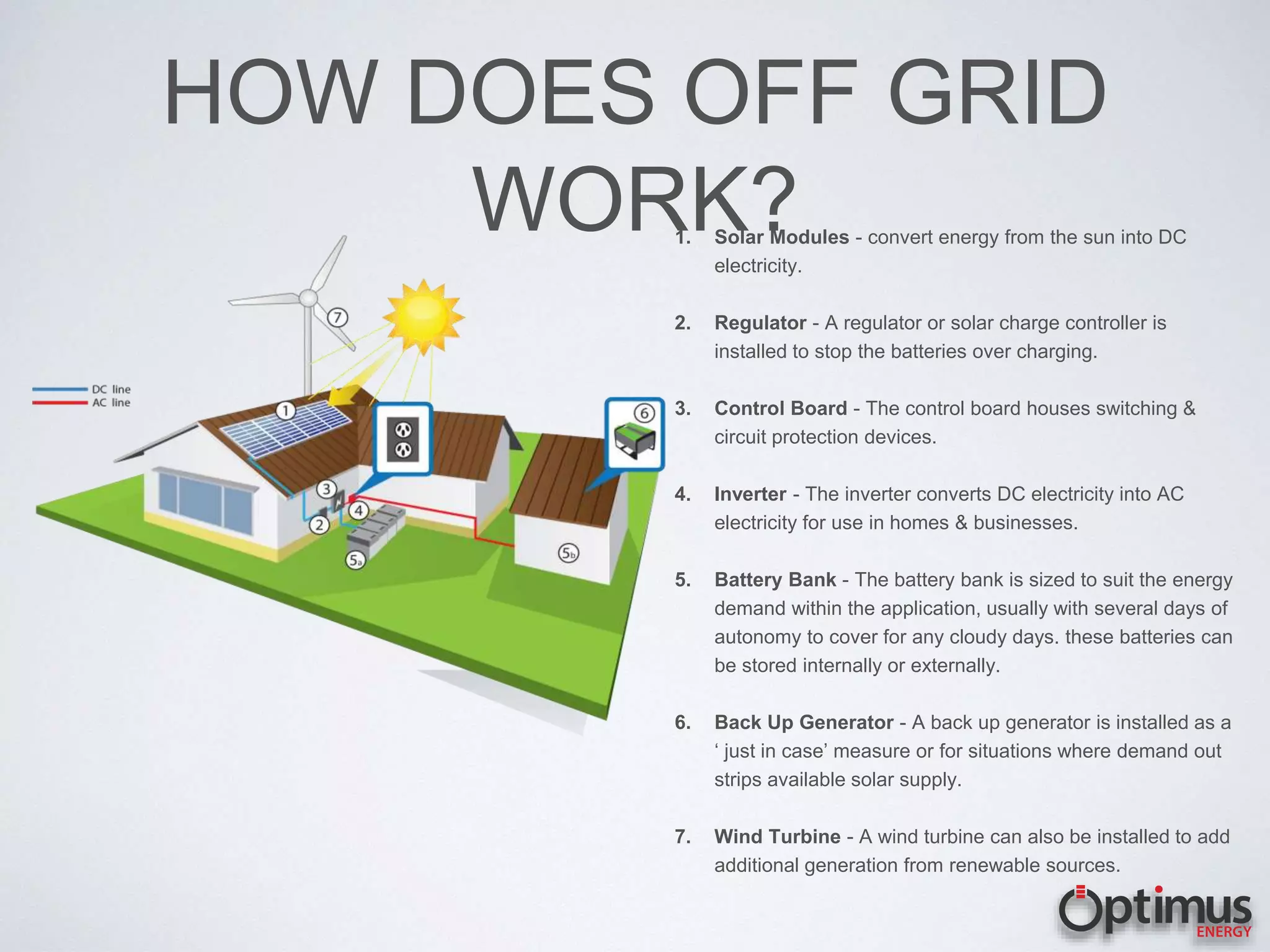
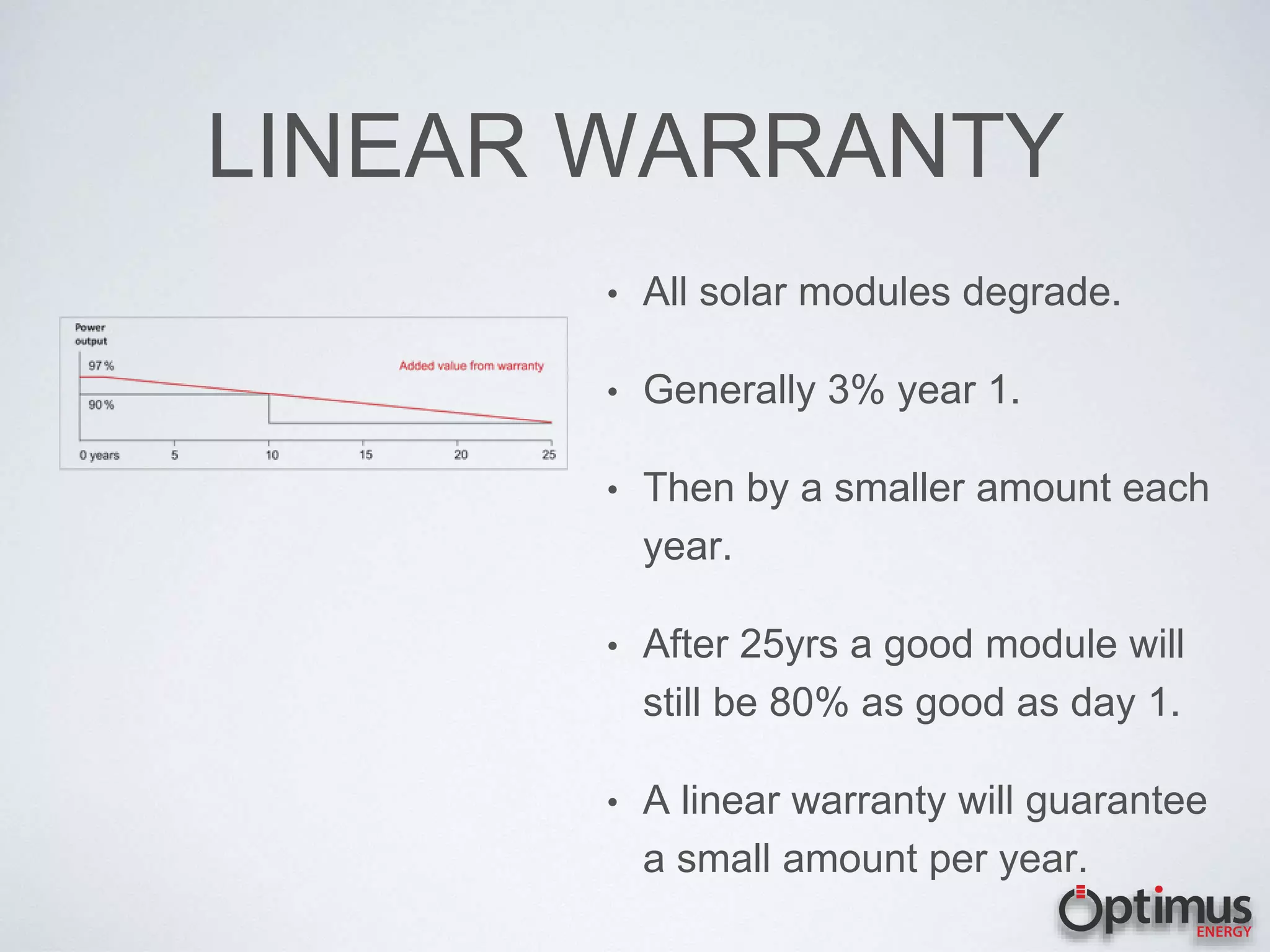
The document discusses the high electricity costs in the Philippines and the associated risks for both industries and homeowners, including competitiveness and increased pressure on budgets. It presents solar energy as a viable solution, outlining how solar systems work, the different types of solar modules, and the advantages of using solar energy. Various solar technologies and components are described, such as inverters and battery systems, along with the importance of high-quality modules and warranties.