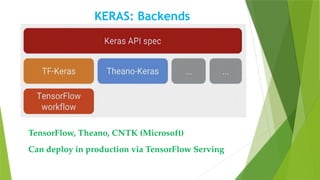
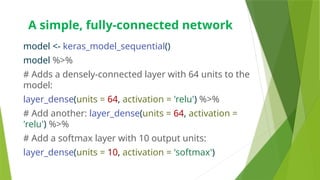
The document presents a comprehensive overview of Keras, a high-level deep learning library in Python designed for user-friendliness and quick prototyping. It outlines the installation of Keras in R, including the necessary packages and code snippets to build a simple model. Key advantages of Keras include its intuitive interface, modularity for connecting layers, and ease of extension for custom functions.