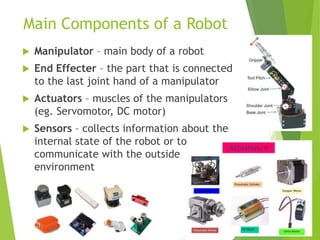
Robotics is the study and application of robot technology. A robot is a mechanical device that performs tasks automatically or through remote control. There are three main types of robots: industrial robots, mobile robots, and educational robots. The main components of a robot are its manipulator, end effector, actuators, sensors, controller, processor, and software. Learning robotics in education improves students' creativity and engagement, prepares them for technological changes, builds programming and teamwork skills, and develops perseverance, while also being fun.