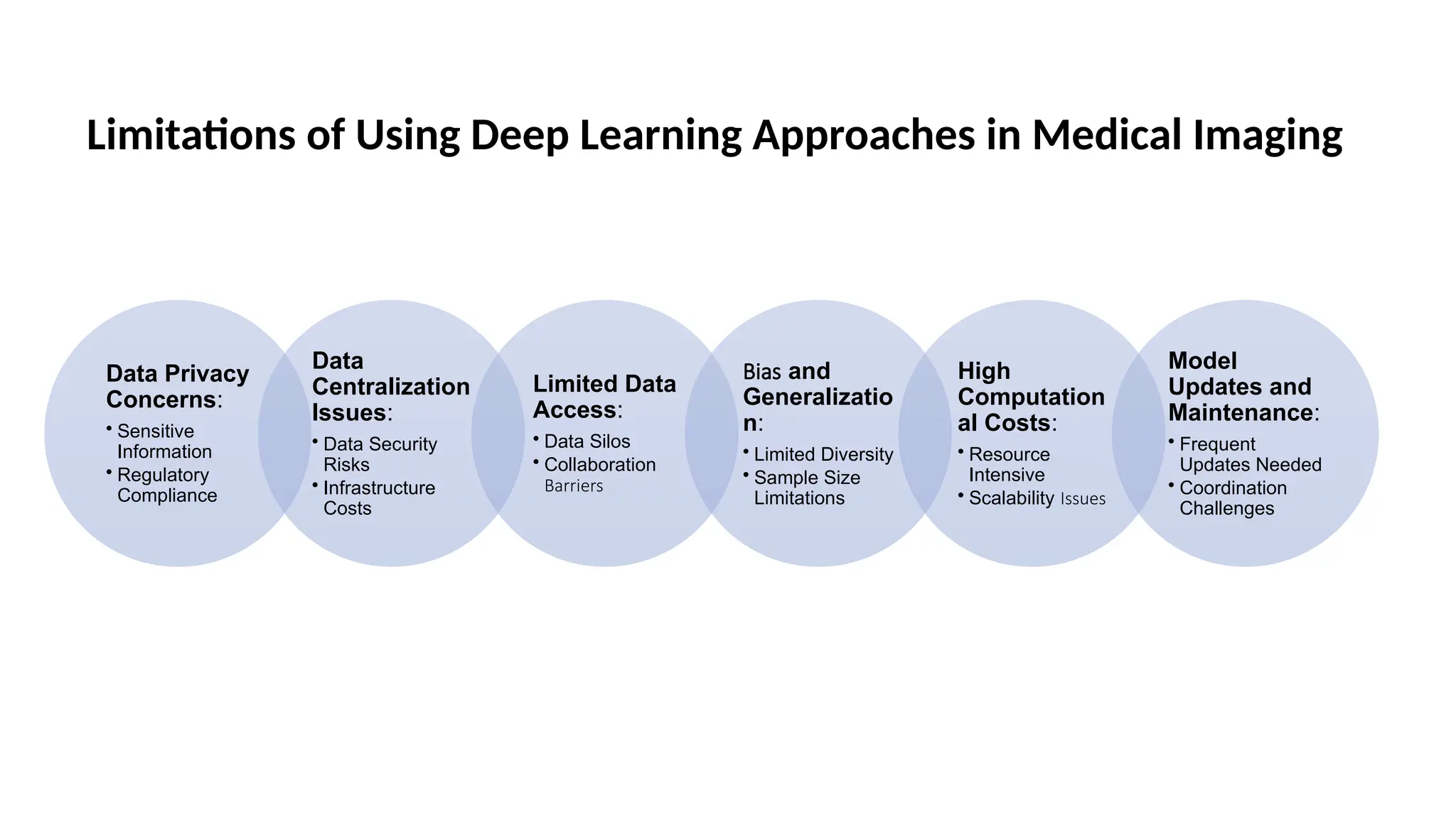
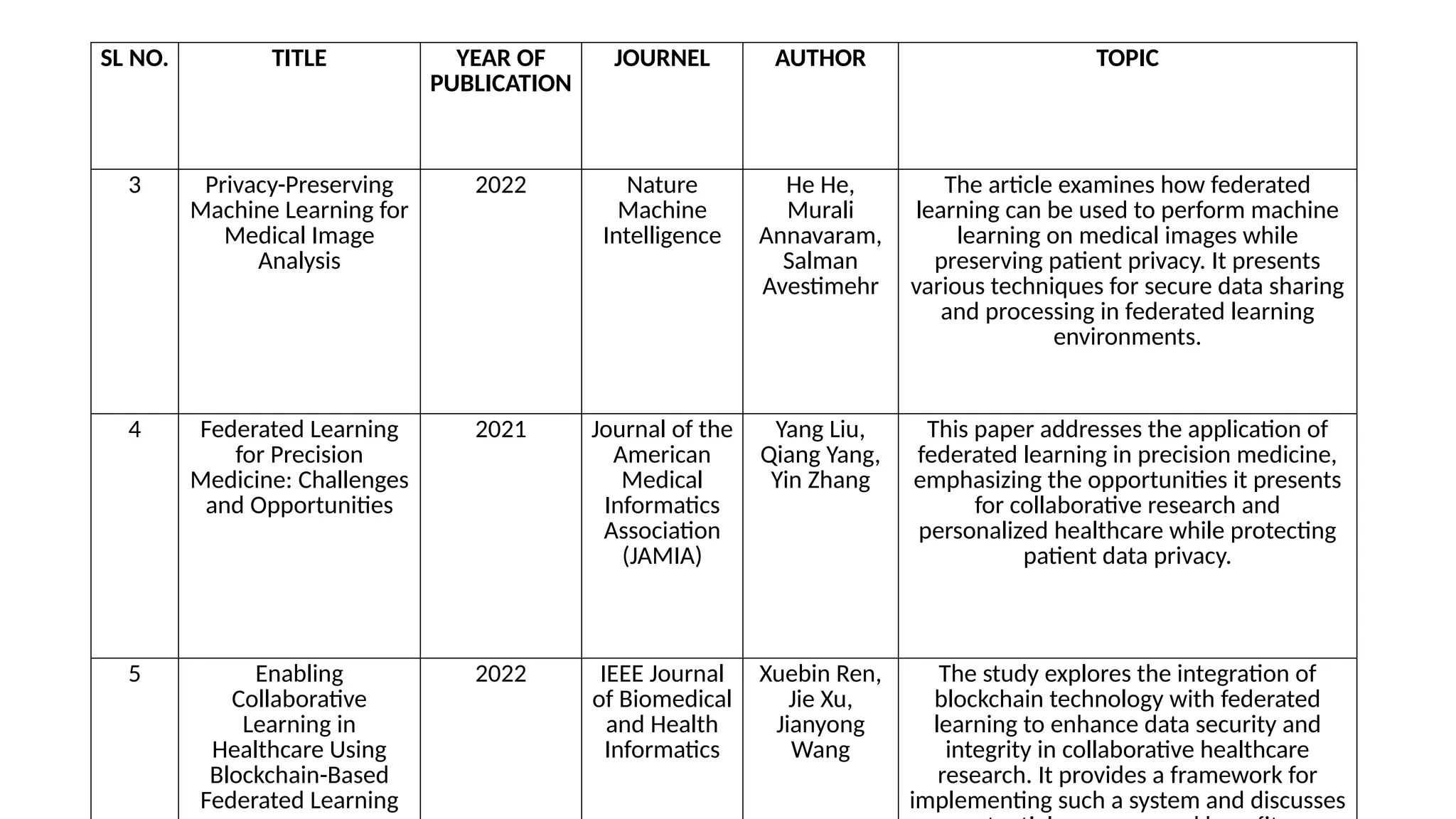
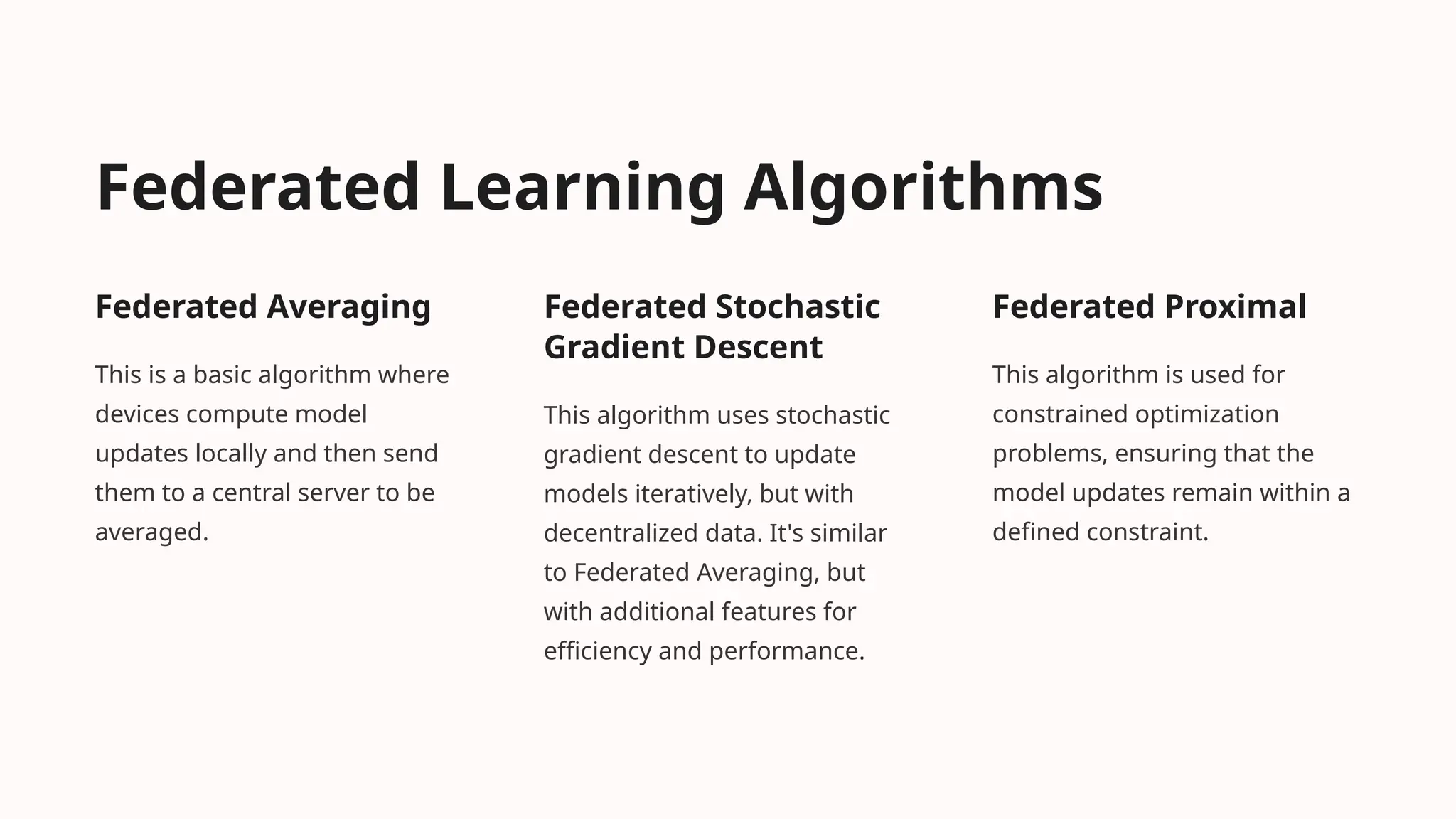
This document discusses federated learning as a decentralized machine learning technique particularly beneficial for medical imaging, emphasizing data privacy and security. It outlines the challenges of traditional deep learning, such as data centralization and high computational costs, and highlights the benefits of federated learning in mitigating these issues. A literature survey on federated learning applications and frameworks is included, along with future directions for advancements and integration with other technologies.