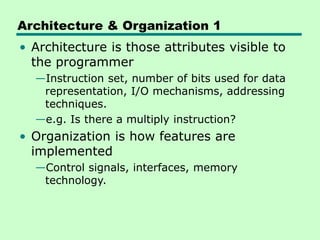
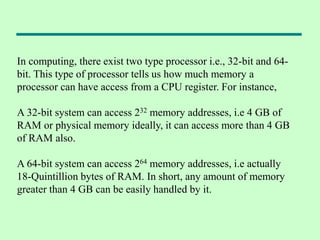
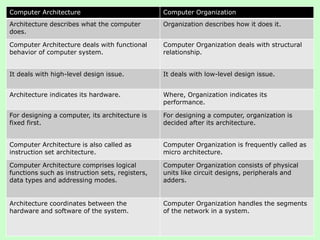
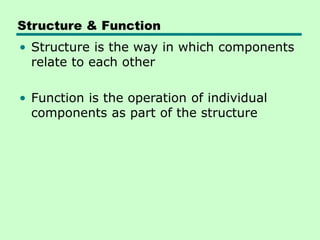
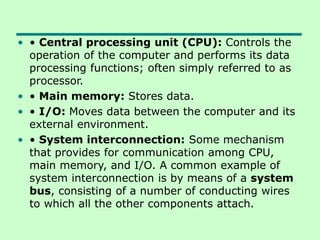
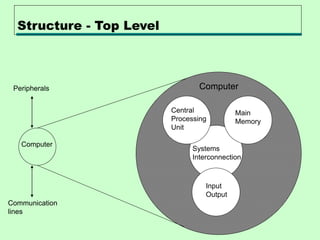
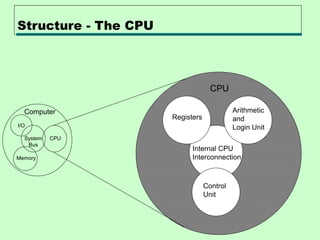
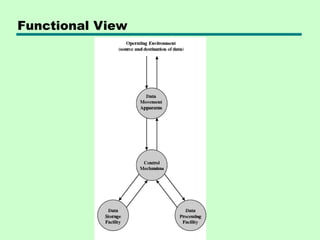
The document discusses computer architecture and organization. It defines architecture as the attributes visible to programmers, such as instruction sets, while organization refers to how features are implemented physically. Architecture describes what a computer does at a high level, while organization describes how it does it at a low level. Architecture deals with functional behavior and indicates performance, while organization deals with structural relationships and physical implementation.