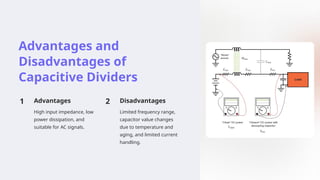
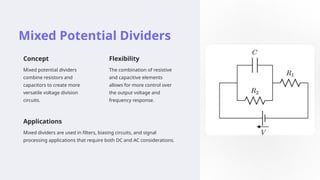
Potential dividers are circuits used to divide a voltage source into smaller voltages, using resistors, capacitors, or both. They have applications in various electronic systems like volume controls and signal processing, with advantages such as simple design and high input impedance but also disadvantages like power dissipation and sensitivity to component value changes. Mixed potential dividers leverage both resistive and capacitive elements for enhanced voltage control and frequency response, applicable in filters and sensor interfaces.