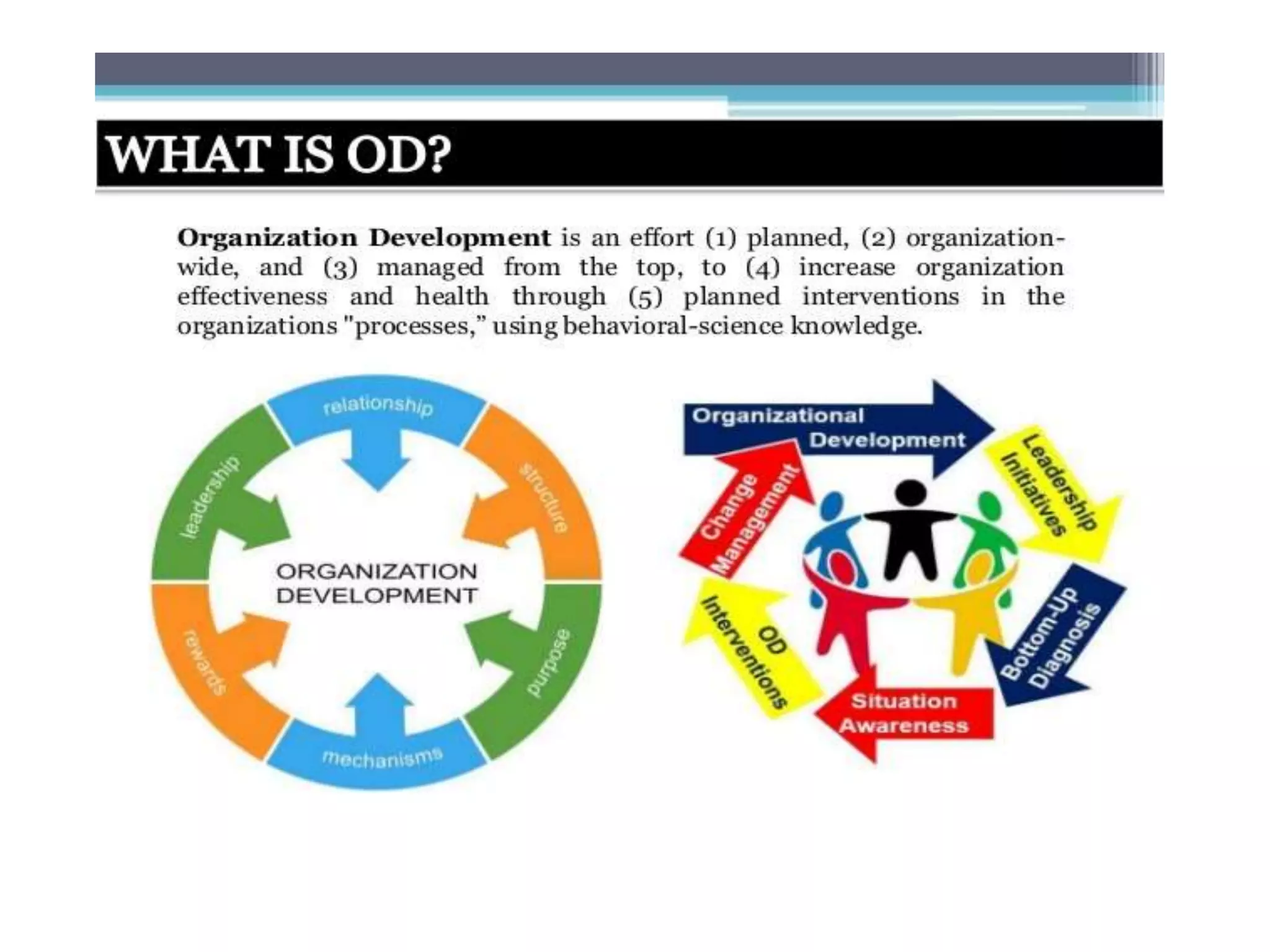
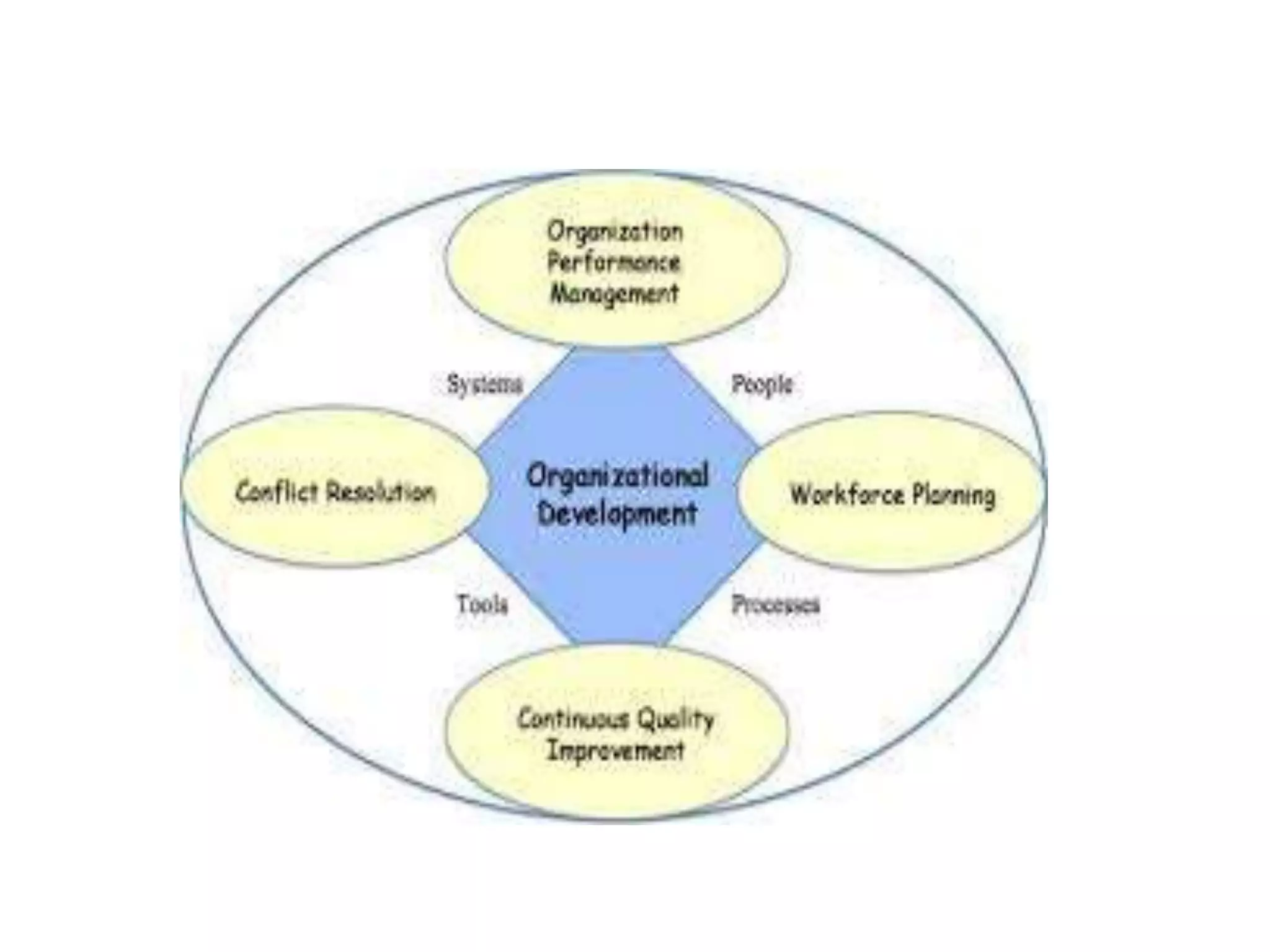
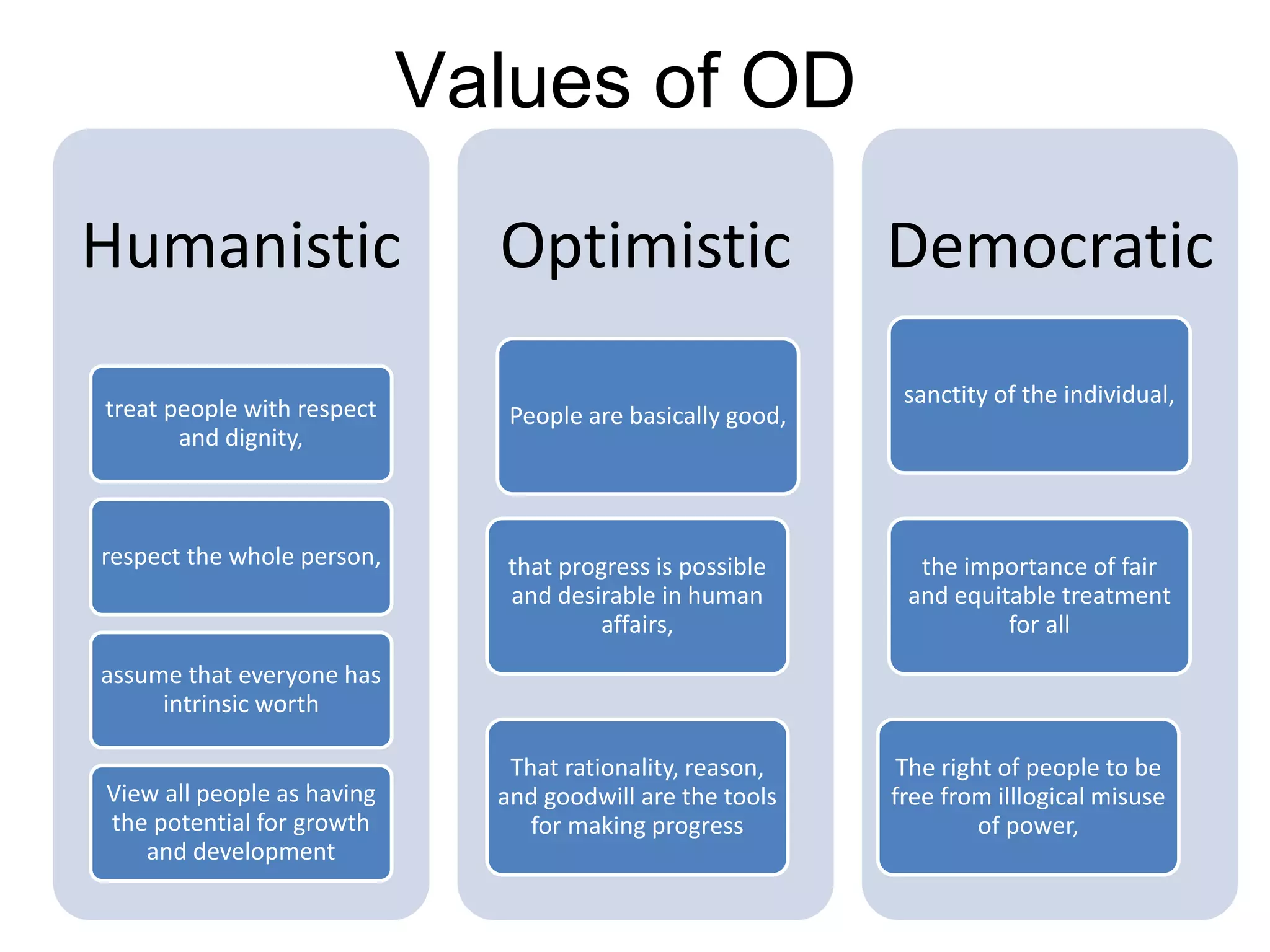
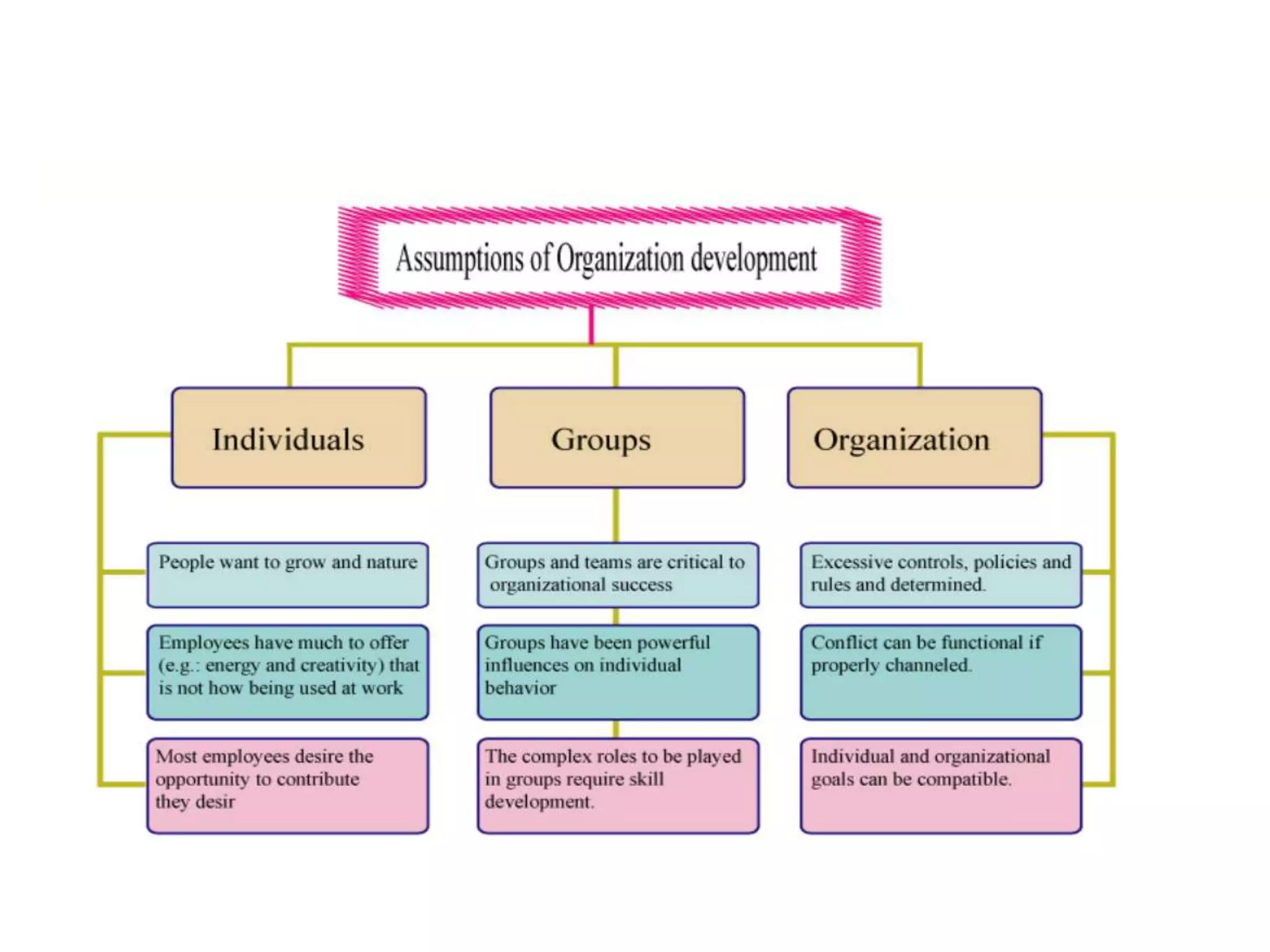
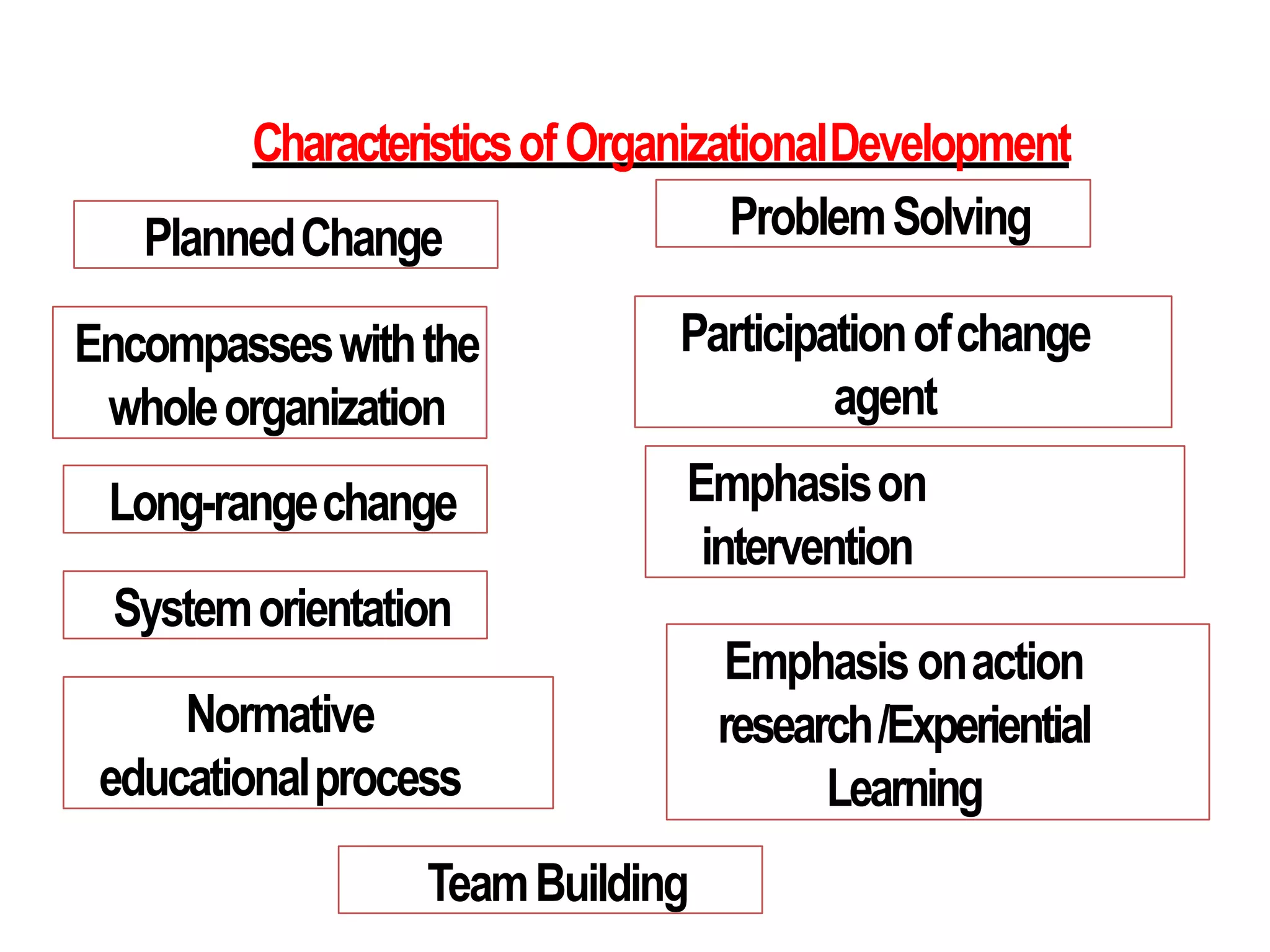
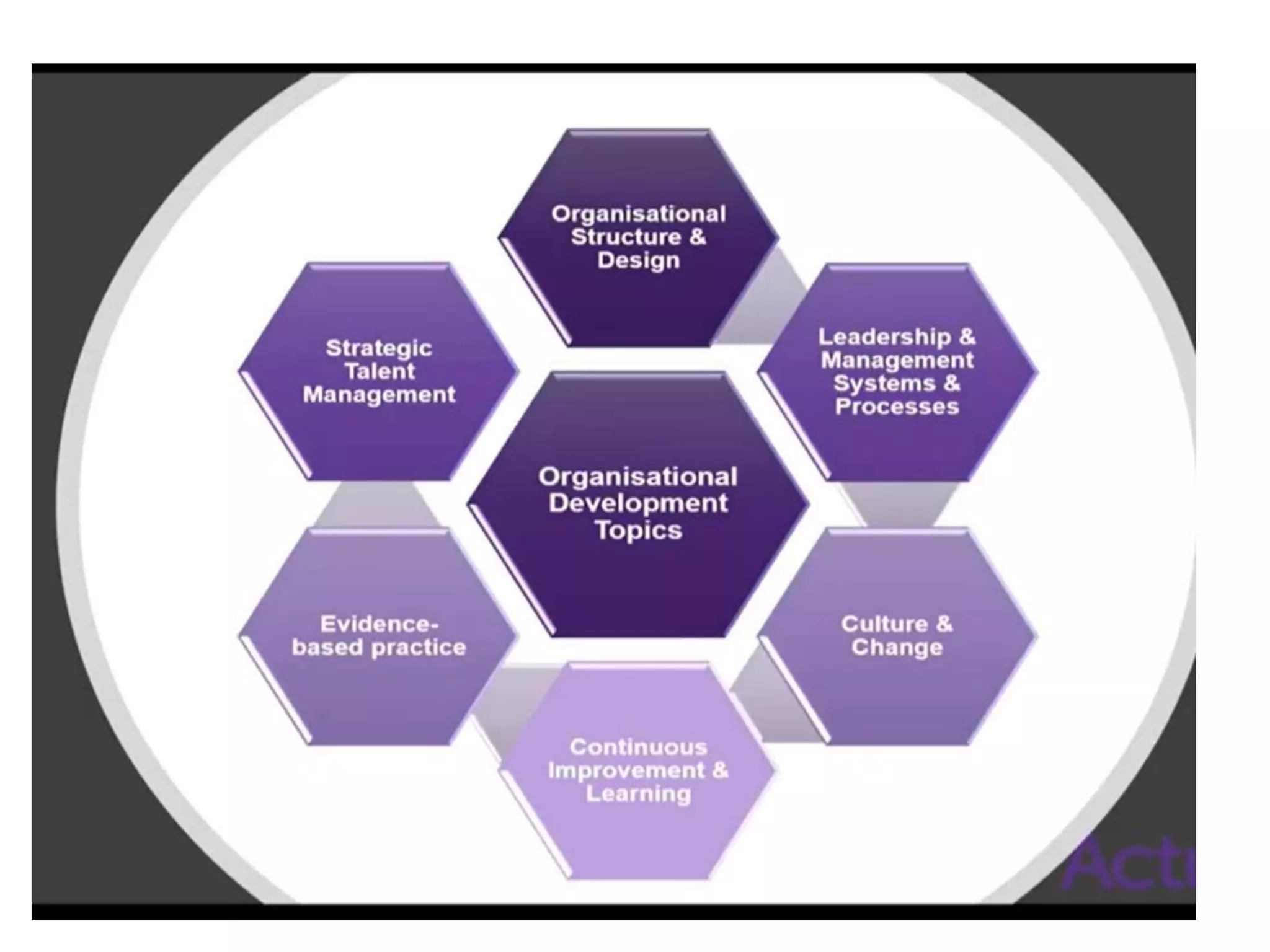
Organization development (OD) emerged in the 1960s as a way to systematically improve organizations using scientific methods. OD aims to enhance performance, adaptability, and human well-being in organizations. Key values of OD include treating people with dignity, assuming potential for growth, and believing in rational problem-solving and progress through democratic participation. Common OD techniques include action research, team building, and problem-solving groups. Globalization, technology, and new management approaches continue to shape the relevance of OD today.