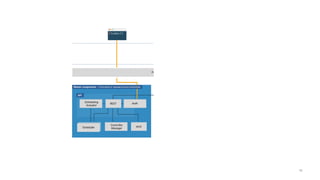
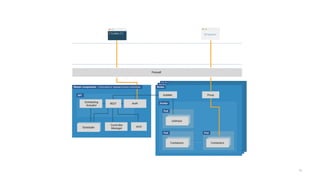
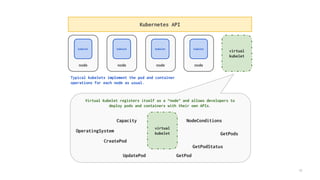
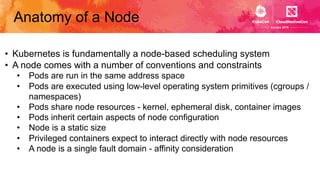
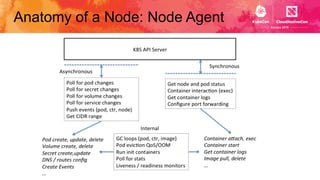
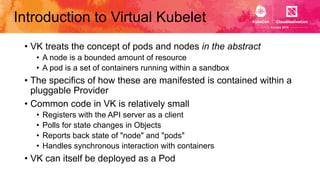
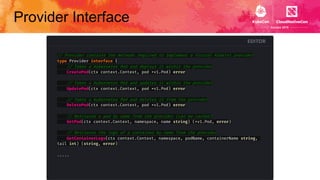
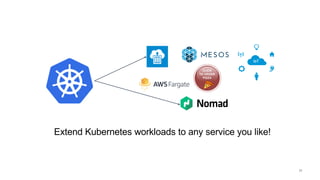
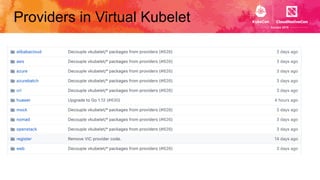
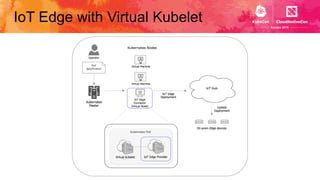
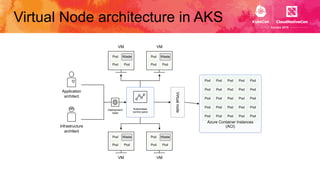
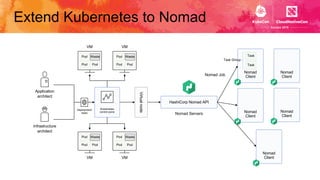
This document introduces Virtual Kubelet, which extends the Kubernetes API to serverless container platforms. It treats the concept of pods and nodes abstractly, allowing pods to run on platforms like ACI and Fargate. Virtual Kubelet implements a provider interface to manage the pod lifecycle on these platforms. It also allows hybrid use cases like running traditional and serverless pods together. The document demonstrates how Virtual Kubelet can schedule pods to ACI from an AKS cluster and to Nomad from a Kubernetes cluster.