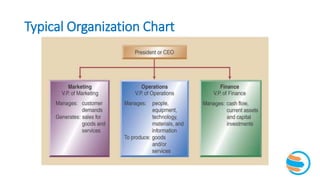
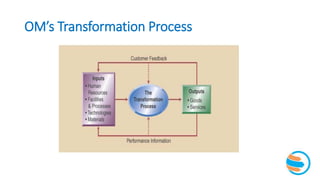
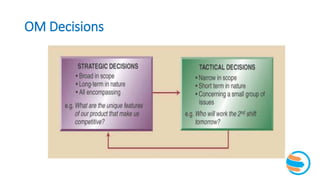
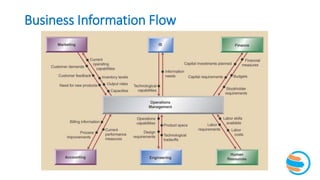
This document provides an overview of operations management (OM). It defines OM as the business function responsible for planning, coordinating, and controlling resources to produce products and services. The role of OM is to transform inputs like people, materials, and money into outputs of goods and services. OM makes both strategic and tactical decisions. While manufacturing and service organizations differ in their tangible outputs, they both face similar operational challenges. The document traces the historical development of OM concepts and trends shaping today's dynamic business environment, emphasizing the importance of OM working closely with other functions like marketing, finance, and human resources.