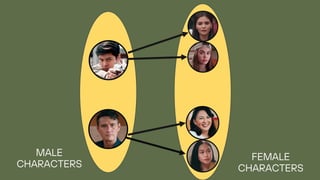
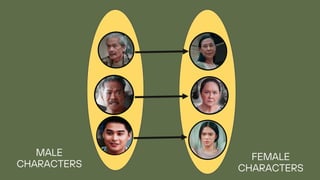
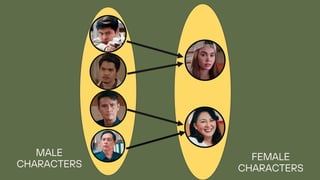
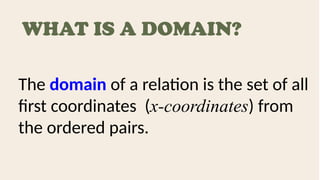
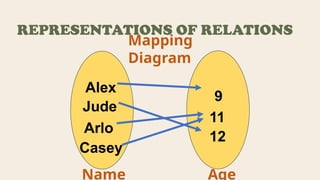
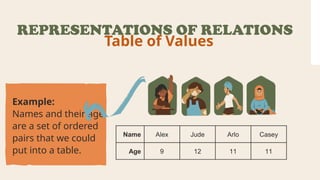
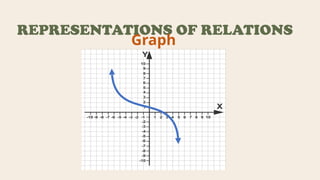
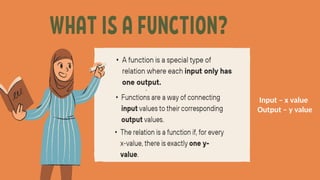
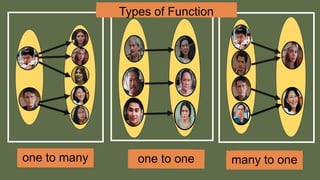
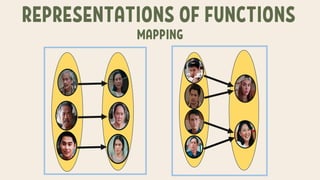
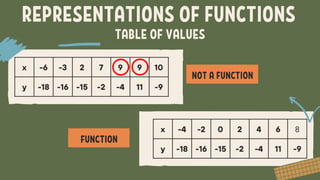
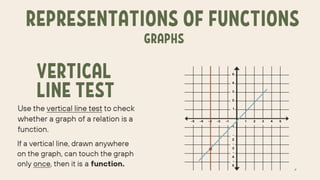
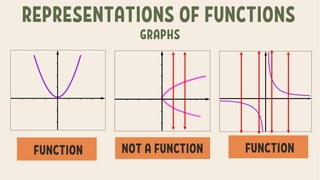
The document explains the concepts of relations and functions, including definitions, domain and range, and representation methods such as ordered pairs and graphs. It provides examples of functions and their evaluations, demonstrating how to determine the output based on given inputs. Additionally, it covers mappings and specific examples related to real-life scenarios like savings and plant growth.