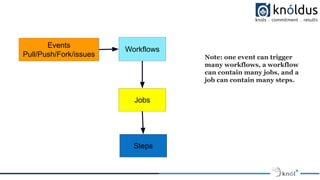
The document presents an introduction to GitHub Actions, outlining its core concepts, functionalities, and etiquette for participants in related sessions. GitHub Actions automates workflows and supports CI/CD directly within GitHub, enabling developers to build, test, and deploy code efficiently. It also provides various use cases, emphasizing automation and integration with third-party tools, and highlights the advantages of using a GitHub-native CI/CD tool.





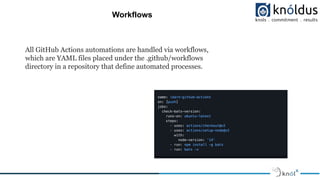

![Workflows support a number of different automations ranging from pull requests and branch
merging—plus, third-party integrations with your 5 preferred tools such as chat app
notifications, testing suites, container management, and more via the GitHub Marketplace.
You can leverage automated workflows to build, test, and deploy code directly into a virtual
machine or a Docker container. GitHub Actions also supports “matrix builds,” which enables
you to simultaneously test builds across multiple operating systems and runtime versions.
jobs:
example_matrix:
strategy:
matrix:
version: [10, 12, 14]
os: [ubuntu-latest, windows-latest]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontogithubactions-220613103021-d41beb74/85/Introduction-to-Github-Actions-8-320.jpg)