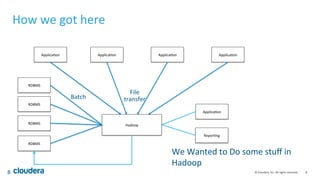
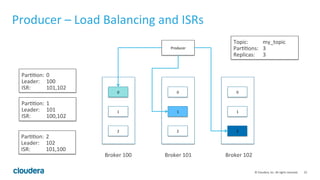
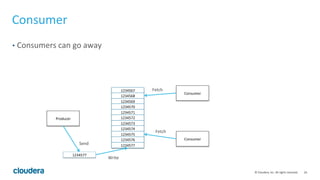
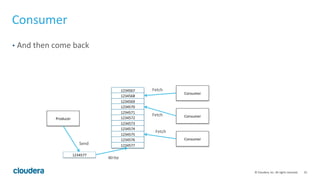
The document provides an introduction to Apache Kafka, a high throughput, low latency, and fault-tolerant publish/subscribe messaging system. It covers key concepts, such as producers, consumers, topics, and partitions, and explains how data can be retained and managed within the Kafka ecosystem. Additionally, it addresses the importance of schema in data integration and outlines various use cases for Kafka, including real-time stream processing and log aggregation.