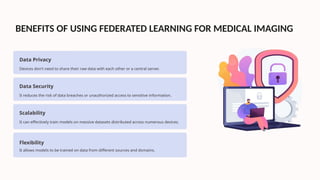
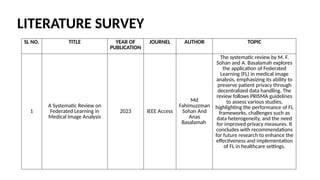
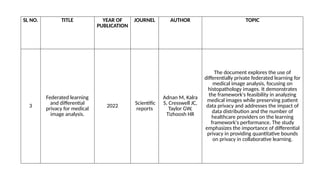
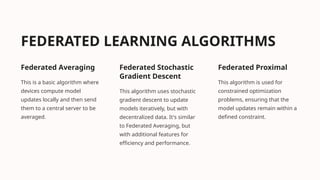
The document discusses federated learning as a decentralized machine learning method beneficial for medical imaging, focusing on its ability to preserve data privacy while allowing device collaboration without data sharing. It outlines the benefits, limitations, and challenges of federated learning, including issues related to data heterogeneity and communication overhead. The document also reviews various studies and algorithms related to federated learning, emphasizing its potential applications in healthcare and future directions for advancement.