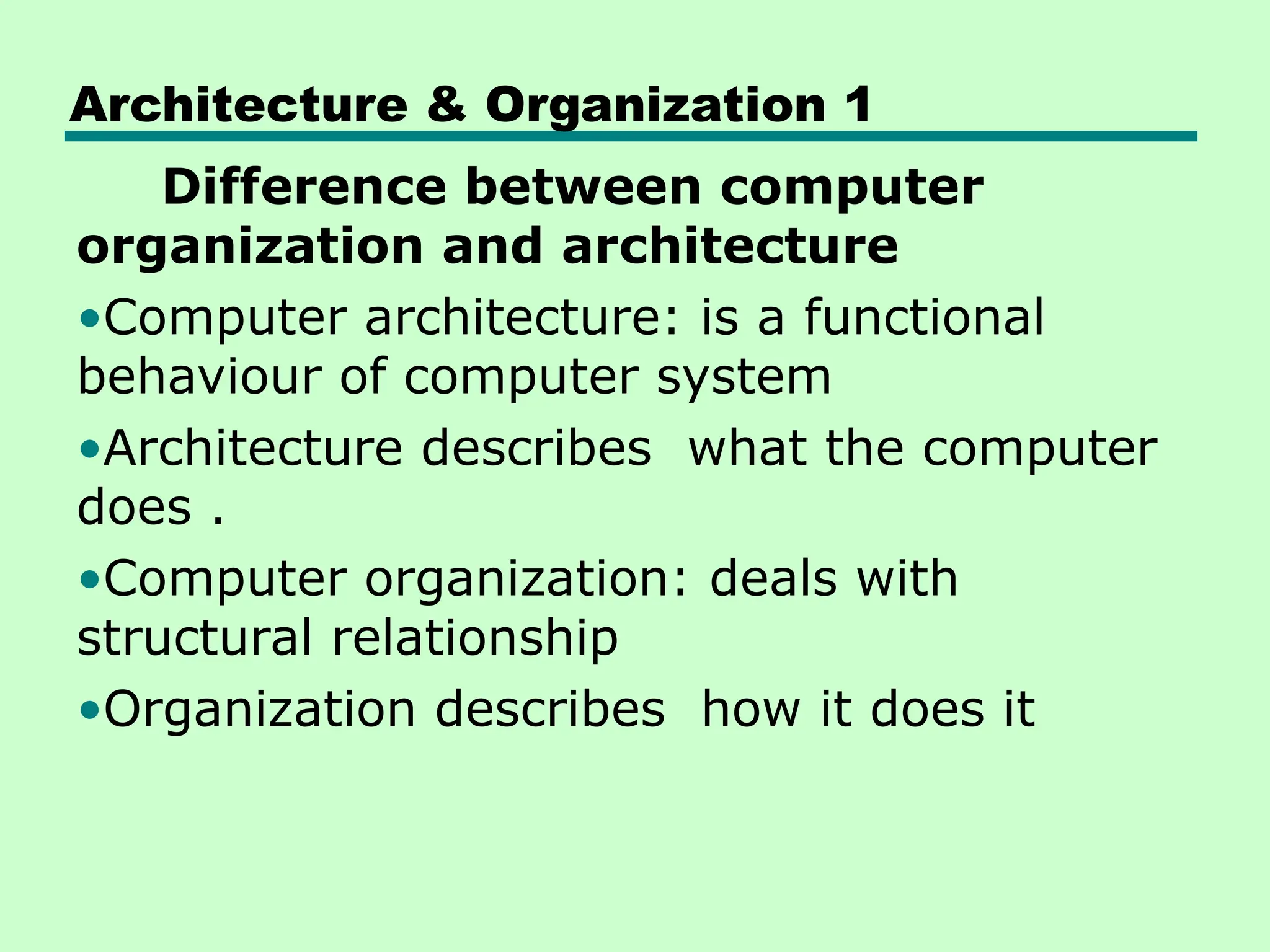
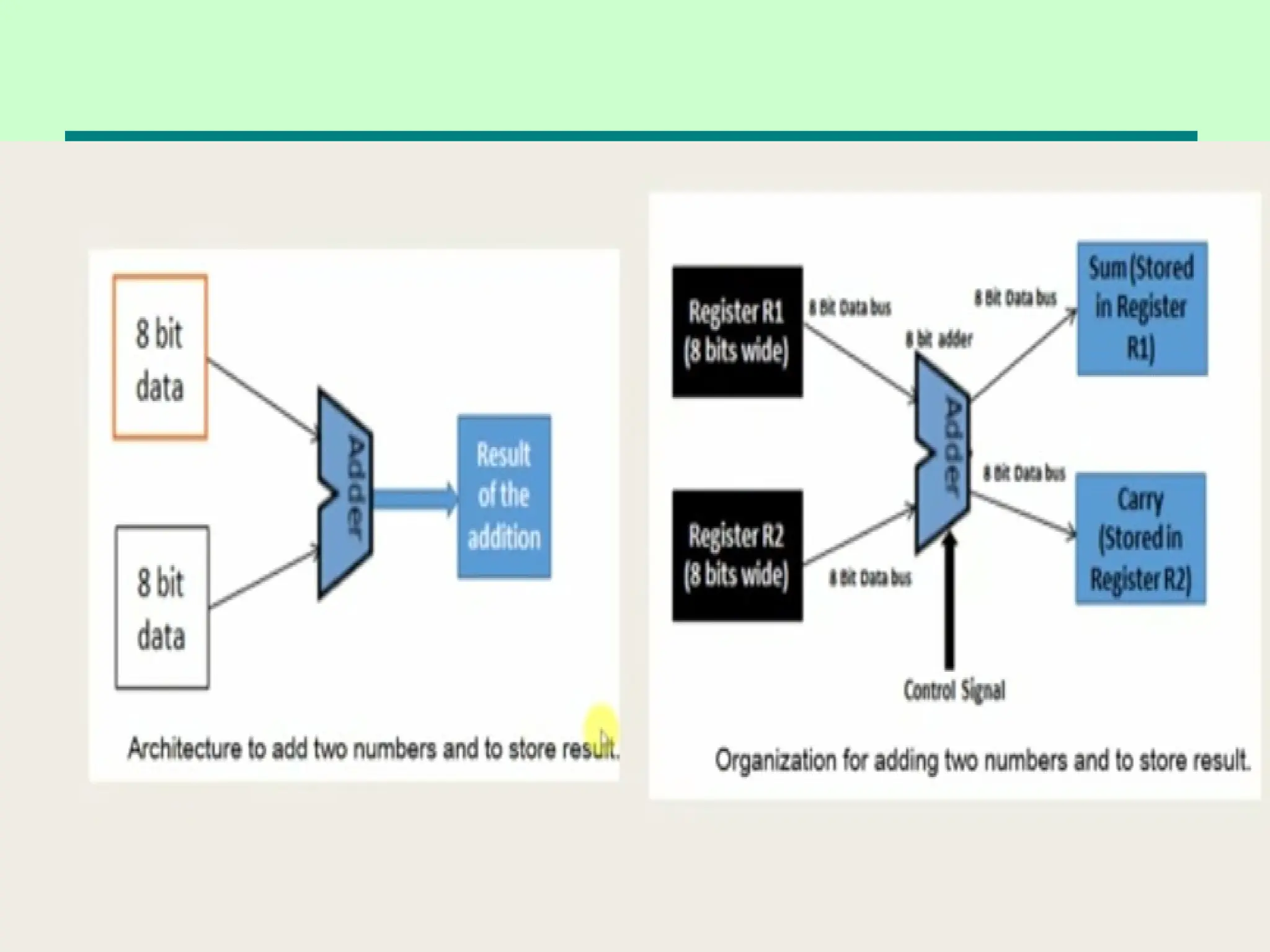
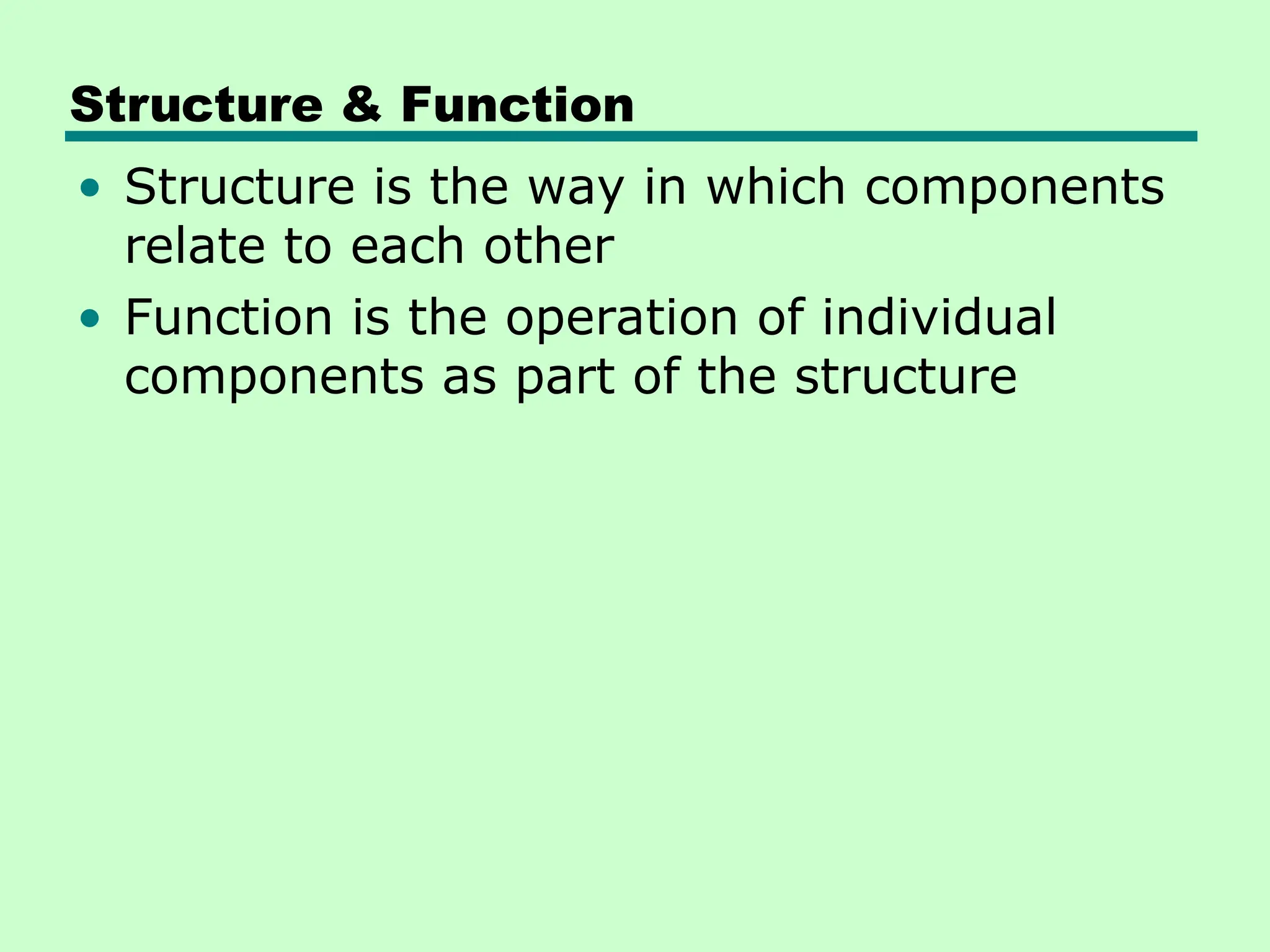
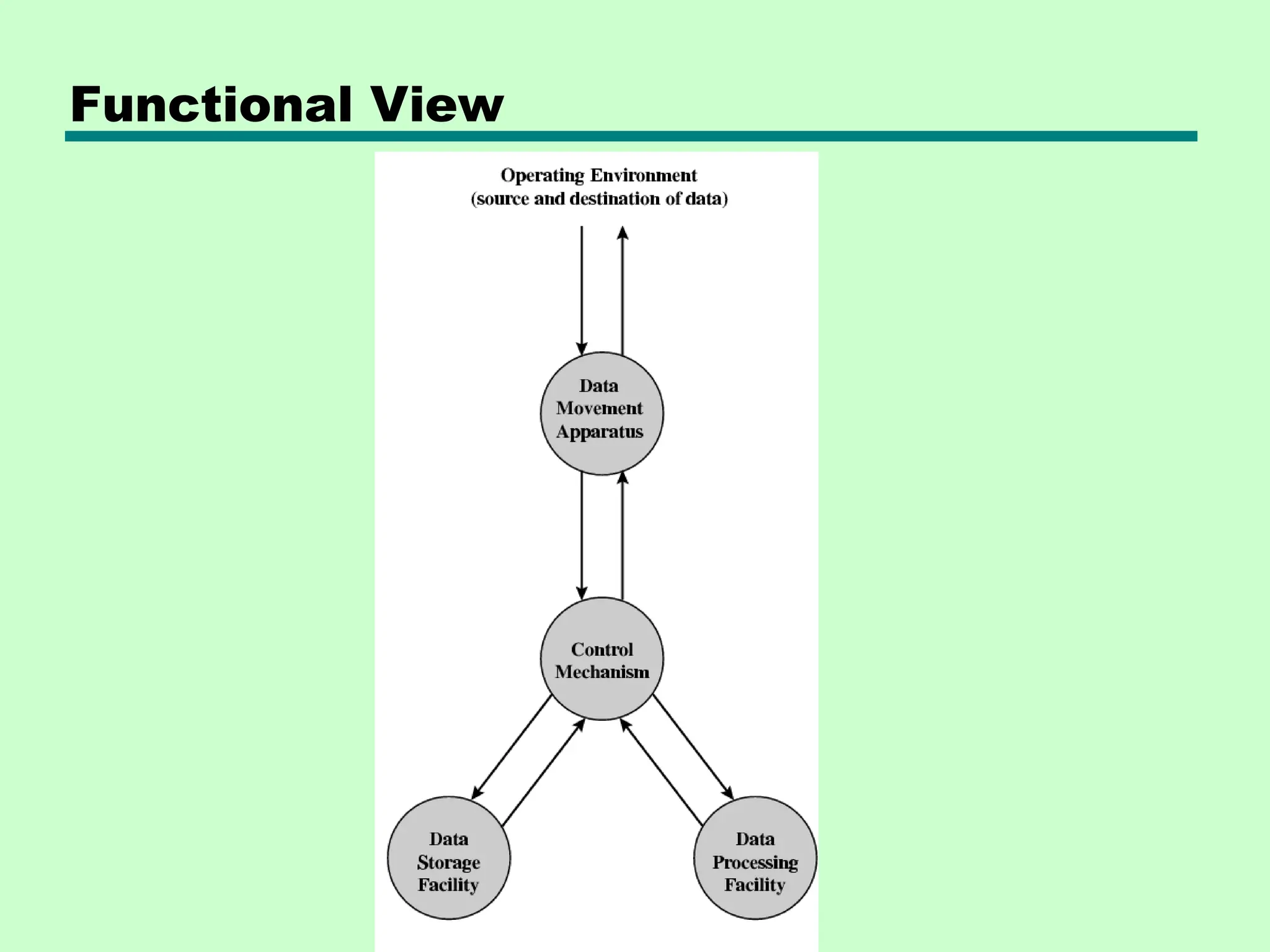
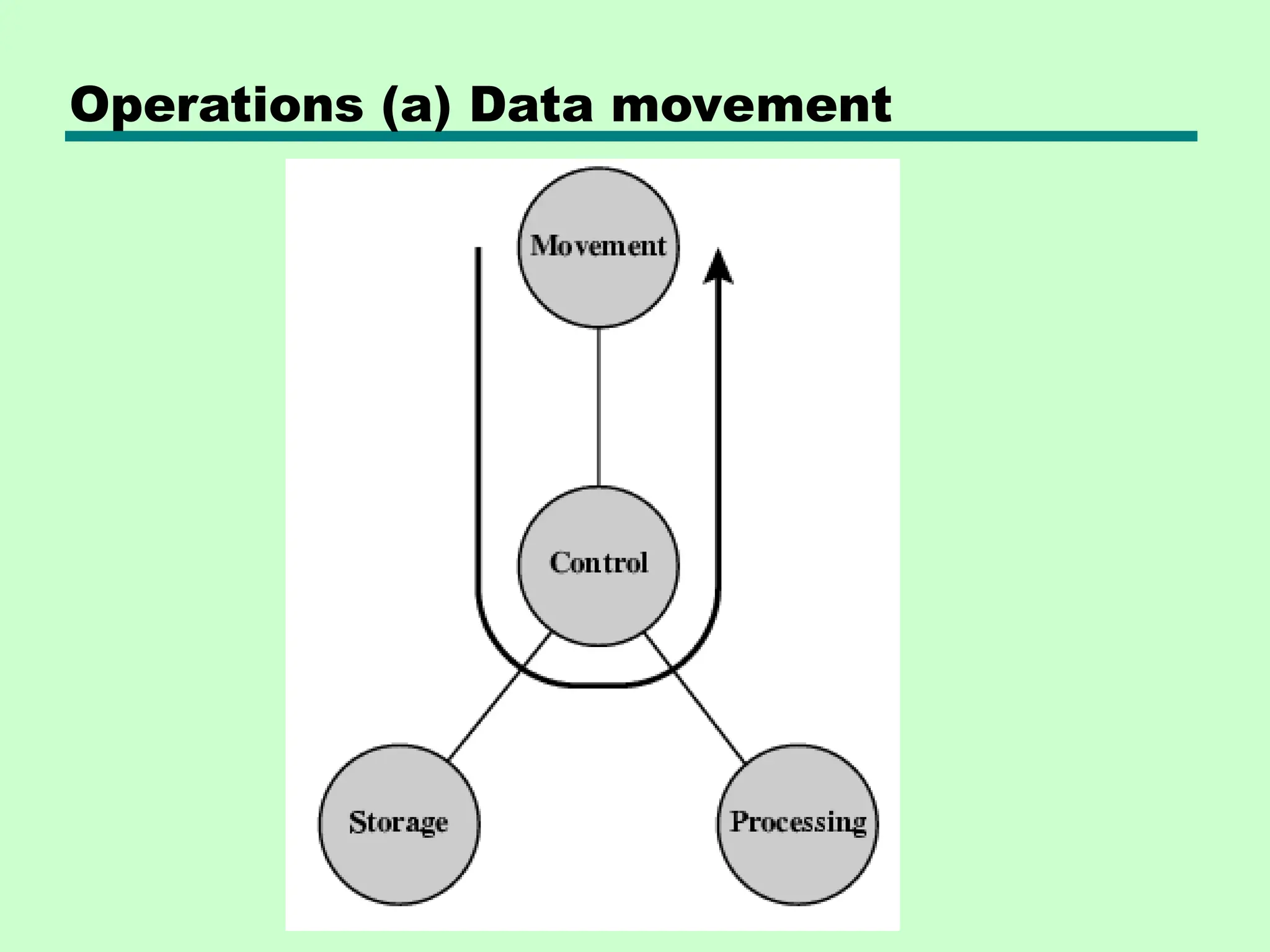
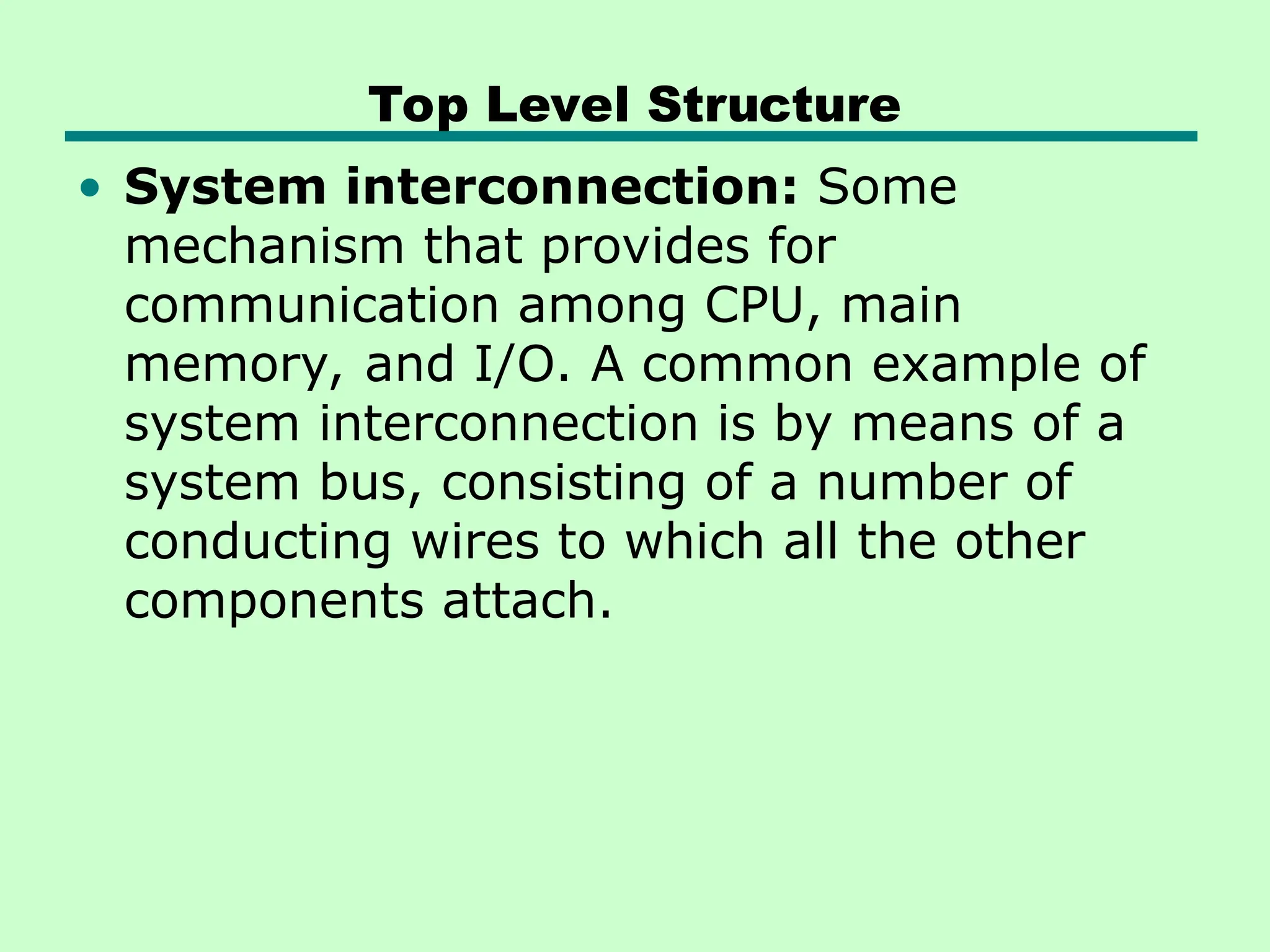
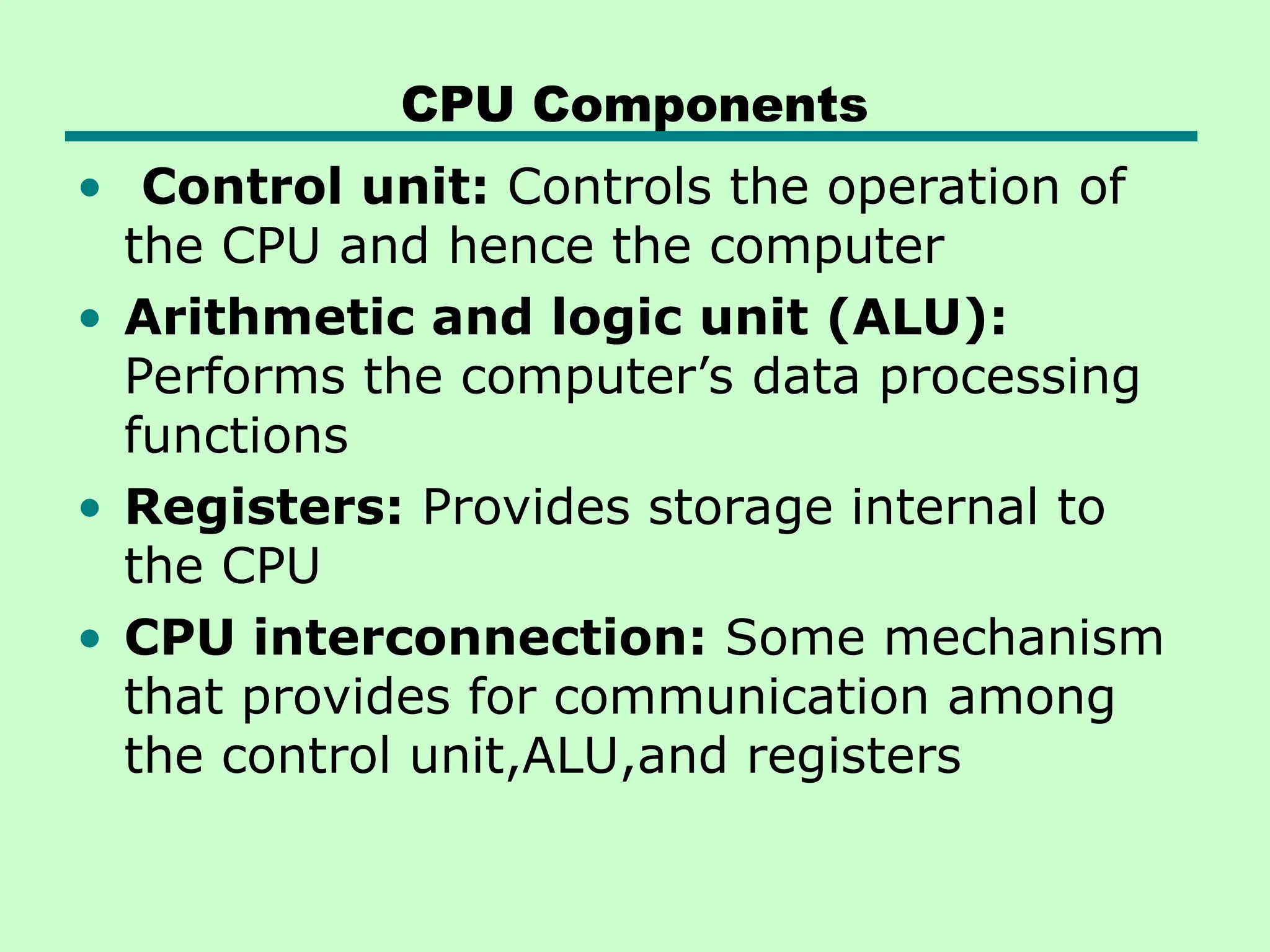
This document introduces key concepts in computer organization and architecture, highlighting the differences between the two. It explains that computer architecture refers to the functional behavior of a computer system while organization pertains to the structural relationships. The document outlines components such as the CPU, main memory, and I/O systems, as well as their interconnections, detailing their roles in data processing, storage, and movement.