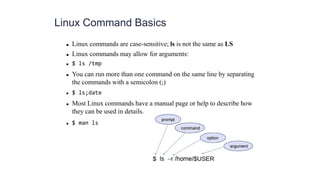
The document provides an introduction to Linux commands and lists the top 50 commands. It includes brief descriptions of common commands like ls, cd, mkdir, rmdir, ps, kill, cat, head, cp, mv, comm, ln, history, wget, curl, find, grep, sed and more. It then provides a lab exercise with 17 steps to practice basic file navigation and directory creation/deletion using these commands.