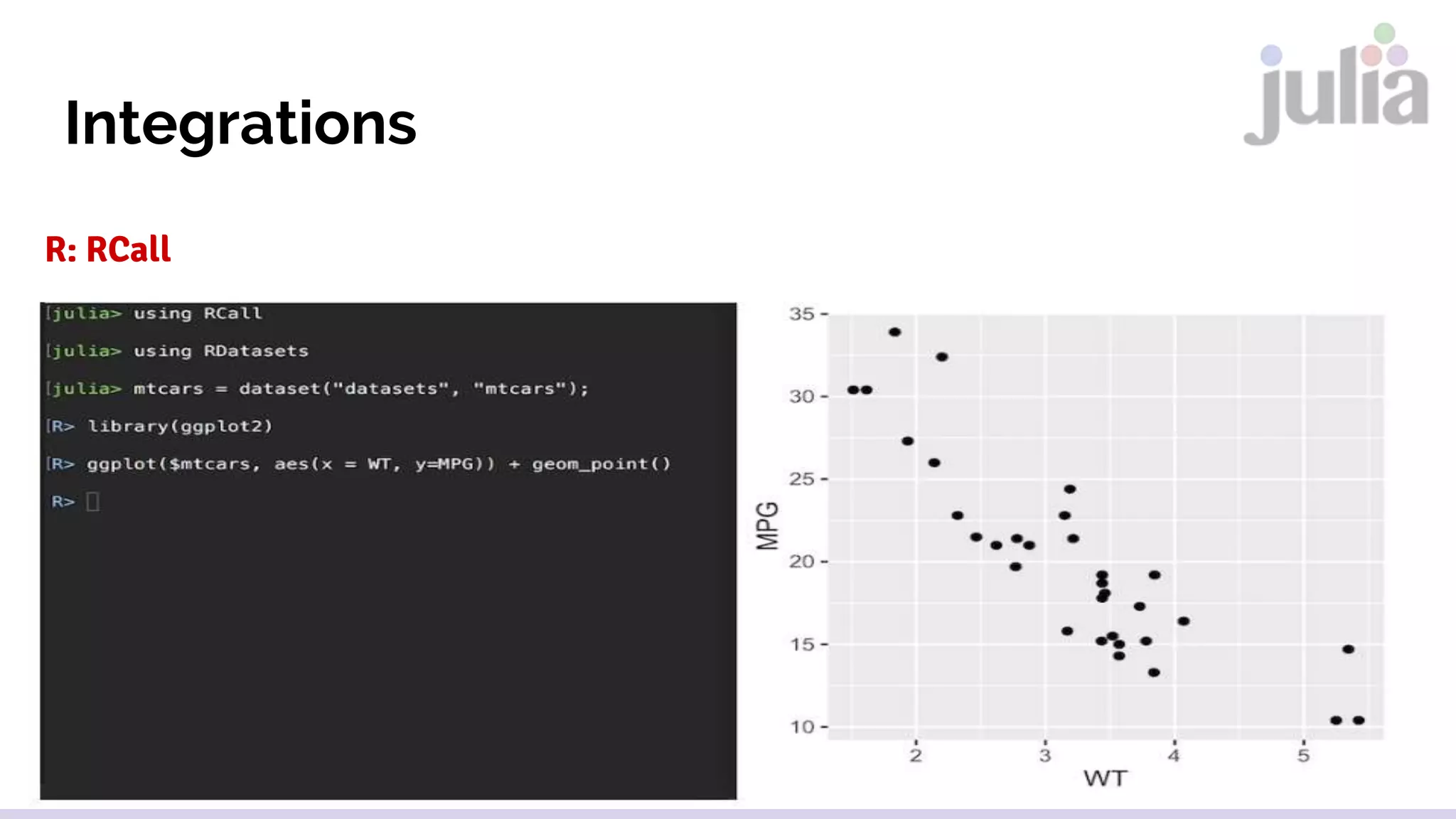
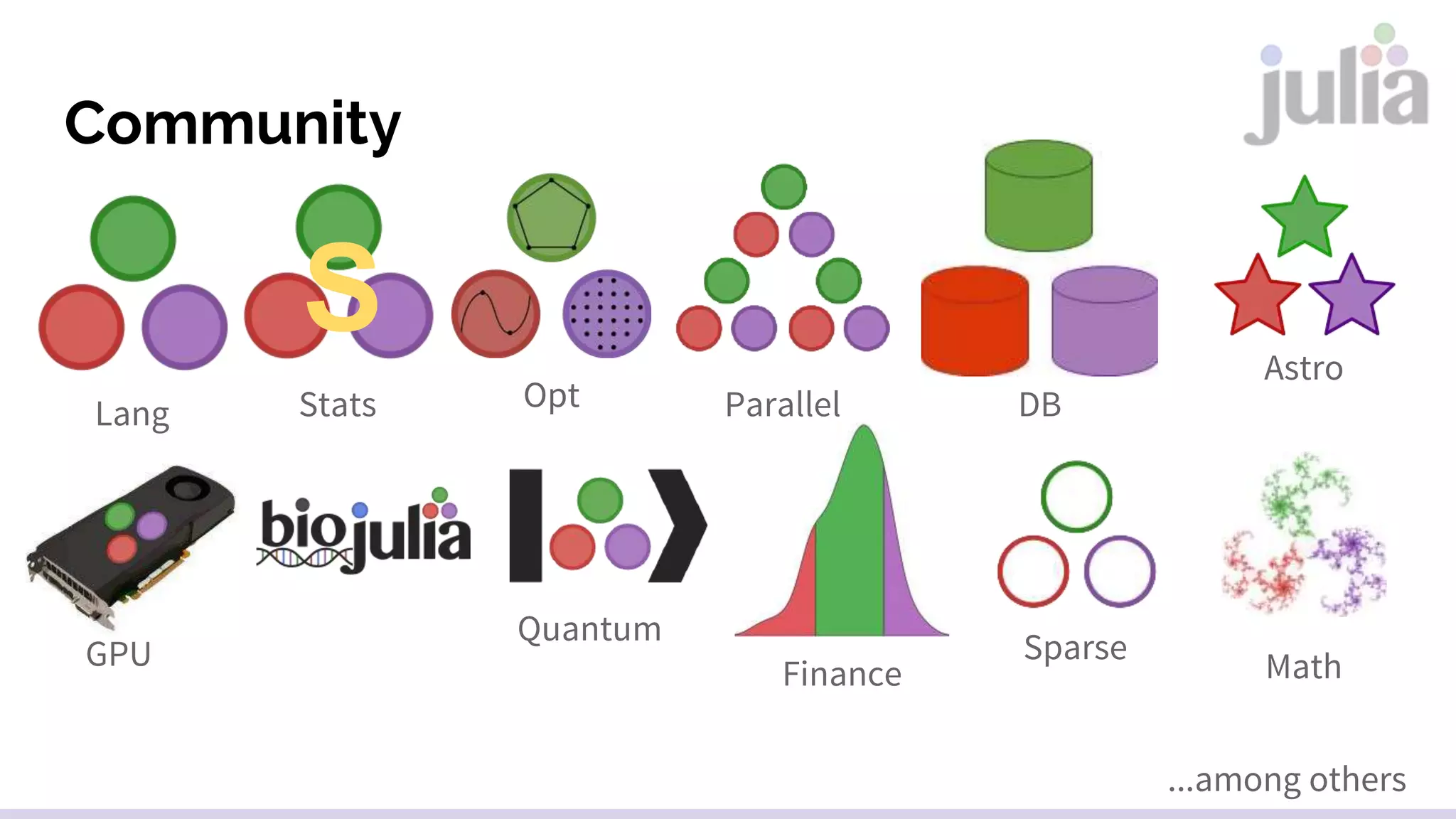
The document provides an introduction to the Julia programming language, highlighting its features and applications in data science, machine learning, and scientific computing. It outlines the installation process, core syntax, data types, function definitions, control flow, and libraries available for various purposes. Additionally, it discusses integration with Python and R, as well as important community projects.







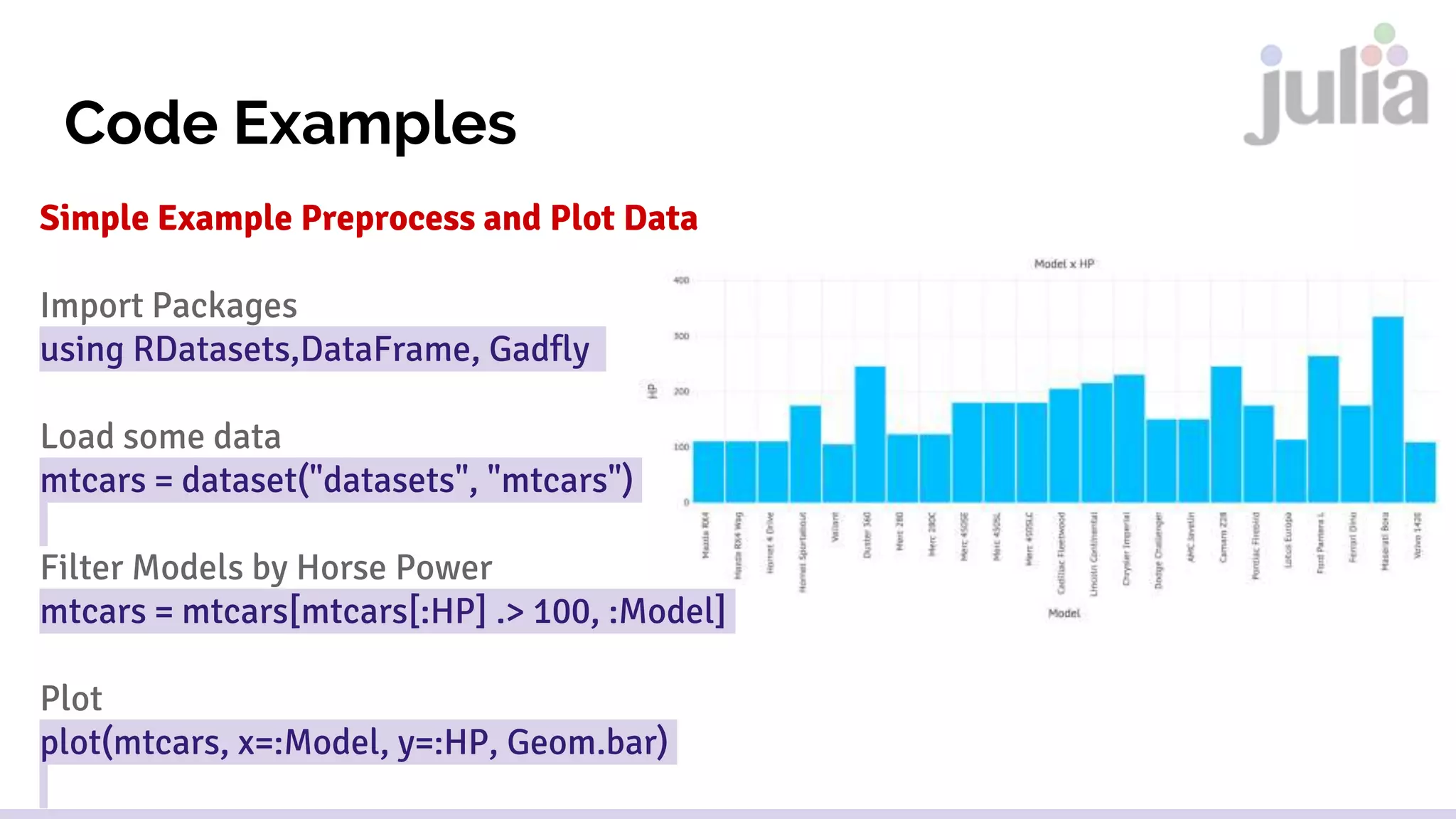
![Code Examples
Simple Example Preprocess and Plot Data
Import Packages
using RDatasets,DataFrame, Gadfly
Load some data
mtcars = dataset("datasets", "mtcars")
Filter Models by Horse Power
mtcars = mtcars[mtcars[:HP] .> 100, :Model]
Plot
plot(mtcars, x=:Model, y=:HP, Geom.bar)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2016-08-25-introduction-to-julia-language-160901112519/75/Introduction-to-Julia-Language-13-2048.jpg)