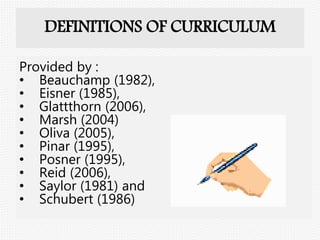
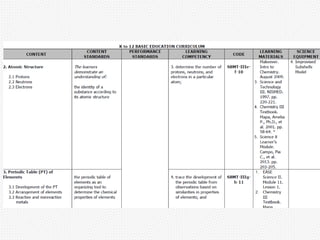
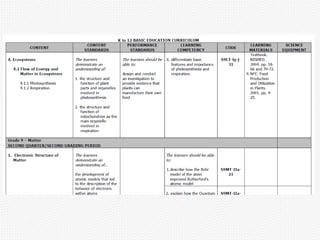
Curriculum can be defined and categorized in several ways. It includes the intended learning outcomes, the actual lessons and activities taught, and what students ultimately learn. There are different types of curriculum such as the ideal curriculum proposed by experts, the official written curriculum, how it is implemented in the classroom, what students achieve, what is tested, what society believes students should learn, how it is supported by resources, excluded topics, and the hidden curriculum of unintended lessons learned from school culture. Curriculum is a dynamic field that aims to define the knowledge and skills students will acquire.