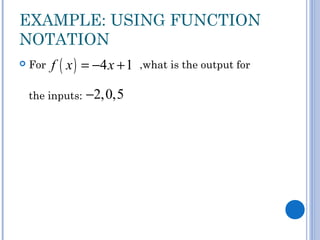
This document discusses functions, equations, and graphs. It defines relations and functions, and how to represent them using ordered pairs, mapping diagrams, and graphs. Functions are defined as relations where each input corresponds to exactly one output. The vertical line test can be used to determine if a graph represents a function. Function rules use function notation to represent the relationship between inputs and outputs algebraically. Examples are provided to illustrate these concepts.