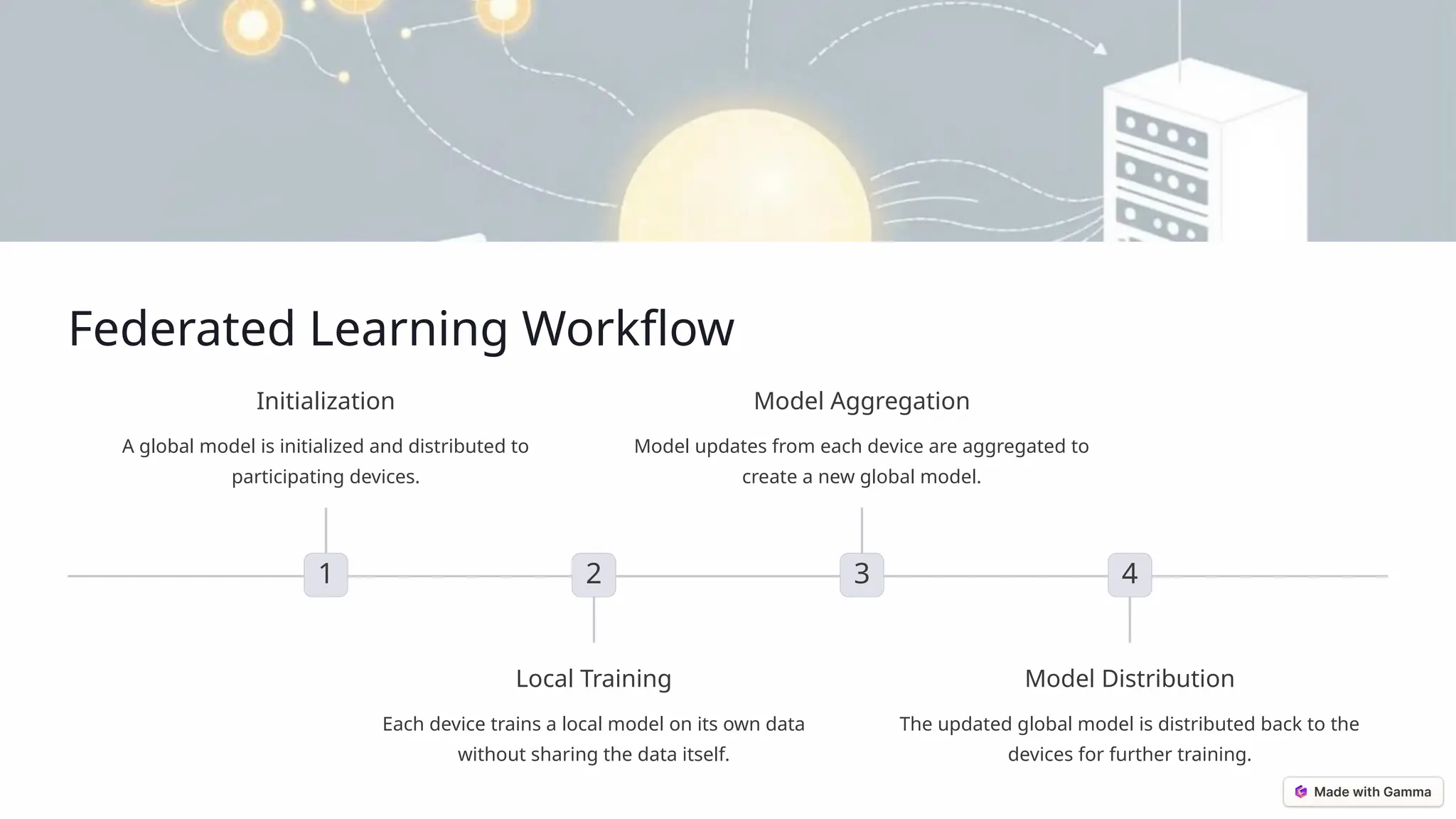
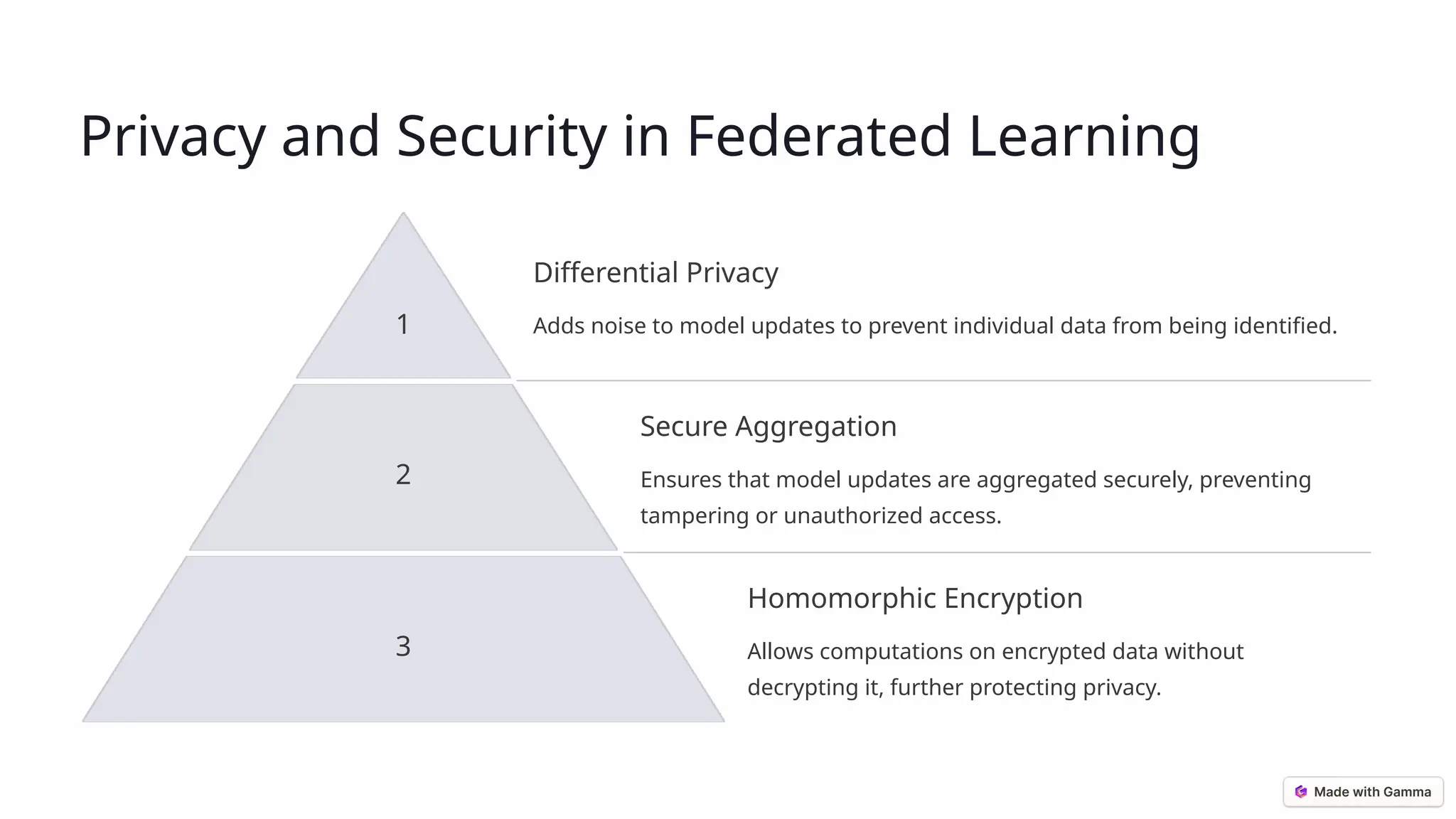
Federated learning is a decentralized approach to training AI models while keeping data on individual devices, thus enhancing privacy and security. It addresses challenges in traditional machine learning, such as data privacy, silos, and security vulnerabilities by using techniques like model aggregation and differential privacy. This method is set to revolutionize AI development across various fields, including healthcare and finance, as it grows in adoption and effectiveness.