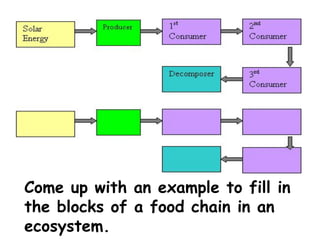
1) Organisms in an ecosystem can be producers, consumers, or decomposers. Producers like plants generate their own food through photosynthesis. Consumers cannot make their own food and eat other organisms, including primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers. Decomposers break down dead organisms.
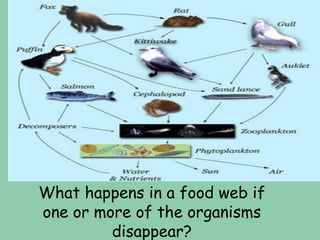
2) Food chains show the transfer of energy as organisms eat each other. Producers are first, then primary, secondary, etc. consumers. Food webs show overlapping food chains and how organisms can play different roles.
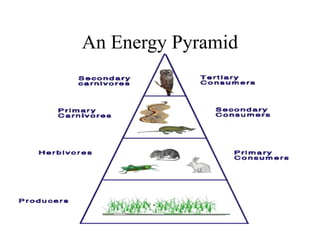
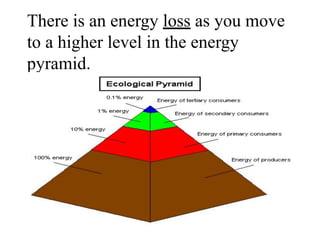
3) Energy pyramids illustrate the loss of energy at each trophic level, with 10% transferred to the next level and 90% used for life processes.