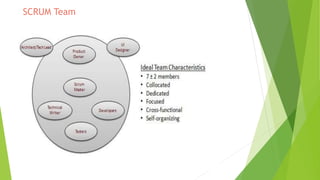
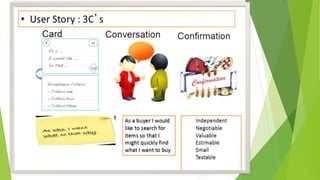
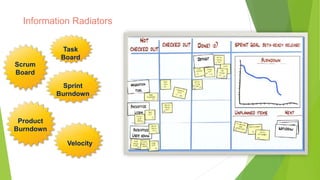
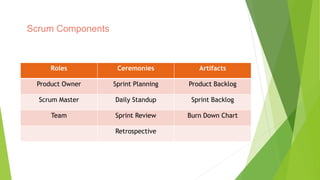
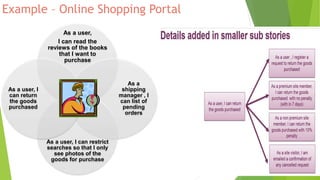
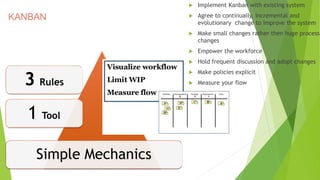
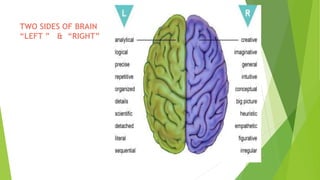
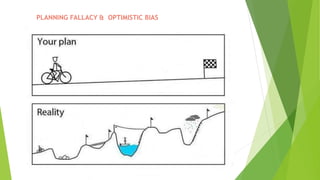
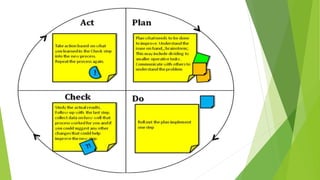
The document provides an introduction to Agile methodologies, focusing on key concepts like the Agile Manifesto and Scrum processes, including roles, ceremonies, and artifacts. It emphasizes continuous improvement, customer collaboration, and maintaining a sustainable work pace while adapting to changes. Additionally, it touches upon cognitive biases such as planning fallacy and the impact of facial expressions on communication, suggesting that effective teamwork and open discussions can drive success.