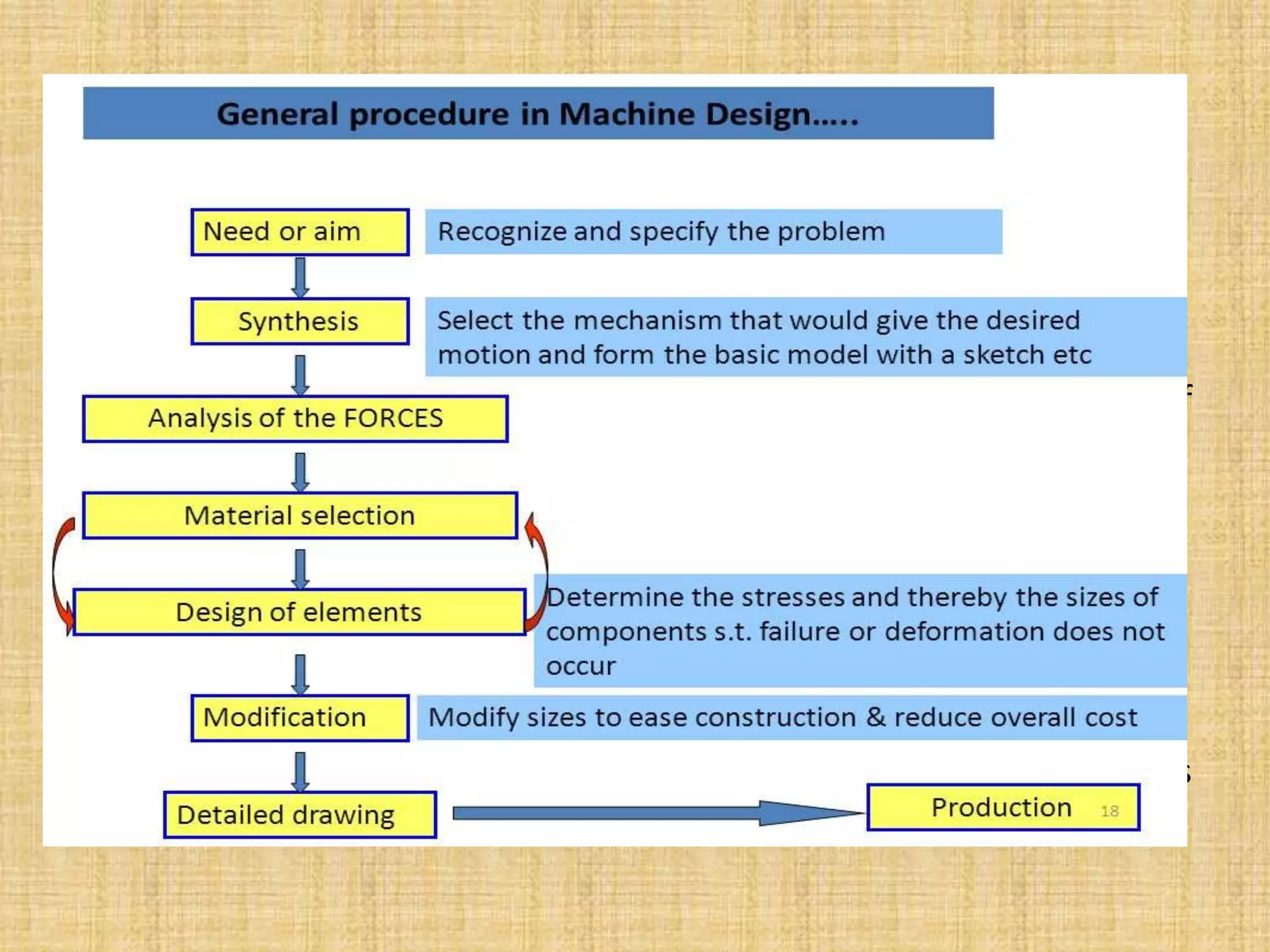
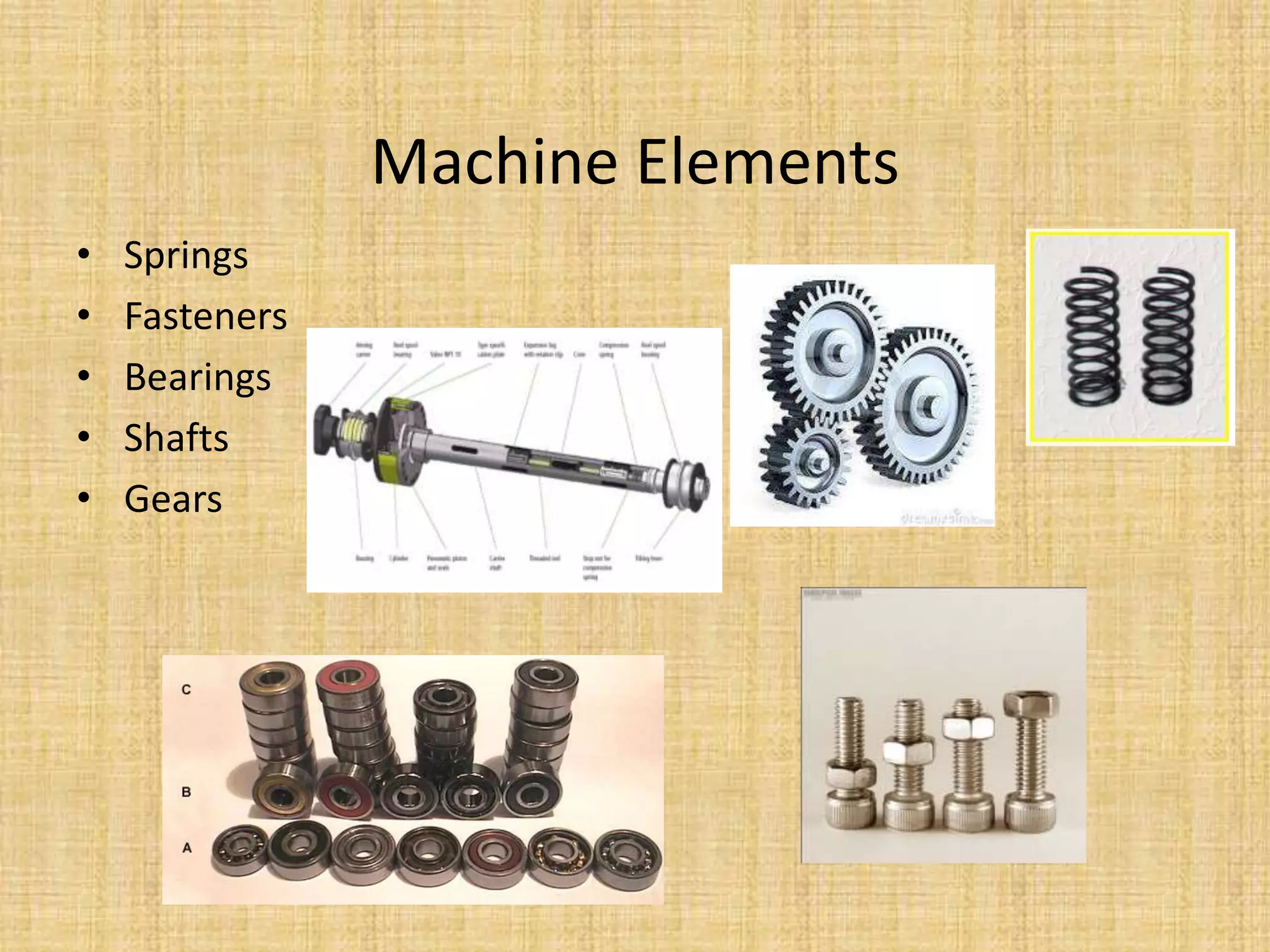
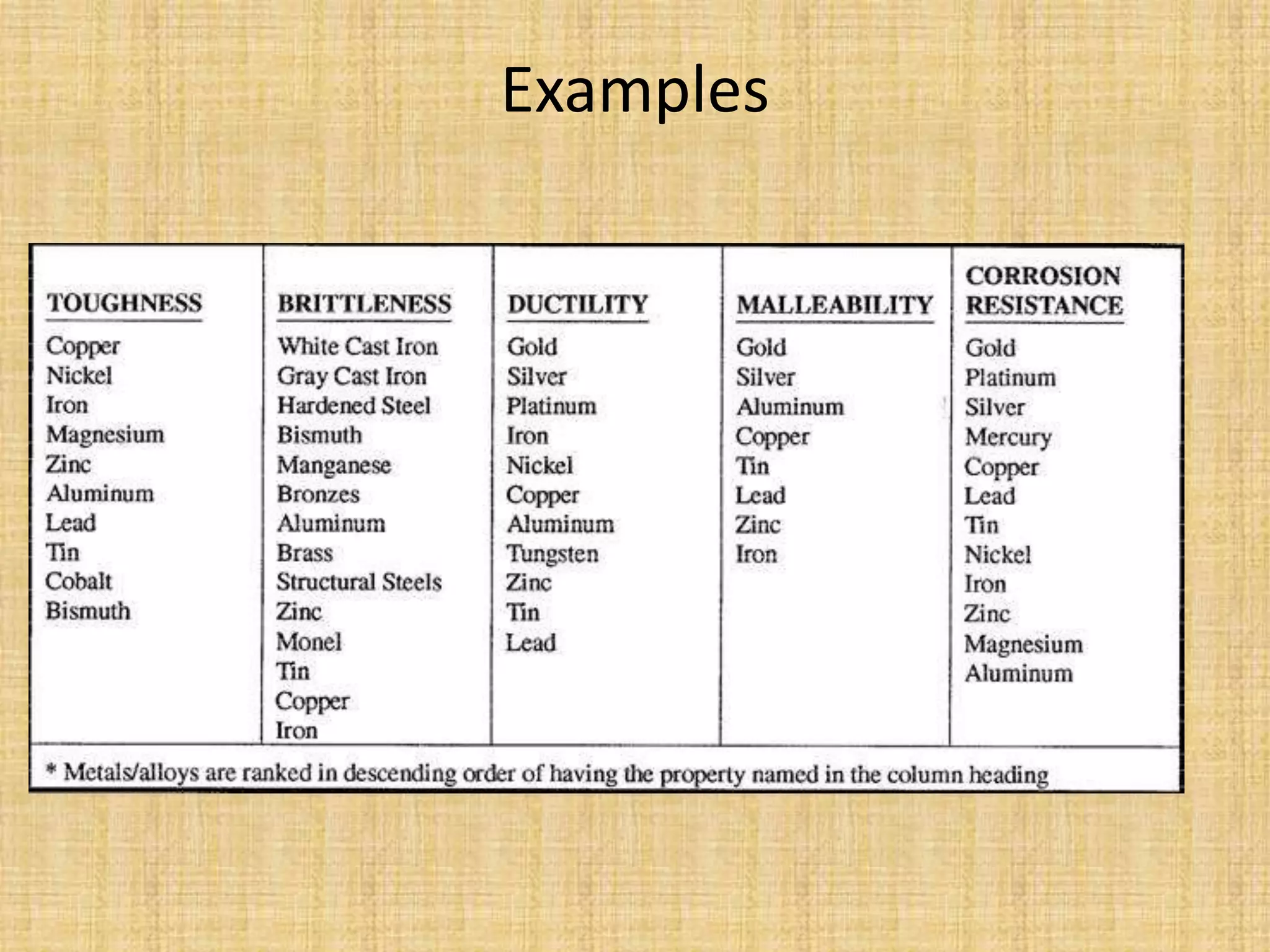
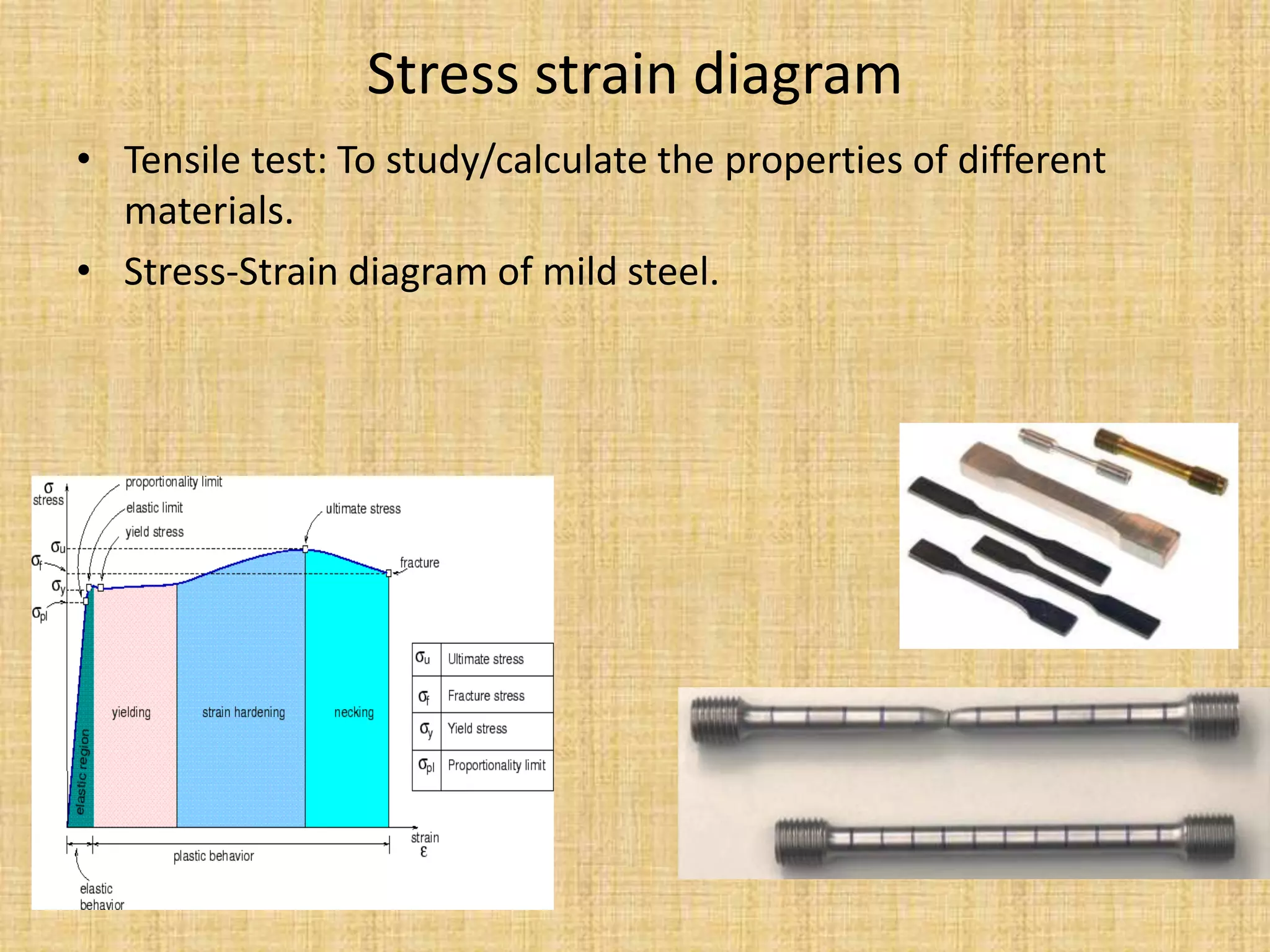
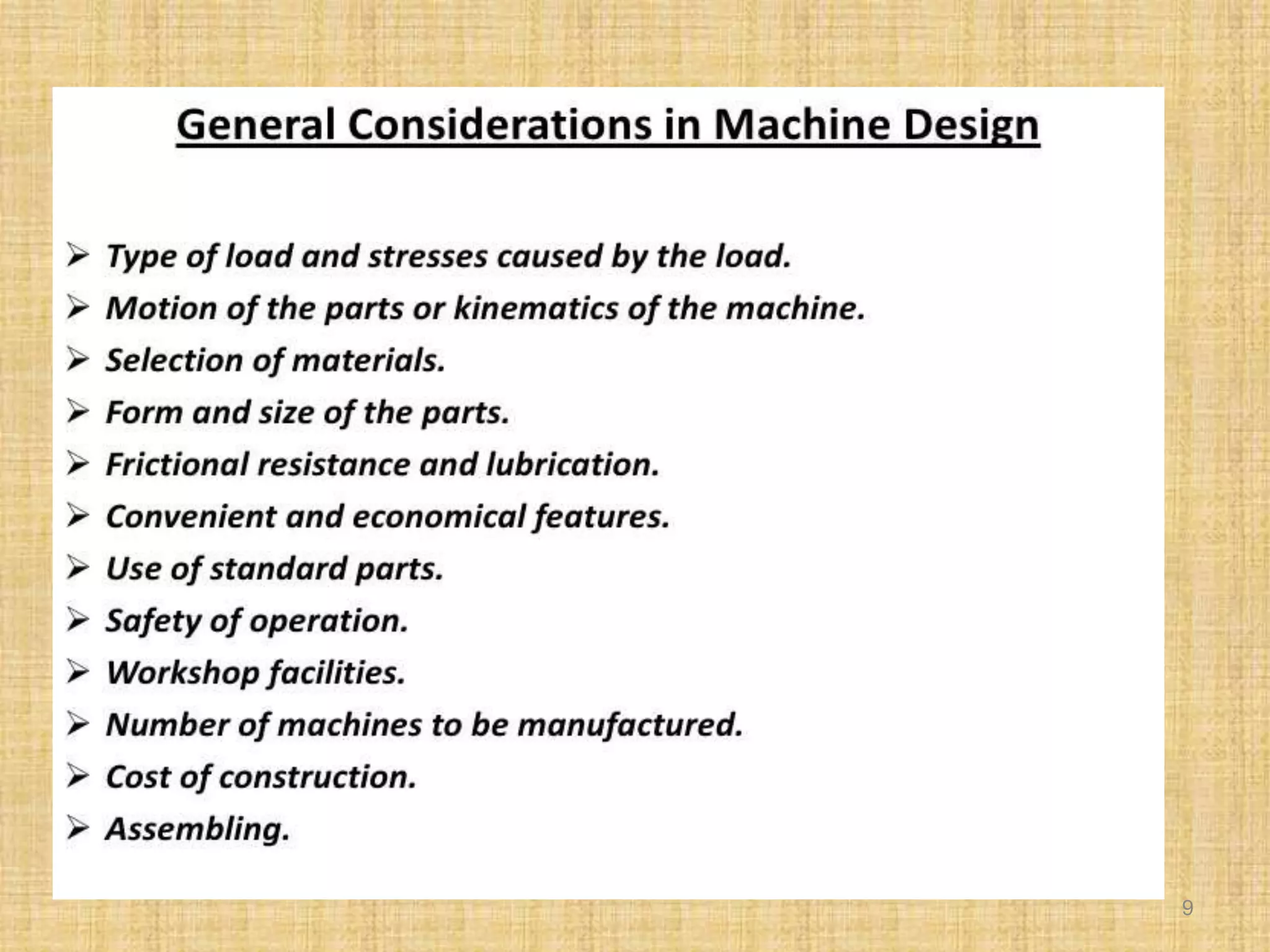
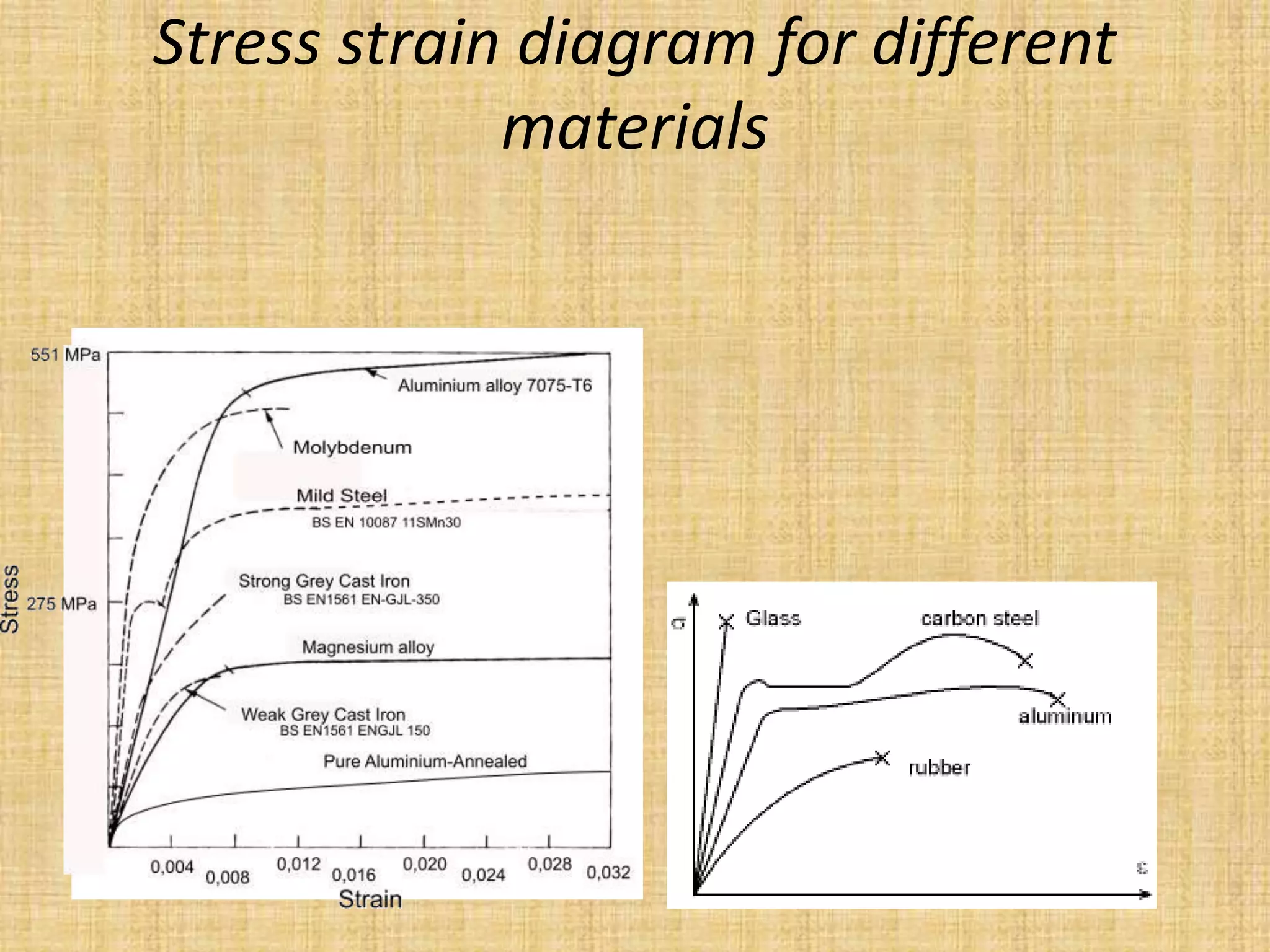
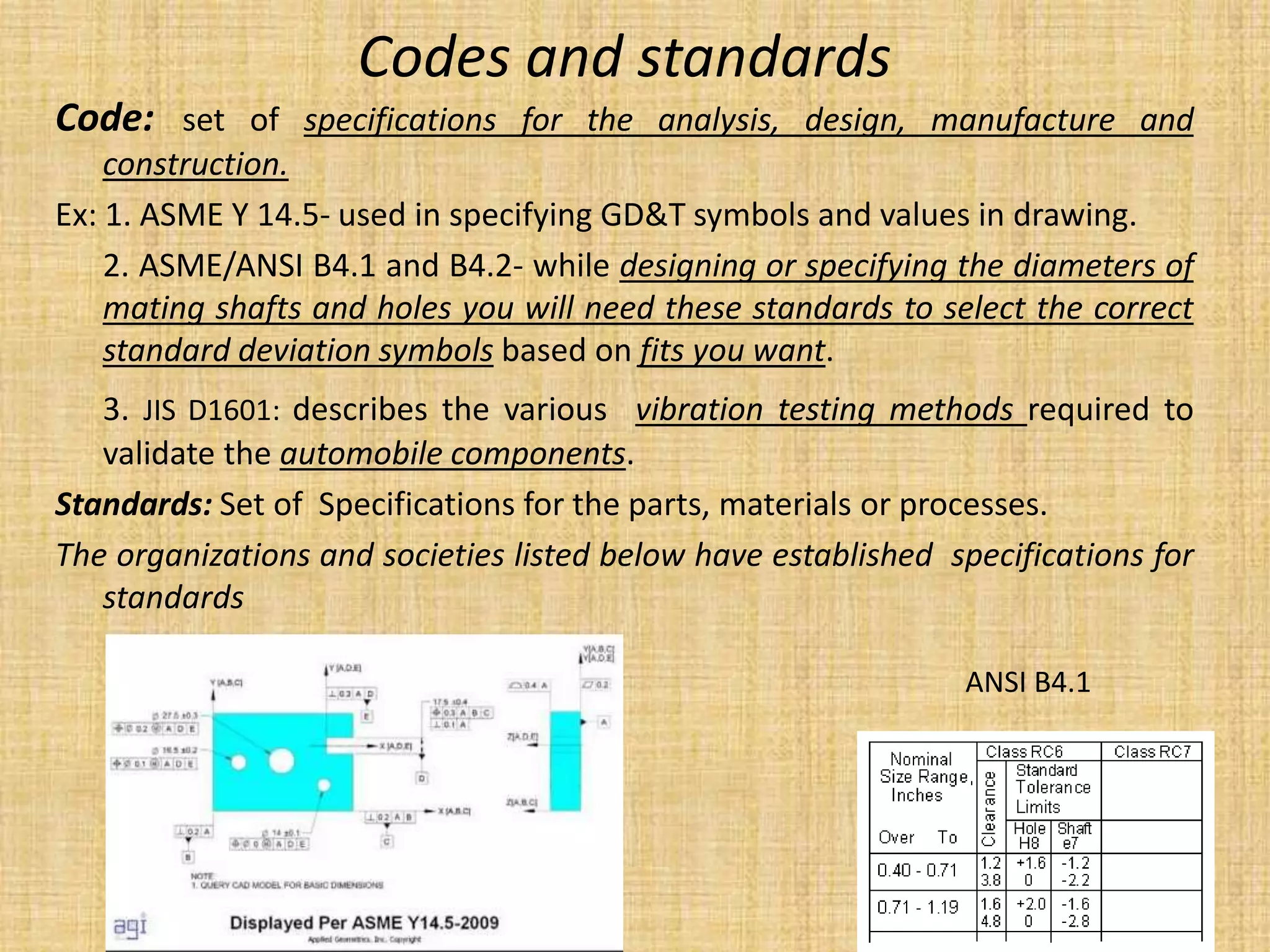
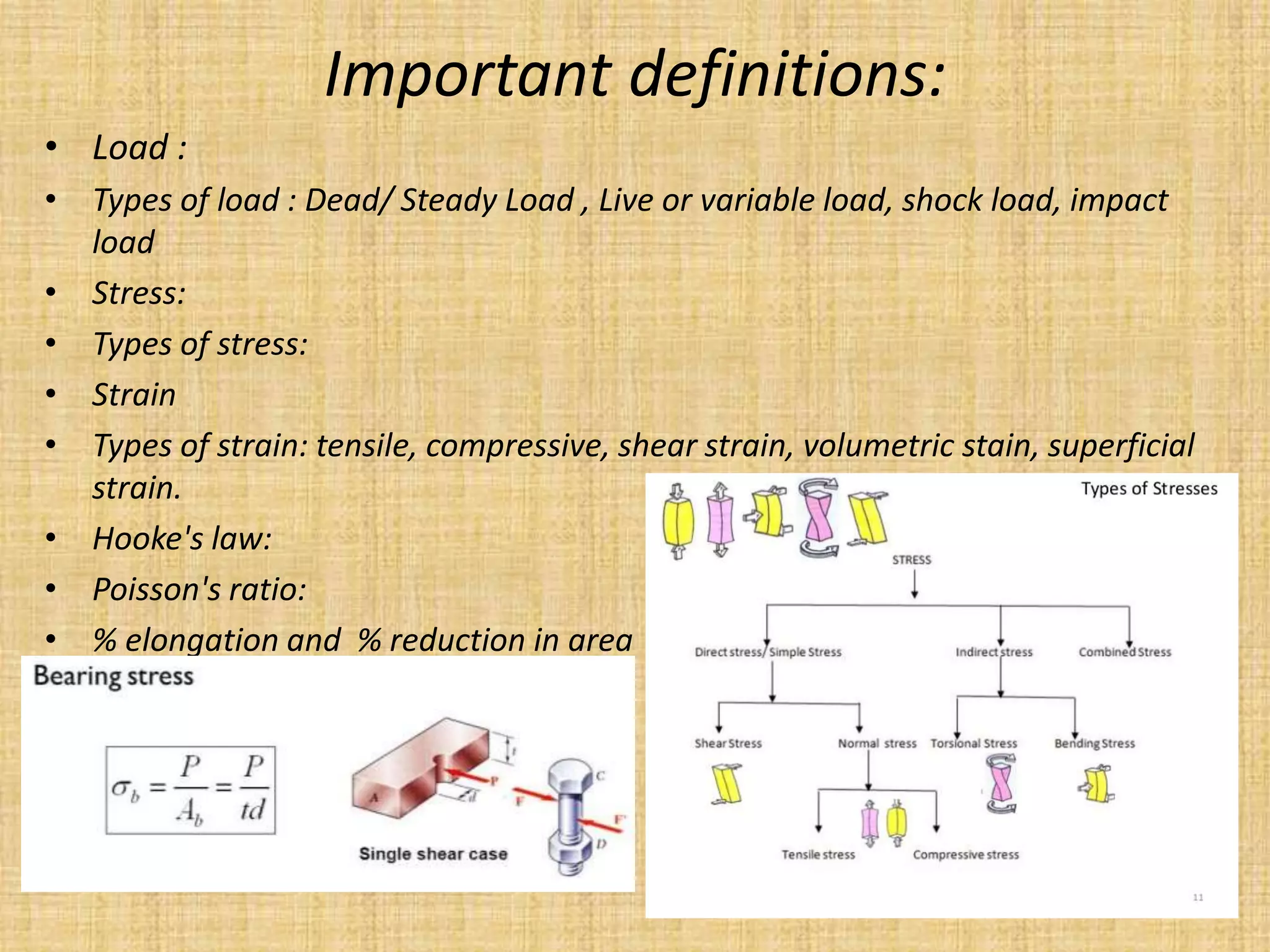
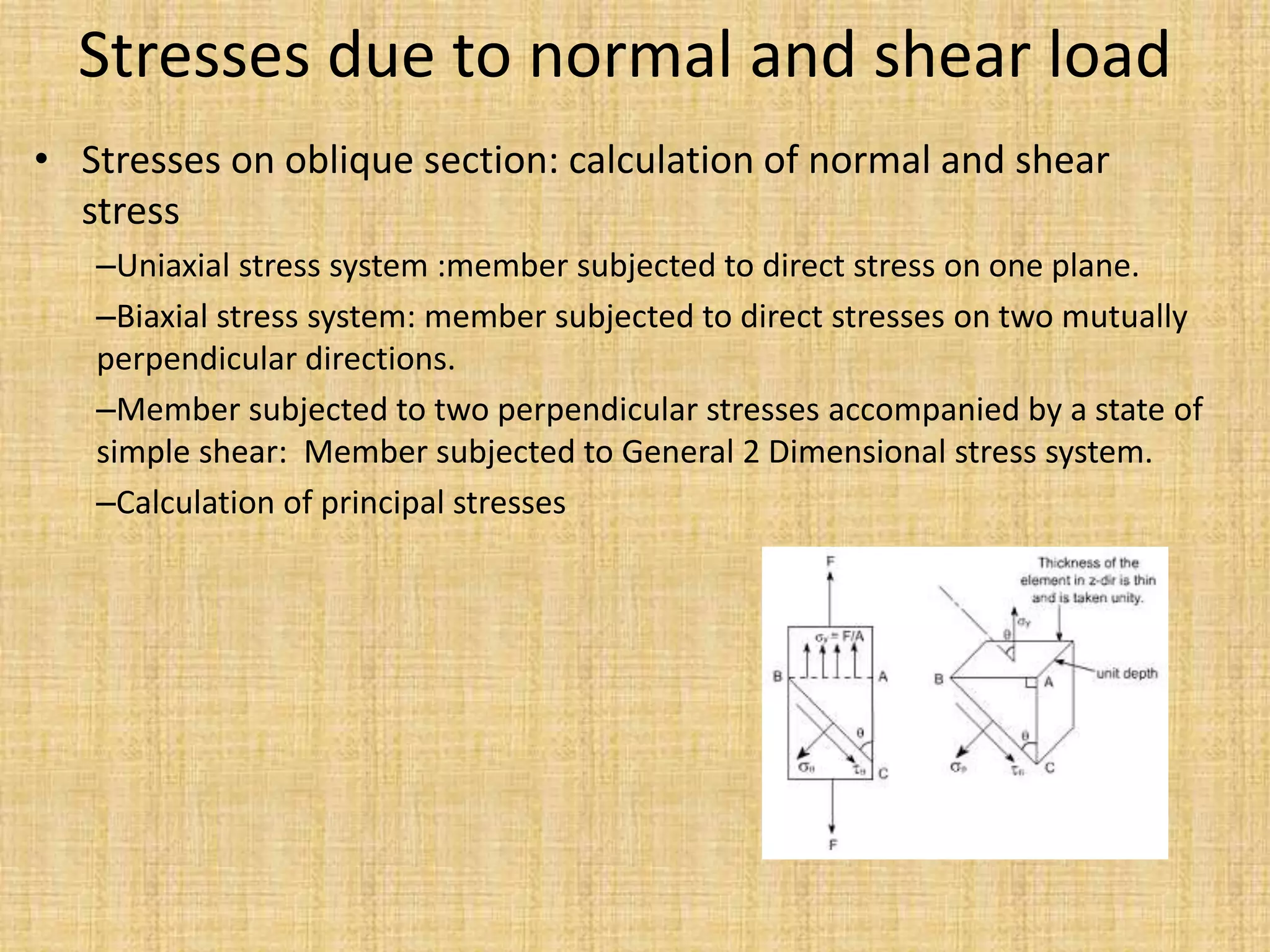
This document provides an introduction to machine design concepts and principles. It defines machine design as using scientific principles and imagination to design machines to perform specific functions efficiently. The document outlines the machine design process, including defining the problem, analyzing requirements, selecting appropriate mechanisms and materials, and preliminary design. It also discusses important machine elements, mechanical properties of materials, stress-strain diagrams, and industry codes and standards relevant to machine design. Key definitions are provided for terms like load, stress, strain, and stress systems.