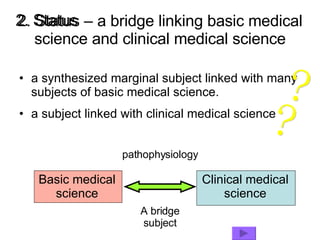
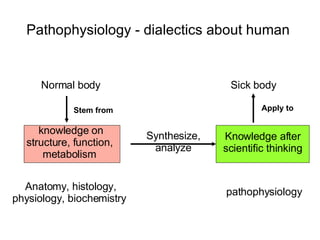
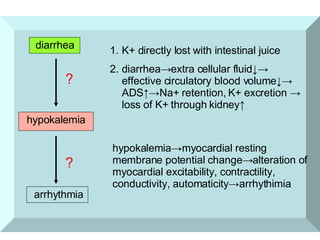
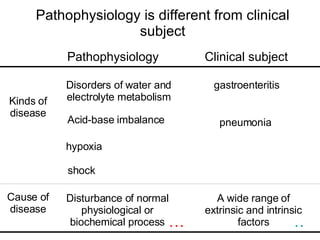
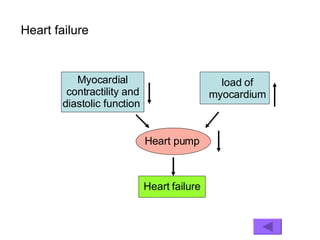
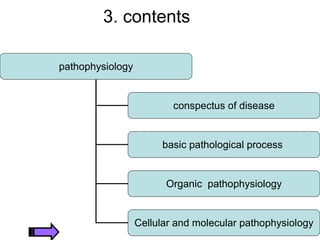
The document provides an overview of pathophysiology as an academic subject. It discusses pathophysiology as exploring the mechanisms underlying disease development and functional/metabolic changes in the body. The goals are to investigate disease occurrence and progression. Pathophysiology acts as a bridge between basic medical sciences and clinical practice. It synthesizes knowledge of normal and abnormal body structure/function. The content includes disease concepts/etiologies, common pathological processes, and organ/cellular/molecular pathophysiology. Learning pathophysiology requires understanding causes, pathogenesis, and functional/metabolic alterations while using systems-thinking approaches.