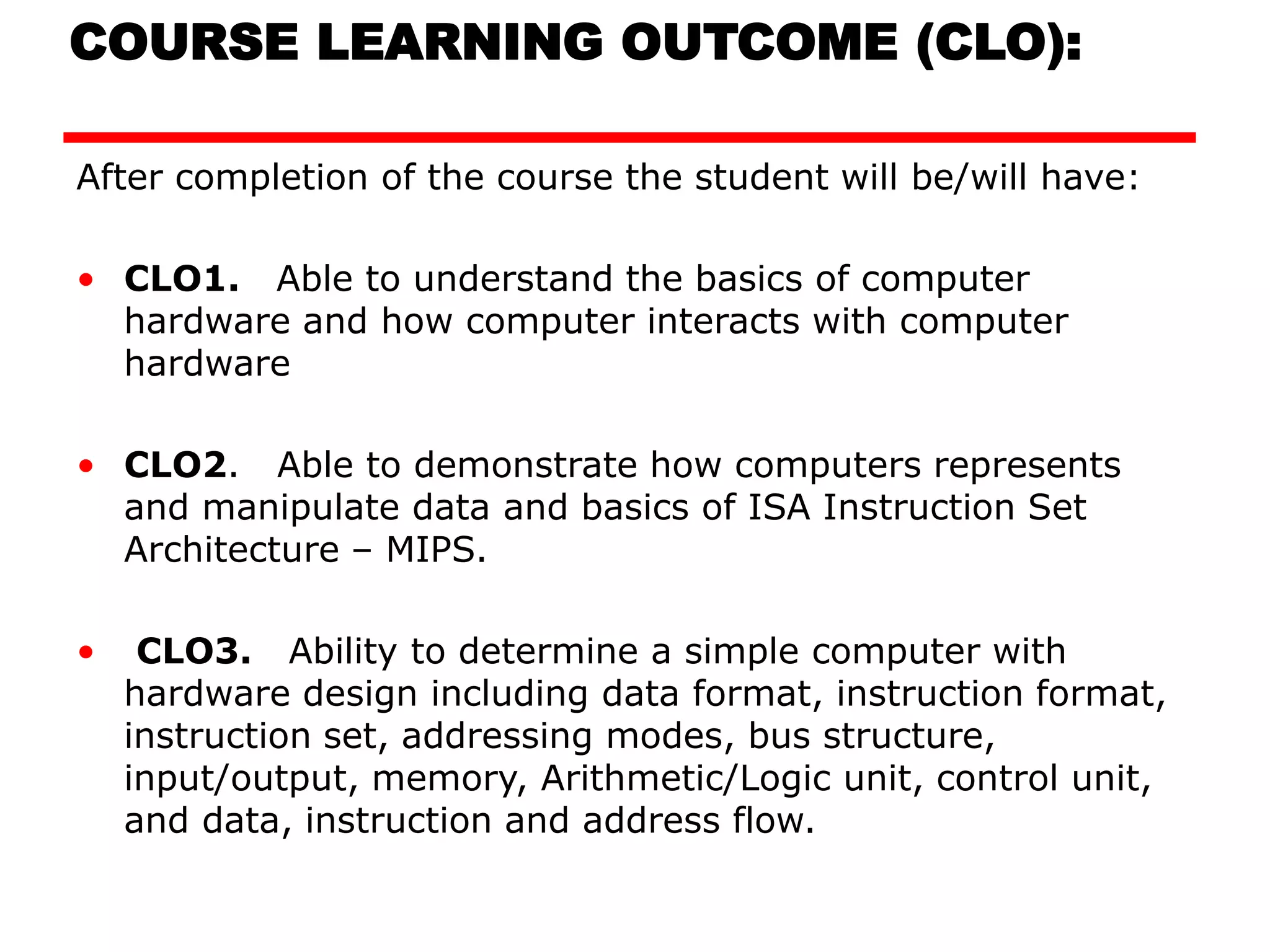
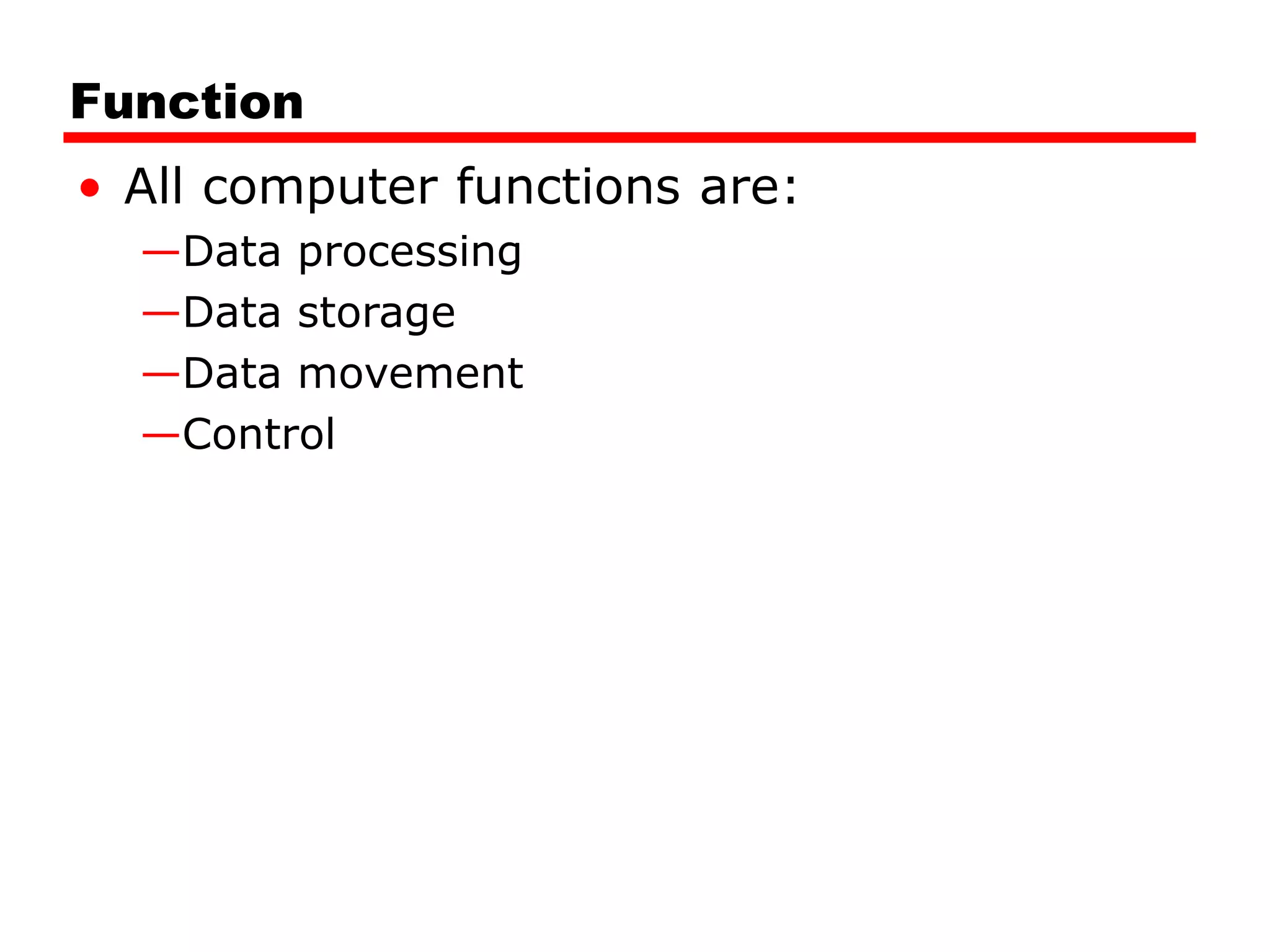
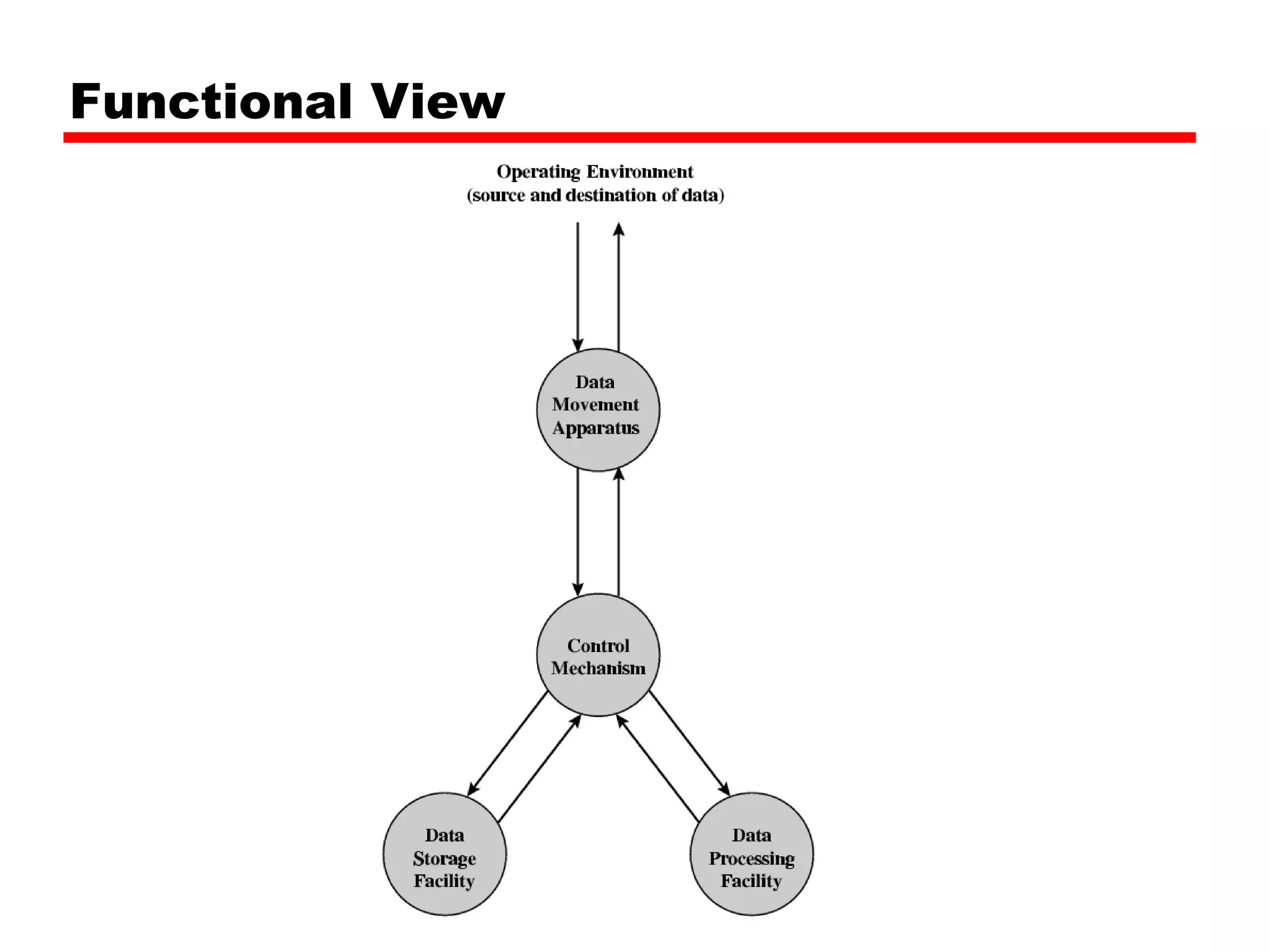
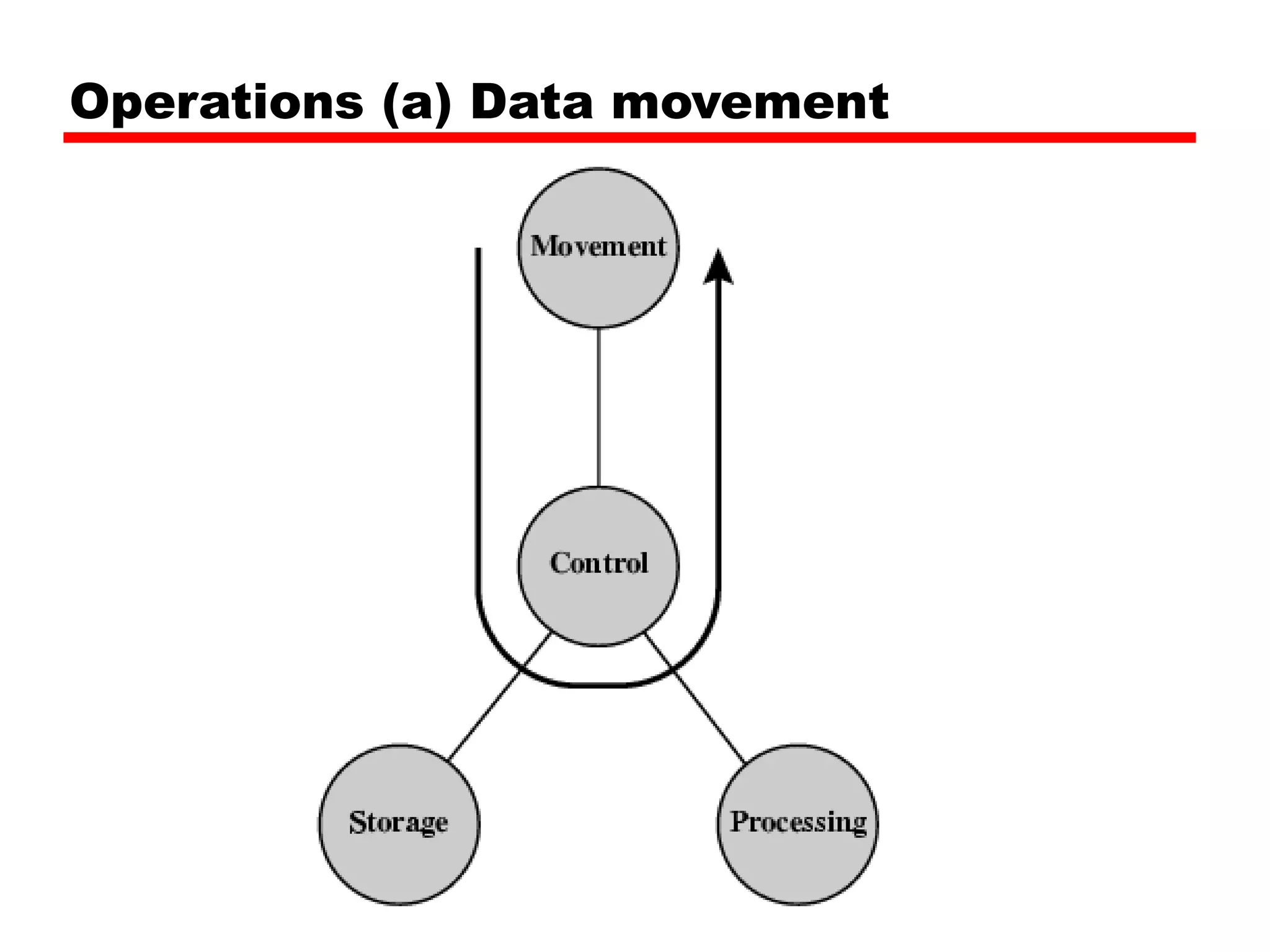
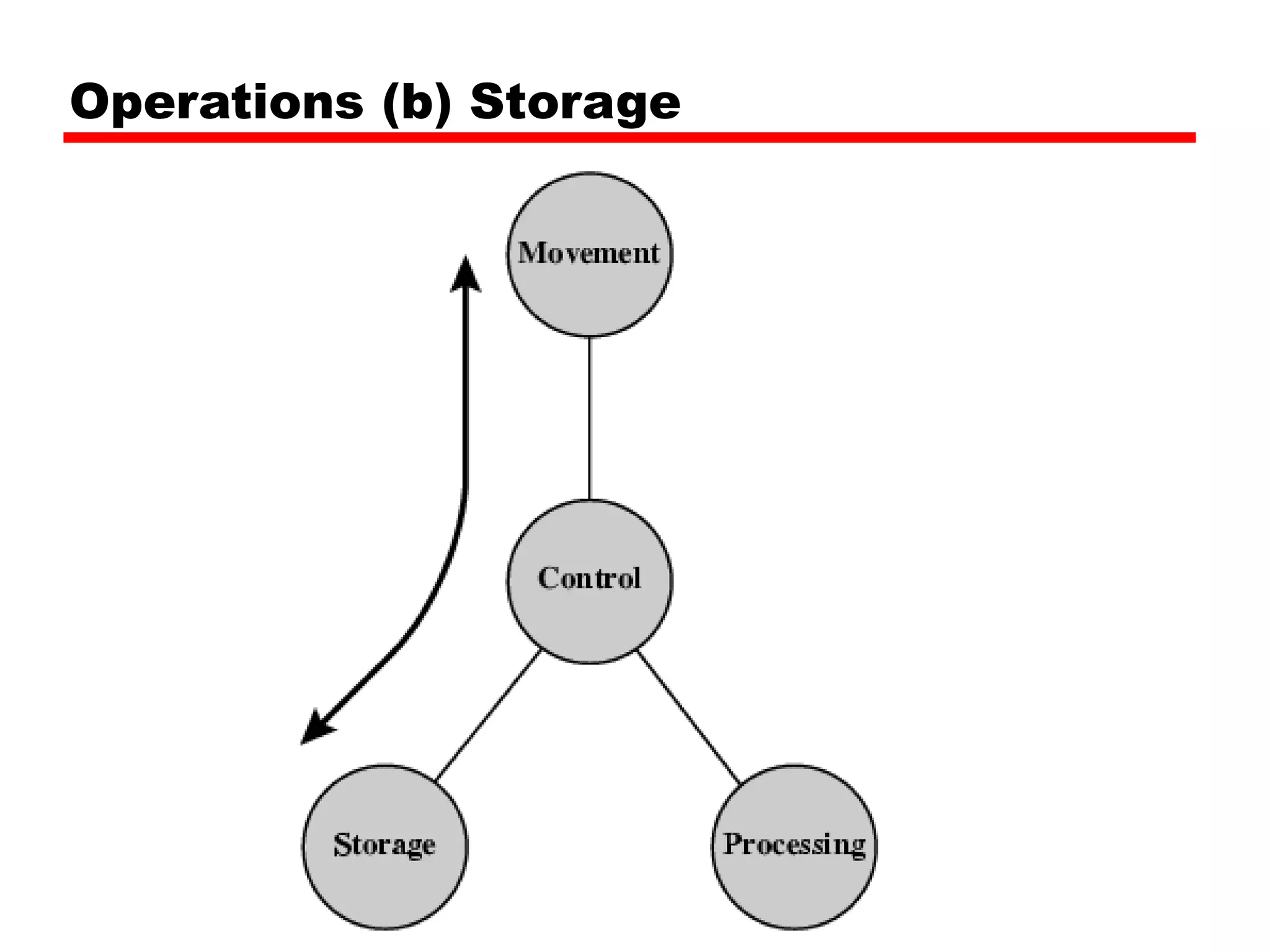
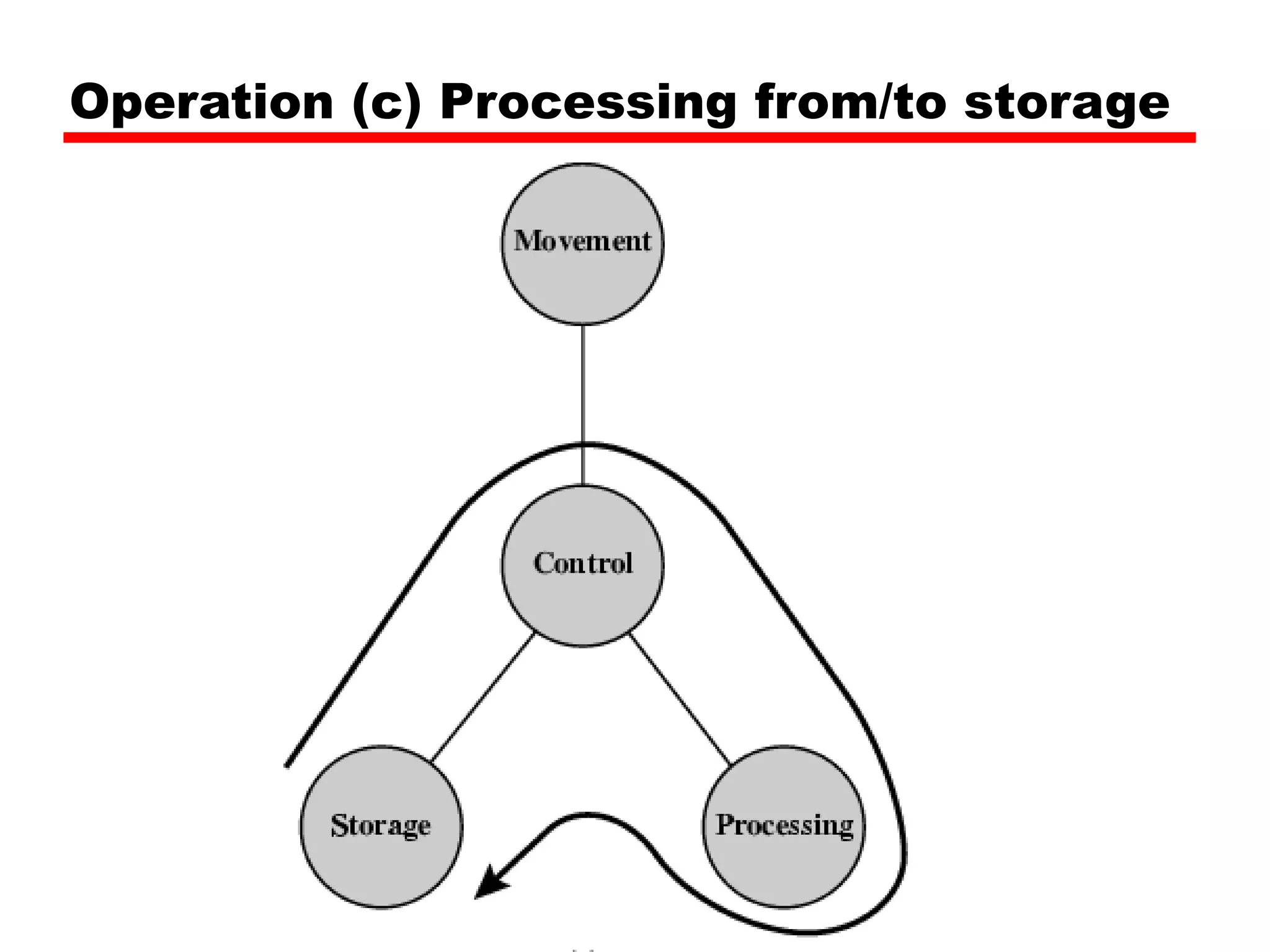
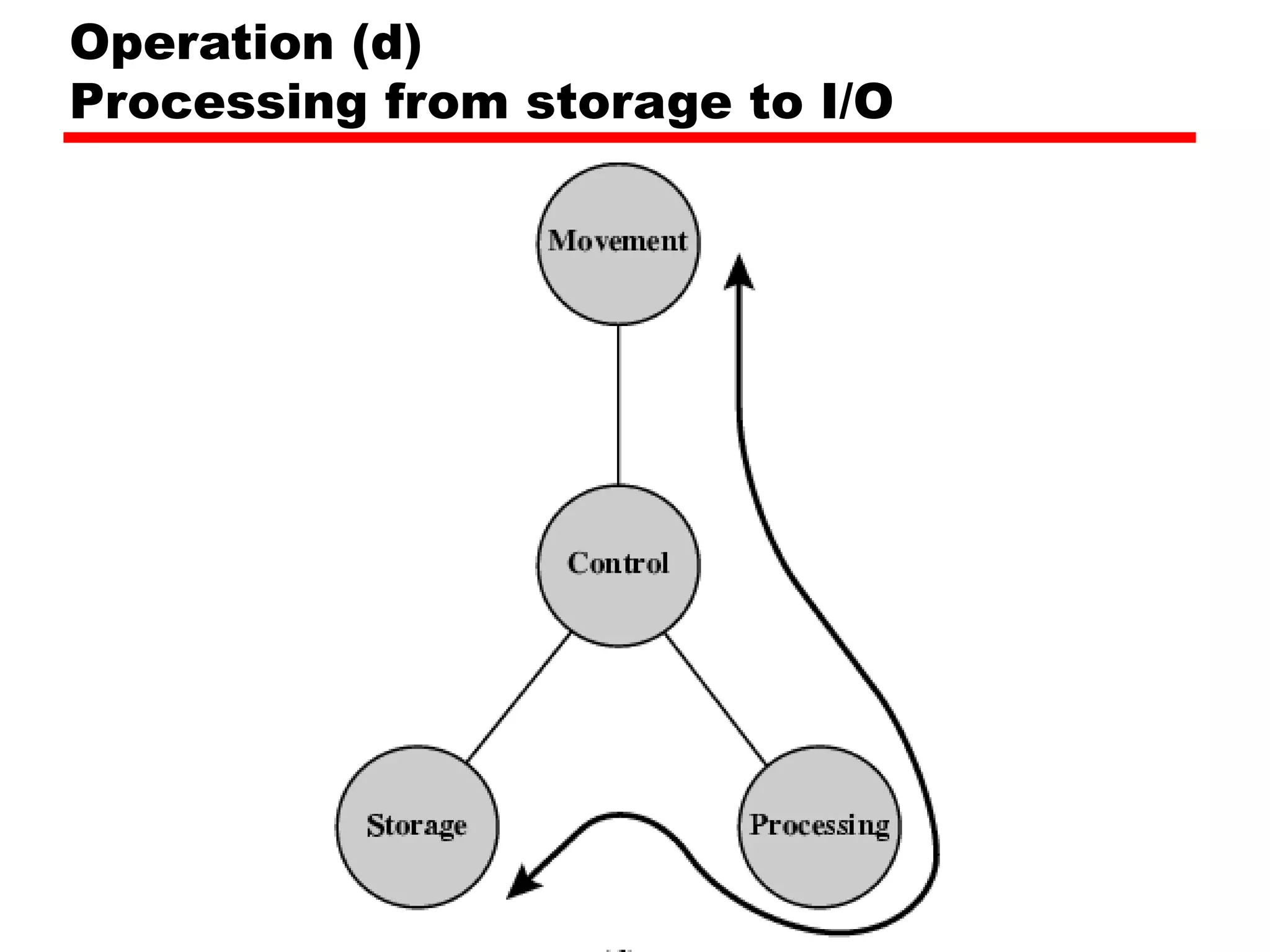
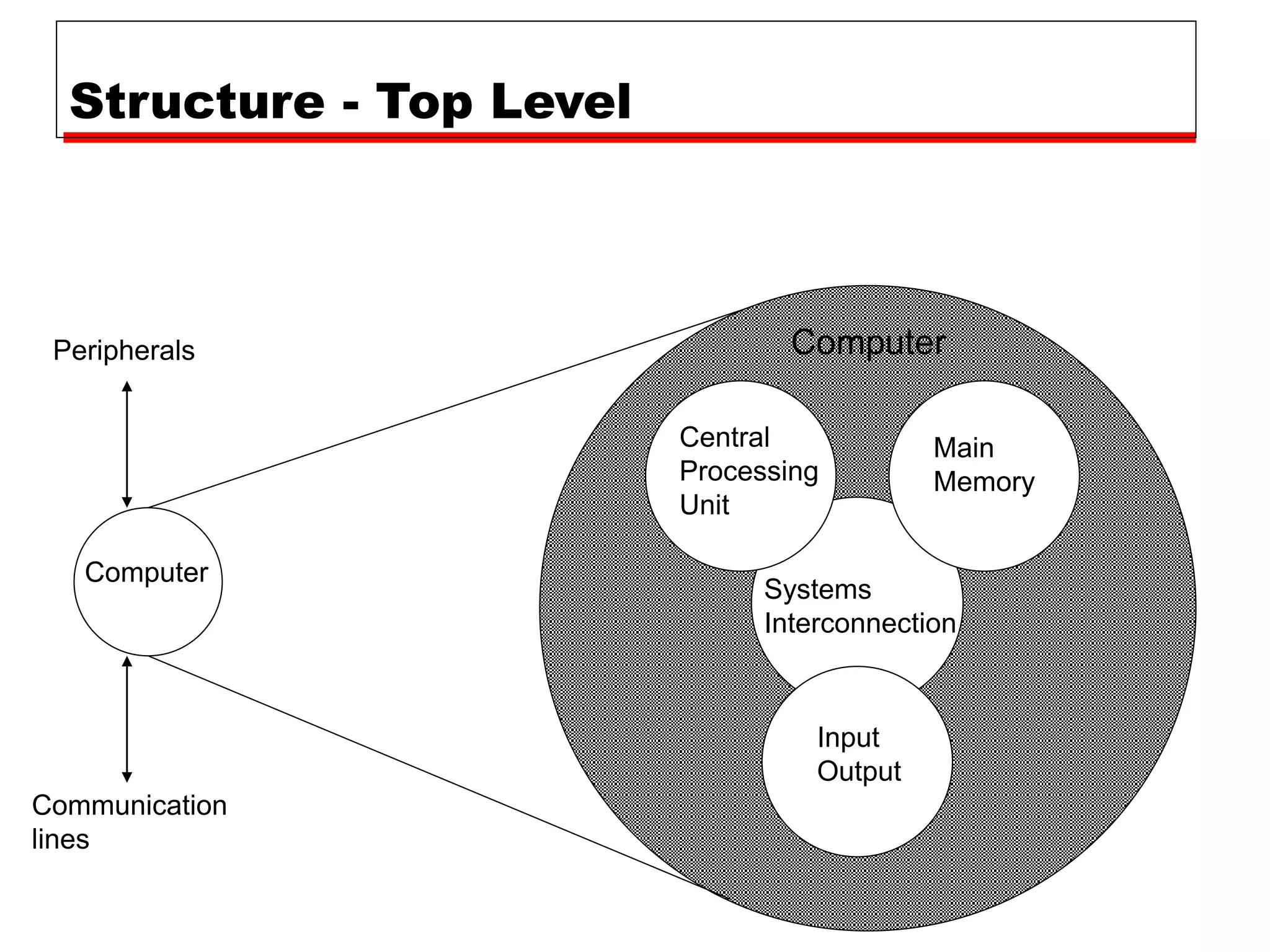
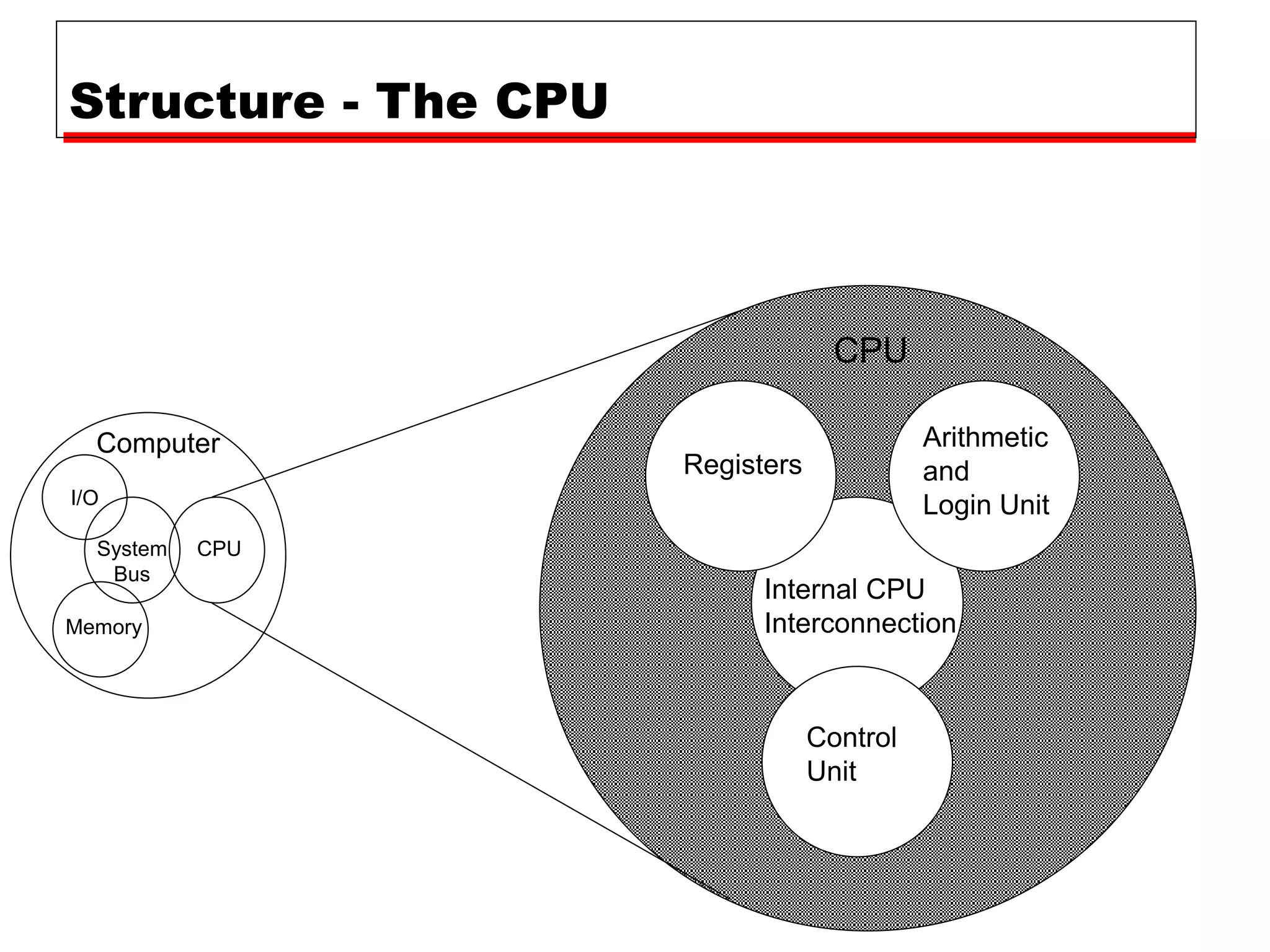
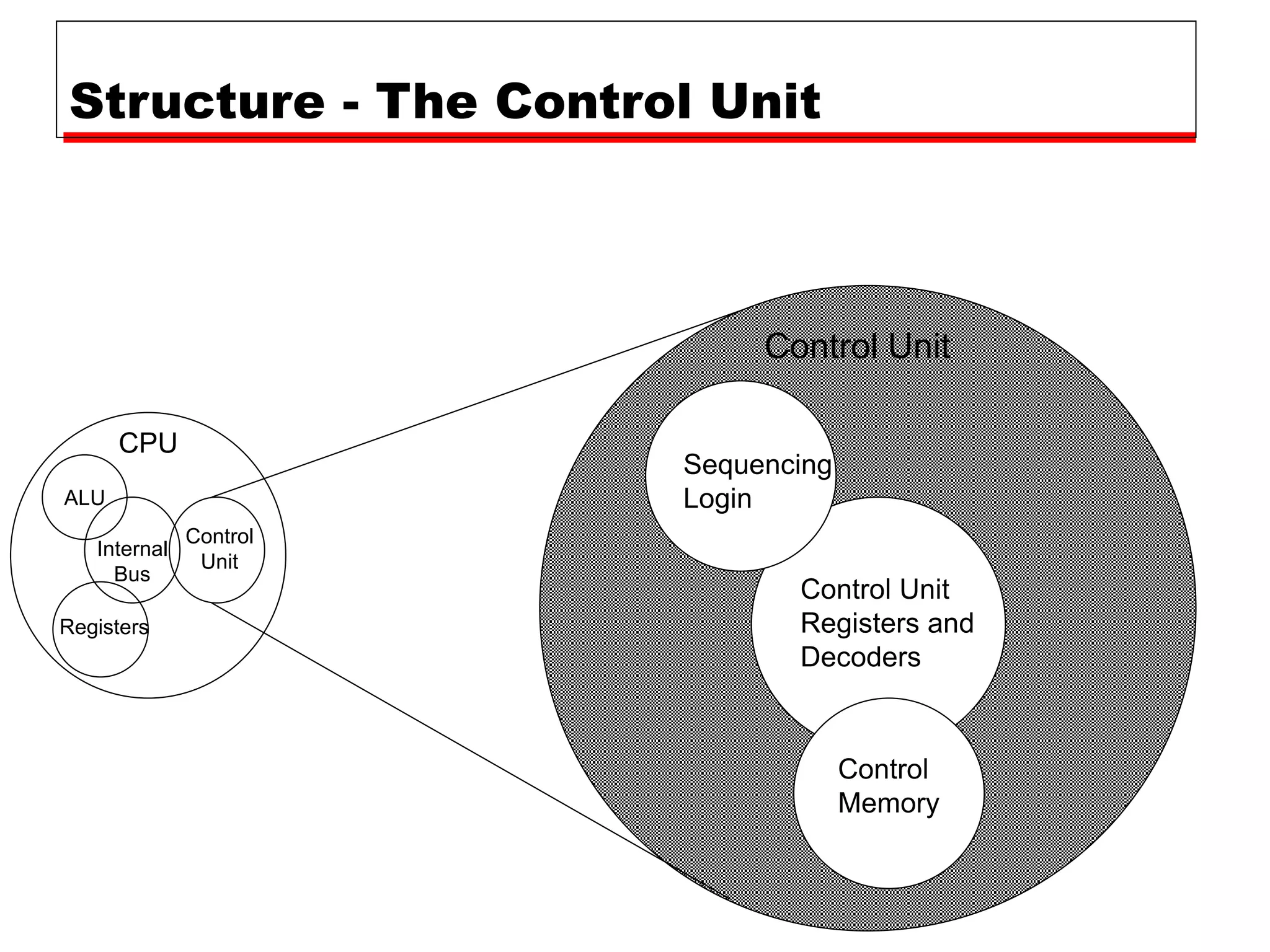
This document provides information about a course on computer architecture and organization. The course will cover the basics of computer hardware, how computers represent and manipulate data, and the MIPS instruction set architecture. Students will learn how a simple computer is designed, including components like data format, instruction format, addressing modes, and the data, instruction, and address flow. The course assessments include assignments, presentations, and an open book exam. Key topics that will be covered include computer structure and function, CPU organization, instruction sets, and control unit operation. Recommended textbooks are also provided.