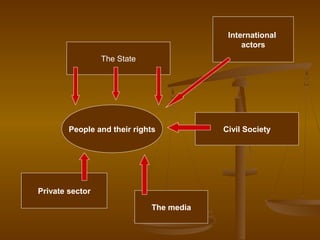
This document discusses human rights and the role of the state in realizing human rights. It introduces the five traditional types of human rights and explains that states have three core obligations - to respect, protect, and fulfill human rights. It also discusses four procedural obligations of states regarding non-discrimination, adequate progress, participation, and effective remedies for rights violations. The document uses examples to illustrate how different actors like states, communities, private sectors, and civil society organizations can work to realize specific rights like education and fair trials.