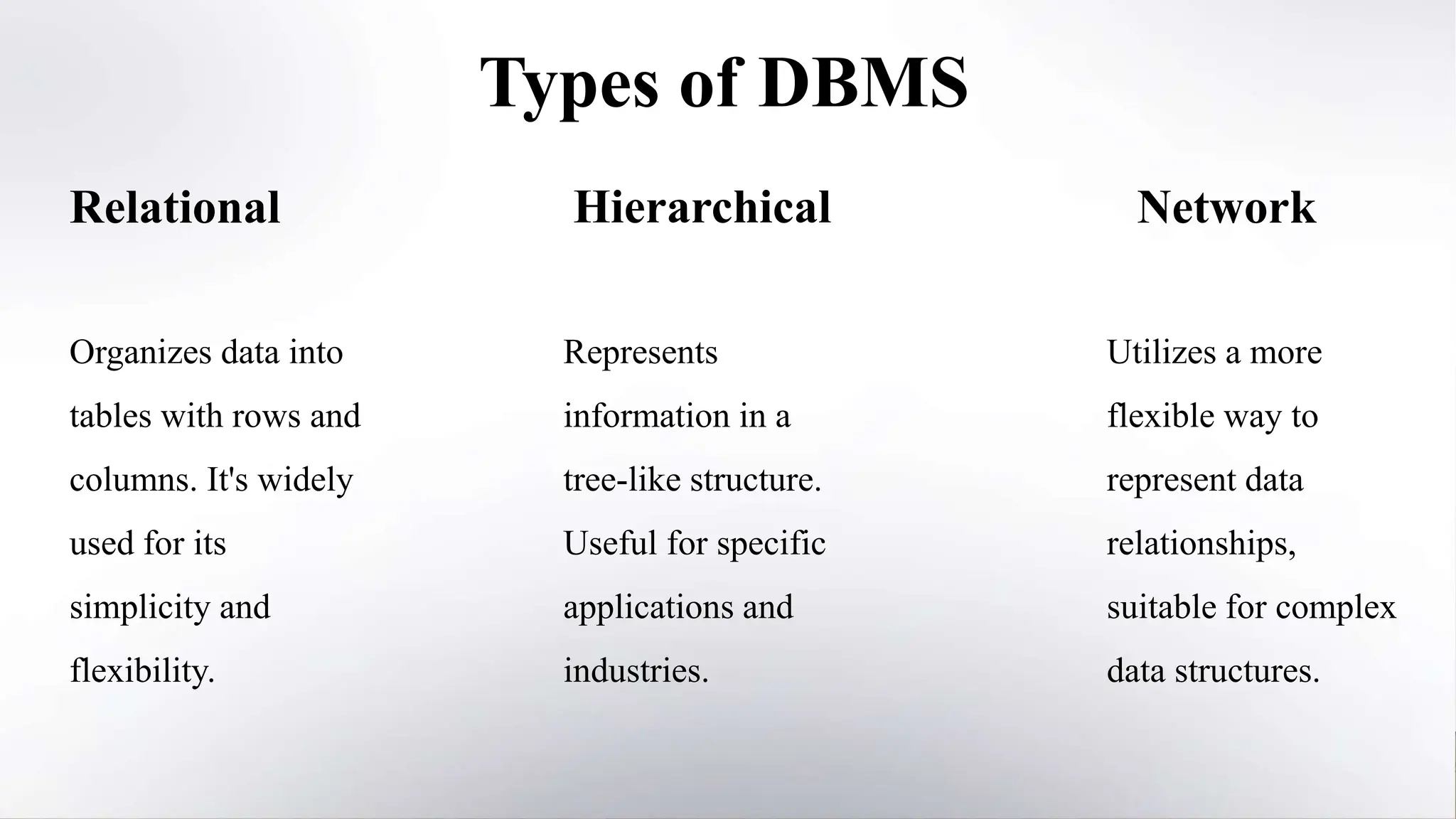
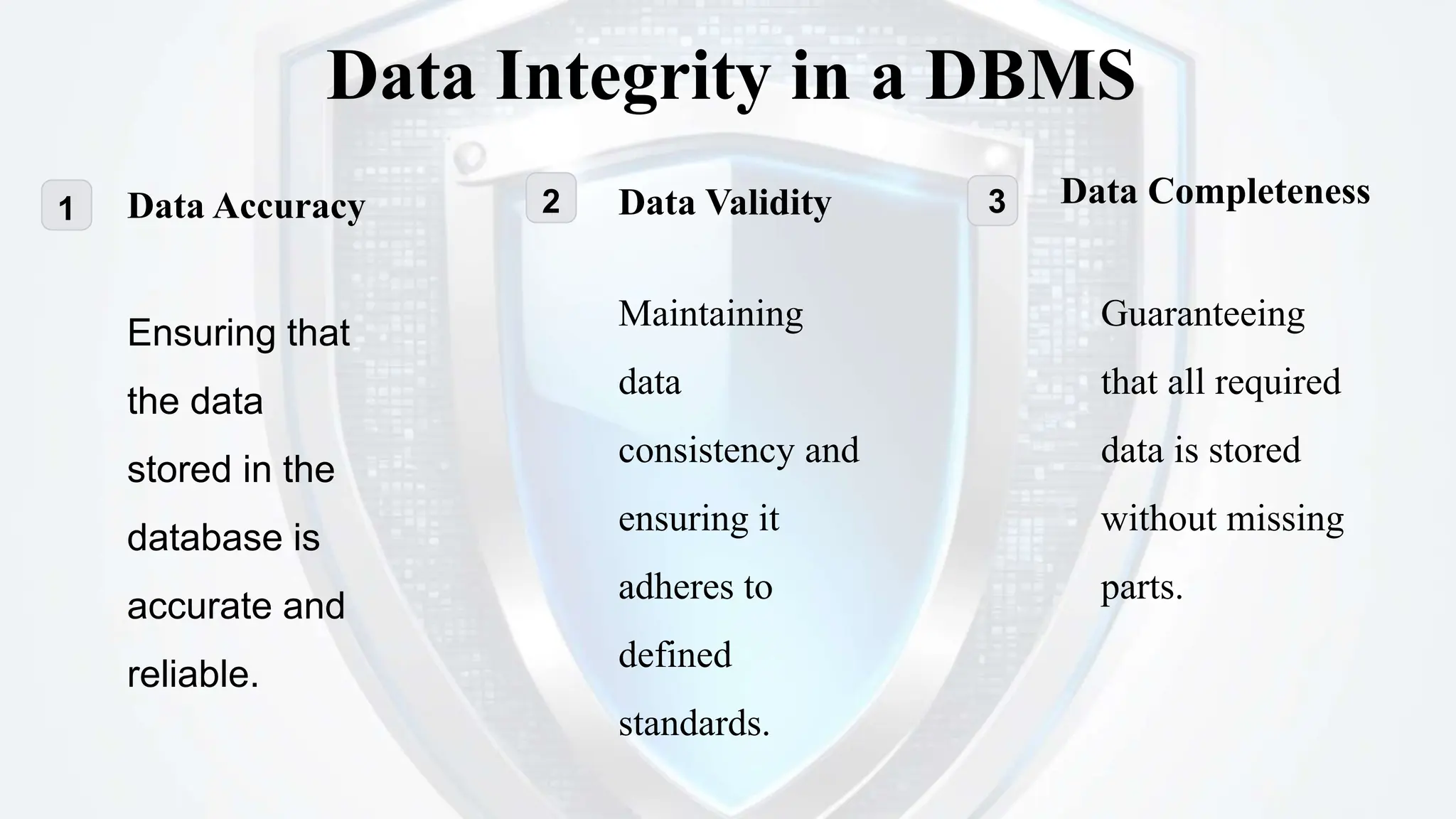
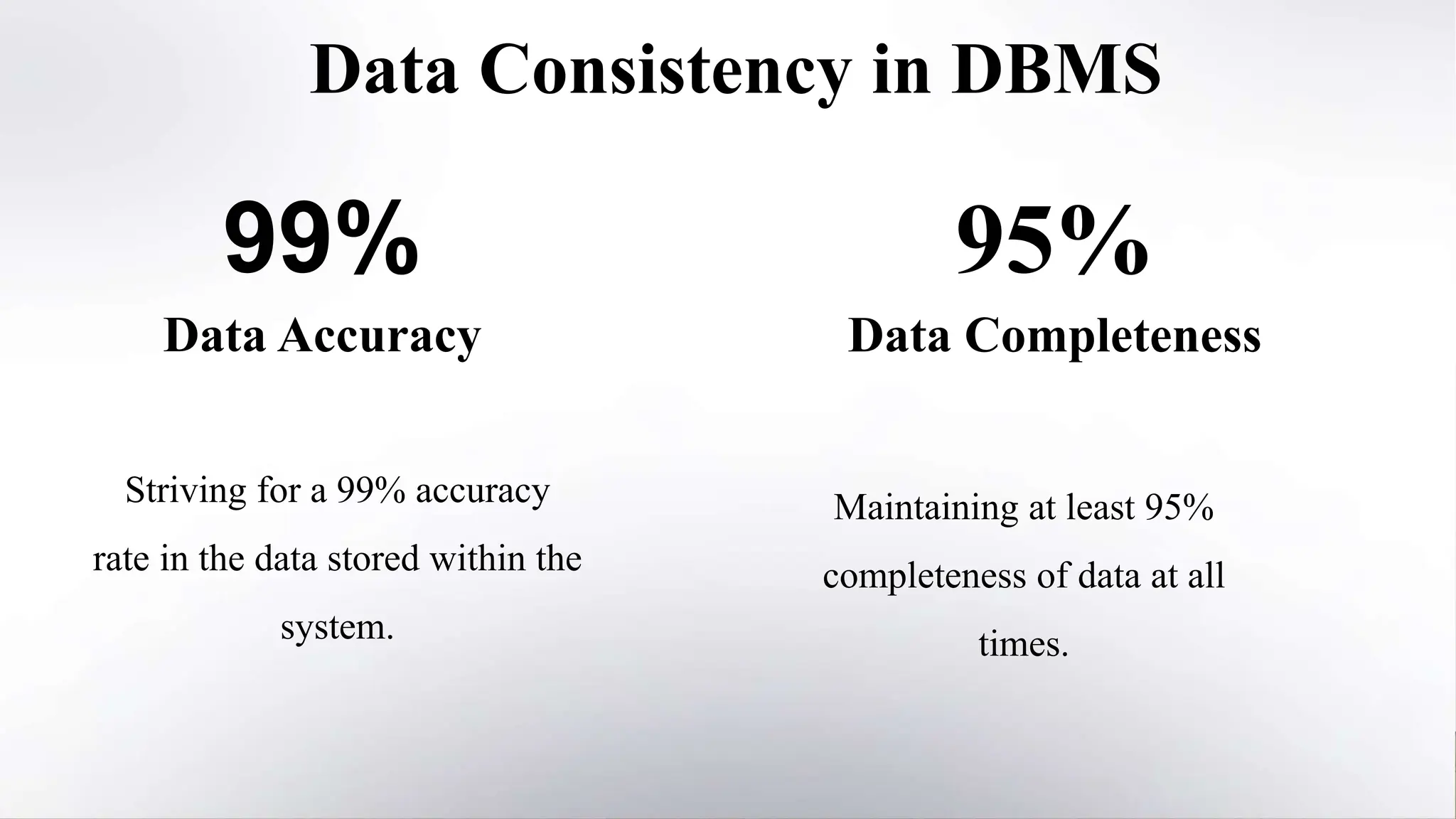
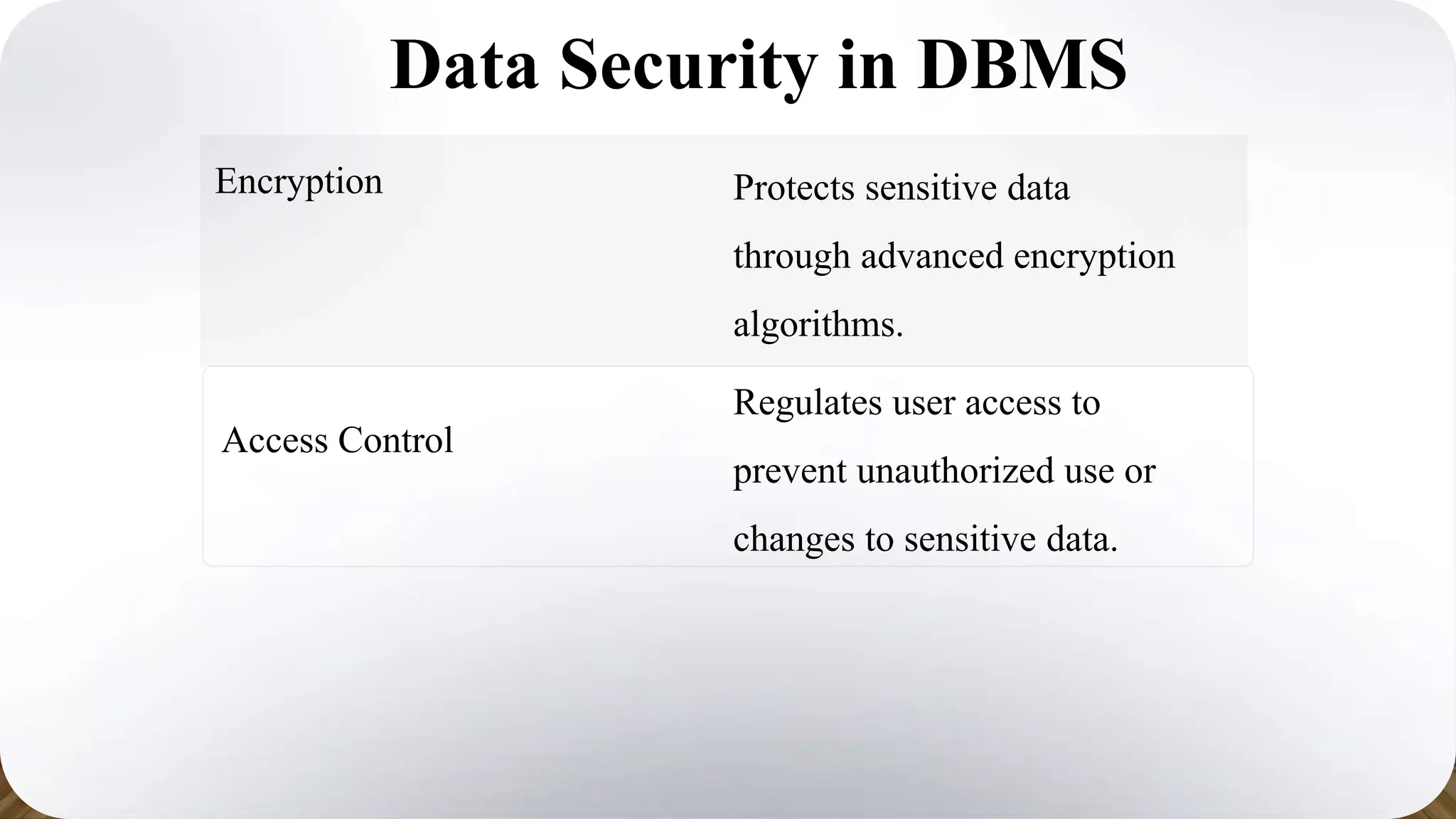
This document provides an overview of the key characteristics of database management systems (DBMS). It discusses the main types of DBMS (relational, hierarchical, network), aspects of data integrity like accuracy, validity and completeness, consistency, security through encryption and access control, persistence through reliability and durability, non-redundancy through elimination of duplicates and normalization, and independence through isolation, decentralization and modularity. The presentation was given by Shyam Kumar Sahu, a 3rd year CSE student at Bengal College of Engineering & Technology.