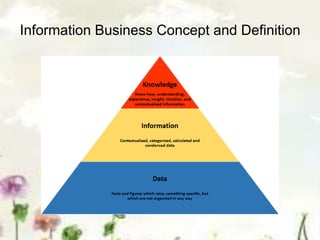
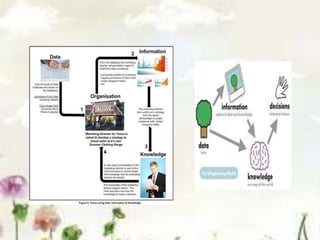
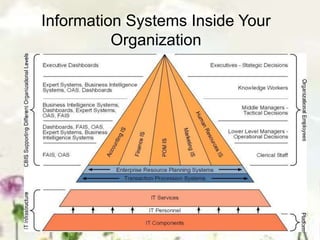
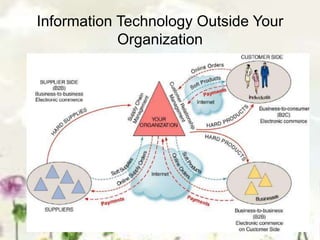
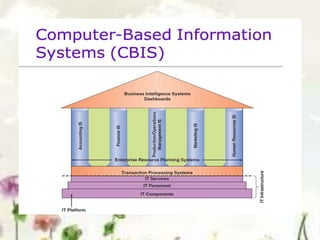
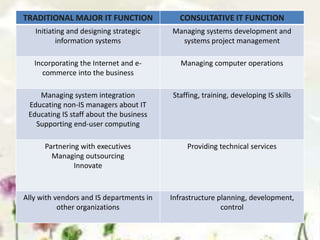
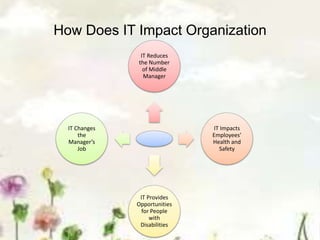
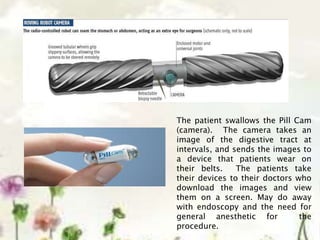
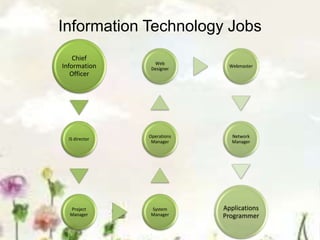
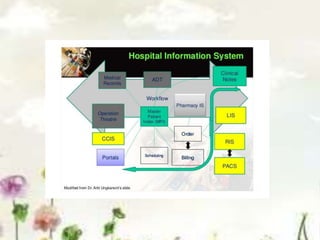
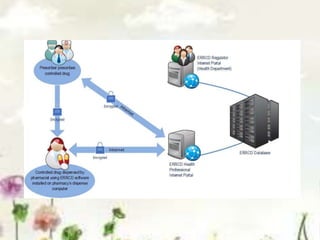
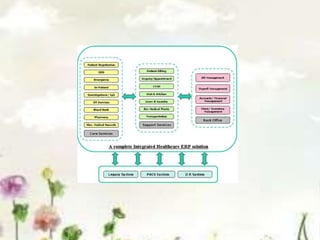
This document provides an introduction to information systems. It defines key terms like information technology architecture and infrastructure. It describes the traditional and consultative roles of IT functions in organizations. It also discusses how IT impacts organizations through reducing middle managers, affecting employee health and safety, and providing opportunities for disabled people. Additionally, it outlines important IT jobs and provides examples of how IT improves quality of life and healthcare through technologies like robots and medical devices. Finally, it discusses how a pharmacy information system can help with clinical screening, prescription management, patient drug profiles, and inventory management.